Science Worksheet Rocks and Layers
Are you a science teacher searching for a comprehensive and engaging resource to teach your students about rocks and layers? Look no further! This blog post will introduce you to a fantastic set of worksheets that will captivate your students' attention and help them grasp the essential concepts related to rocks and layers. With the incorporation of visually appealing graphics and thought-provoking questions, these worksheets are perfect for middle school students looking to expand their knowledge in Earth Science.
Table of Images 👆
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What are sedimentary rocks?
Sedimentary rocks are types of rocks formed from the deposition and solidification of sediments derived from preexisting rocks or organic materials. These sediments are typically carried and deposited by water, wind, or ice, and over time, they undergo compaction and cementation to form sedimentary rocks. Examples of sedimentary rocks include sandstone, limestone, and shale.
How do sedimentary rocks form?
Sedimentary rocks form through the deposition and subsequent lithification of sediments such as sand, mud, and organic material. These sediments are typically carried by water, wind, or ice and accumulate in layers over time. As more layers build up and are compacted, the weight of the overlying material causes the sediments to harden into solid rock. Processes like cementation, compaction, and chemical precipitation can also play a role in the formation of sedimentary rocks.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks and minerals on the Earth's surface into smaller pieces through physical, chemical, or biological means, while erosion involves the transport and movement of these weathered materials by natural agents like water, wind, or ice. Weathering breaks down rocks, while erosion carries away the weathered particles to new locations. Weathering prepares material for erosion by breaking it down, and erosion then moves this material to create landforms and shape the Earth's surface.
How do igneous rocks form?
Igneous rocks form when molten magma cools and solidifies either below the Earth's surface, creating intrusive igneous rocks like granite, or on the surface, creating extrusive igneous rocks like basalt. The rate at which the magma cools determines the size of the crystals in the rock, with slower cooling leading to larger crystals. As igneous rocks cool and solidify, they can also undergo processes like crystallization, fractional crystallization, and assimilation, which can further modify their composition and appearance.
What are the three types of rocks?
The three types of rocks are igneous, formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava; sedimentary, formed from the accumulation of sediment over time; and metamorphic, formed from the alteration of pre-existing rocks due to high temperature and pressure.
What is the rock cycle?
The rock cycle is a continuous process where rocks are formed, broken down, and transformed into different types through various geological processes such as weathering, erosion, melting, cooling, and crystallization. This cycle includes three main categories of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, with each type being interrelated and transitioning from one form to another over millions of years.
How are fossils formed?
Fossils are formed when a plant or animal dies and is quickly buried by sediment, preventing decomposition. Over time, the organic material in the remains is slowly replaced by minerals, leaving a rock-like imprint of the organism behind. Fossils can also form when the remains are preserved in tar, ice, amber, or in an anoxic environment, protecting them from decay.
What is the principle of superposition?
The principle of superposition states that in a linear system, the response to multiple inputs is the sum of the responses to each individual input separately. This principle allows for a simpler analysis of complex systems by breaking them down into simpler components and then summing their effects to predict the overall system behavior. It is a fundamental concept in fields such as physics and engineering for understanding the behavior of systems with multiple inputs and interactions.
How can scientists use layers of rock to determine the age of fossils?
Scientists can use layers of rock to determine the age of fossils through relative dating methods such as stratigraphy. By examining the position of fossils in relation to the sedimentary layers they are found in, scientists can estimate the age based on the principle of superposition, which states that in undisturbed layers of rock, the youngest layer is on top and the oldest is on the bottom. Additionally, scientists can also use absolute dating techniques like radiometric dating to determine the actual age of the rocks and fossils by measuring the decay of radioactive isotopes in them.
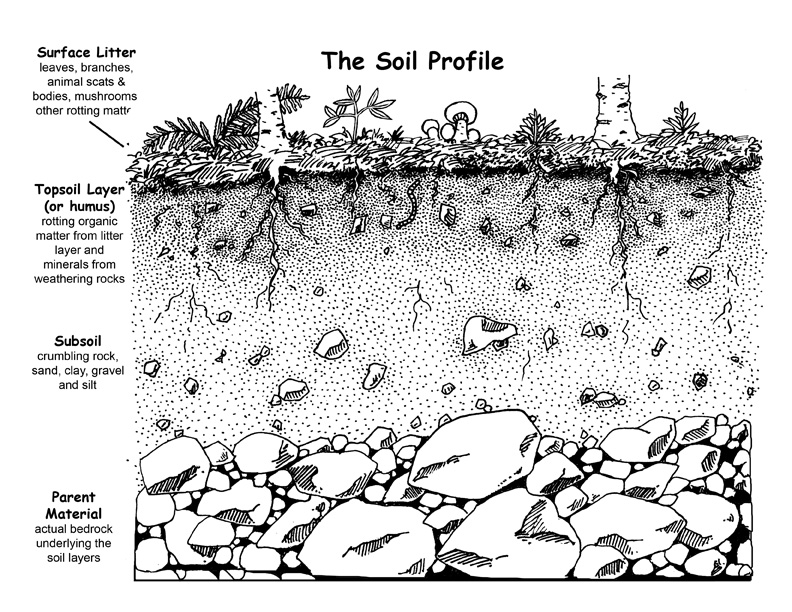
How can studying layers of rock help us understand Earth's history?
Studying layers of rock can help us understand Earth's history because each layer represents a snapshot of the environment at the time it was formed. By analyzing the type of rock, fossils, and minerals present in each layer, scientists can deduce information about past climates, geological events, and even the evolution of life on Earth. This stratigraphic approach allows us to piece together a timeline of Earth's history and gain insights into the processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments