Roots Stems and Leaves Worksheet
Are you a biology student looking for a helpful resource to enhance your understanding of roots, stems, and leaves? Look no further! We have just the right worksheet for you. This worksheet focuses on the essential concepts related to plant anatomy, helping you grasp the functions and structures of roots, stems, and leaves. Whether you are studying for an exam or simply want to deepen your knowledge, this worksheet will provide you with a valuable tool for learning about these crucial plant components.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
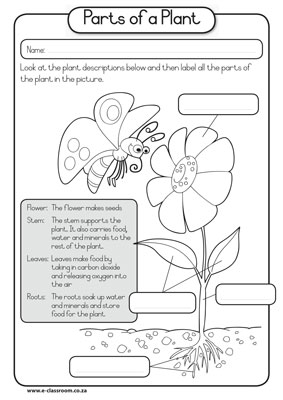
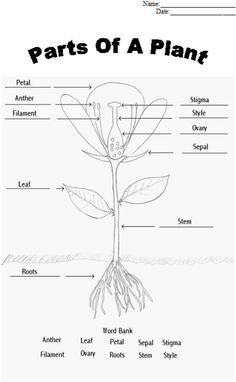
What is the primary function of roots?
The primary function of roots is to anchor plants into the soil, provide stability, and absorb water and nutrients necessary for growth and development.
How do the structures of taproots and fibrous roots differ?
Taproots have a main central root that grows deep into the soil, with smaller lateral roots branching off from it. This type of root system is typically found in dicot plants and helps provide stability and access to deep water sources. In contrast, fibrous roots consist of a dense network of thin roots that spread out close to the surface of the soil. This type of root system is common in monocot plants and helps with anchorage and nutrient absorption from the topsoil.
Describe the process of root absorption.
Root absorption, also known as root assimilation, is the process by which plants absorb water and essential nutrients from the soil through their root systems. This process involves the uptake of water through osmosis and the uptake of minerals and nutrients through active transport mechanisms. The root hairs on the surface of the roots increase the surface area for absorption, and the transport of water and nutrients occurs through the plant's vascular system, ultimately reaching the shoots and leaves where they are utilized for various physiological processes such as photosynthesis and growth.
How do root hairs contribute to nutrient uptake?
Root hairs are vital for nutrient uptake as they increase the surface area of the root system, allowing for greater absorption of water and minerals. These tiny, finger-like extensions of root cells are responsible for absorbing nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the soil. By having a large surface area, root hairs greatly enhance the plant's ability to take in essential nutrients, ultimately supporting growth and overall plant health.
What are the main functions of stems in plants?
The main functions of stems in plants include providing structural support for the plant, transporting nutrients and water from the roots to the leaves, and storing and producing food through photosynthesis. Stems also help in reproduction by producing flowers and fruits, and can facilitate growth by enabling the plant to reach towards sunlight and optimize its positioning for photosynthesis.
Explain the difference between herbaceous and woody stems.
Herbaceous stems are soft, green, and flexible, typically containing less lignin than woody stems while woody stems are rigid, hard, and brown due to the presence of lignin, a strengthening compound. Herbaceous stems only last for one growing season and do not increase in girth, while woody stems last for multiple years and can increase in girth through secondary growth. Woody stems also have distinct growth rings, which are absent in herbaceous stems.
How do the structures of monocots and dicots differ in terms of stem anatomy?
Monocots typically have scattered vascular bundles in their stems, which are not arranged in a ring. In contrast, dicots have vascular bundles arranged in a ring formation. Additionally, monocots lack secondary growth (growth in thickness) while dicots often have secondary growth that results in an increase in stem girth over time.
Describe the process of photosynthesis in leaves.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. In leaves, photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, where chlorophyll absorbs light energy. Water is taken up by the roots and transported to the leaves, where it is split into oxygen and hydrogen ions. Carbon dioxide from the air enters the leaves through tiny pores called stomata and is incorporated into organic molecules by the enzyme Rubisco. The hydrogen ions produced in the water-splitting reaction are used to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose in a series of chemical reactions. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis. Thus, the overall process of photosynthesis in leaves involves the conversion of light energy, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen.
What are the different types of leaf arrangements seen in plants?
There are three main types of leaf arrangements in plants: alternate, opposite, and whorled. In alternate leaf arrangement, a single leaf grows at each node along the stem in an alternating pattern. In opposite leaf arrangement, two leaves grow across from each other at the same node. In whorled leaf arrangement, three or more leaves grow from the same node in a circular or whorled pattern.
How do leaves adapt to different environmental conditions?
Leaves have various adaptations to different environmental conditions, such as size, shape, thickness, color, and surface texture. For example, in hot and dry conditions, leaves may be smaller, thicker, and have fewer stomata to minimize water loss. In shady conditions, leaves may be larger and thinner to maximize light absorption. Additionally, some plants have specialized structures like hairs or waxy coatings to reduce water loss or protect against herbivores. These adaptations help leaves optimize their functions of photosynthesis, gas exchange, and water regulation in various environmental conditions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments