Science Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade
Are you searching for engaging and educational resources to reinforce your 4th-grade students' understanding of electricity? Look no further! Our science electricity worksheets are specifically designed to make the learning process enjoyable and effective for young learners. With a focus on enhancing their knowledge of this fascinating subject, these worksheets provide an excellent opportunity for students to explore different aspects of electricity and deepen their understanding of key concepts.
Table of Images 👆
- Electricity Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
- Static Electricity Worksheet 4th Grade
- 4th Grade Science Weather Worksheets
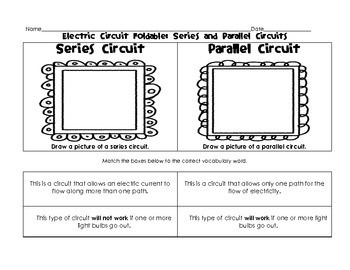
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Science Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
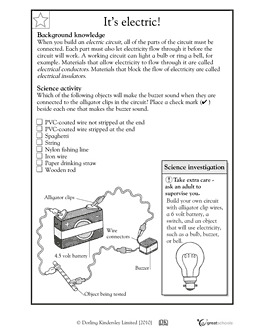
- Conductors and Insulators Worksheet
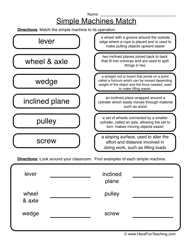
- 1 Simple Machines Worksheet
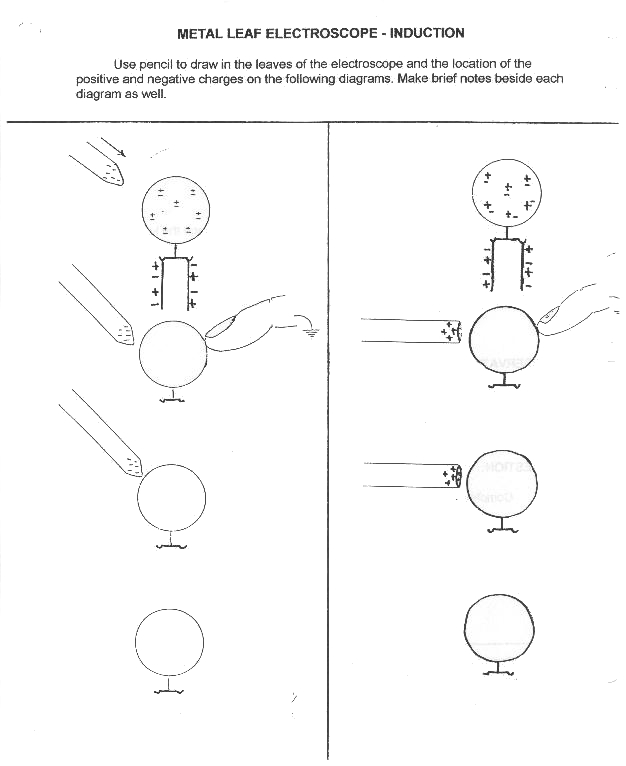
- Static Electricity Worksheets
- Magnetic Attraction Worksheet
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons. It can flow through conductive materials, like metals, and is essential for powering a wide range of devices and systems in today's modern world.
How is electricity produced?
Electricity is primarily produced through the conversion of various energy sources into electrical energy using power plants. This can be achieved through methods such as burning fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, or oil to generate steam that drives turbines connected to generators; harnessing the energy of flowing water through hydroelectric power plants; using nuclear reactions to produce heat and steam for electricity generation in nuclear power plants; capturing sunlight through solar panels to convert it into electricity; or utilizing wind energy to turn turbines and produce electricity in wind farms.
What are conductors and insulators?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electrical current through them, such as metals like copper and aluminum. Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that do not conduct electricity and block the flow of current, like rubber, plastic, and glass. Conductors have high electrical conductivity and low electrical resistance, while insulators have low electrical conductivity and high electrical resistance.
What is an electric circuit?
An electric circuit is a system of interconnected components that allow the flow of electric current. It typically includes a power source, conductive pathways like wires, and components such as resistors, capacitors, and switches. The circuit enables the movement of electrons from the power source through the components and back to complete a continuous loop, allowing electrical energy to be transferred and converted to perform useful work.
What is a switch and what does it do in a circuit?
A switch is an electrical component that is used to break or complete a circuit. When a switch is turned on, it allows the flow of electric current through the circuit, enabling the connected device to function. Conversely, when the switch is turned off, it interrupts the flow of current, effectively shutting down the connected device. Switches are essential for controlling the flow of electricity in a circuit and are commonly used in various electrical and electronic devices to enable or disable their operation.
What are the main parts of a simple circuit?
The main parts of a simple circuit include a power source (such as a battery), conductive pathways (wires) for electrical current to flow, a load (such as a light bulb or motor) that uses the electrical energy, and a switch to control the flow of electricity. These components work together to create a closed loop that allows the flow of electrons and the functioning of the circuit.
How does a series circuit differ from a parallel circuit?
A series circuit has all components connected along a single path, where the current flows through each component in succession. In contrast, a parallel circuit has multiple branches, with each component connected to the same voltage source but independently connected to each other. This means that in a parallel circuit, if one component fails, the others will continue to operate, whereas in a series circuit, if one component fails, the entire circuit will be interrupted.
What is the role of a battery in a circuit?
The role of a battery in a circuit is to provide the necessary energy or voltage to power the electrical components within the circuit. By converting chemical energy into electrical energy, the battery acts as a source of constant voltage that enables the flow of electrons through the circuit, allowing devices to function and perform their intended tasks.
How can you increase or decrease the brightness of a light bulb in a circuit?
To increase or decrease the brightness of a light bulb in a circuit, you can adjust the amount of current flowing through the bulb. Increasing the current will make the bulb brighter, while decreasing the current will make it dimmer. This can be achieved by using a variable resistor (such as a dimmer switch) in the circuit to regulate the flow of electricity to the bulb, thereby controlling its brightness.
What is static electricity and how does it differ from current electricity?
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object. It occurs when there is a transfer of electrons between two objects, leading to an imbalance of positive and negative charges. Unlike current electricity, which involves the constant flow of electrons through a conductor, static electricity involves stationary charges that remain in place until they are discharged, usually through a spark or sudden flow of current. Static electricity is typically generated by friction, induction, or contact between two different materials.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments