Rocks and Minerals Vocabulary Worksheets
To expand your knowledge and understanding of rocks and minerals, incorporating worksheets into your learning routine can be immensely beneficial. These worksheets provide a structured way to reinforce various vocabulary terms related to the subject, such as sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks. By practicing with these worksheets, you can enhance your grasp of rocks and minerals terminology, making it easier to identify different types and characteristics when studying or exploring the subject further.
Table of Images 👆
- Rocks and Minerals Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Rock and Minerals Printables
- Christmas Word Scramble Worksheet and Answers
- Vocabulary Flash Card Template Printable
- 6th Grade Rocks and Minerals Worksheets
- Types of Rocks Worksheets Free
- Printable Worksheets On Rocks and Minerals
- Rocks and Minerals Word Search Printable
- Main Idea and Details Worksheets
- 3 Types of Rocks Worksheet
- Third Grade Science Worksheets
- Tectonic Worksheet Plate Boundaries
- Mineral Identification Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
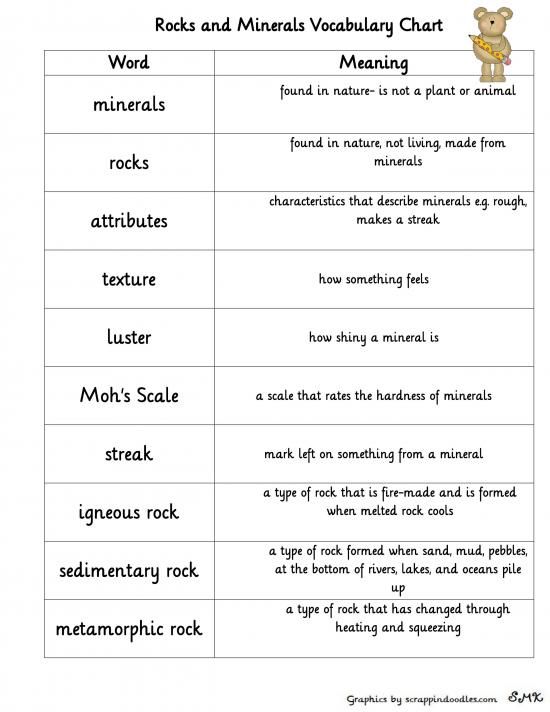
What is the definition of a mineral?
A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid substance with a specific chemical composition and a crystalline structure. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks, and they can be identified by their physical properties such as hardness, color, luster, and cleavage. Minerals play a crucial role in various industries and are essential for the functioning of our planet.
How are igneous rocks formed?
Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Magma is molten rock found beneath the Earth's surface, while lava is molten rock that has reached the surface. As magma or lava cools and hardens, mineral crystals form and interlock, creating the distinctive texture and composition of igneous rocks. The rate of cooling and the chemical composition of the magma/lava influence the type of igneous rock that is ultimately formed, with rapid cooling forming fine-grained rocks like basalt and slower cooling creating coarse-grained rocks like granite.
What is the difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks?
Intrusive igneous rocks form below the Earth's surface through the slow cooling and solidification of magma, resulting in large crystals due to the longer cooling time. On the other hand, extrusive igneous rocks are formed on the Earth's surface from rapidly cooling lava, leading to smaller crystals or glassy textures. The main difference lies in their formation locations, cooling rates, and resulting crystal sizes.
What is the process of weathering?
Weathering is a process that breaks down rocks and minerals on the Earth's surface into smaller pieces. It can occur through physical processes such as the expansion and contraction of rocks due to temperature changes, as well as through chemical processes involving the interaction of minerals with water, air, and other substances. Over time, weathering can result in the erosion and decomposition of rock materials, leading to the formation of sediments and soil.
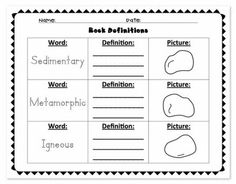
Define the term sedimentary rock.
Sedimentary rock is a type of rock formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments such as silt, sand, clay, and organic material deposited by water, ice, or wind over time. These sediments are compacted and cemented together through various geological processes to create sedimentary rock, which often contains fossils and provides valuable insights into Earth's history and environmental conditions during its formation.
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
Sedimentary rocks are formed through the process of sedimentation, where particles of rock, minerals, and organic matter accumulate and are compacted and cemented together over time. This can occur through the deposition of sediments by water, wind, ice, or gravity. As these sediments accumulate and are subjected to pressure and chemical reactions, they eventually form solid layers of sedimentary rock.
What is the difference between foliated and non-foliated metamorphic rocks?
Foliated metamorphic rocks have a layered or banded appearance due to the alignment of mineral grains, while non-foliated metamorphic rocks lack this alignment and typically have a more random or uniform texture. Foliated rocks form under directed pressure, such as during regional metamorphism, while non-foliated rocks usually result from contact metamorphism or regional metamorphism under conditions lacking directed pressure. Examples of foliated rocks include slate, schist, and gneiss, while examples of non-foliated rocks include marble and quartzite.
How can you distinguish between minerals and rocks?
Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic solid substances with a specific chemical composition, crystalline structure, and physical properties, while rocks are made up of one or more minerals combined together. One way to distinguish between minerals and rocks is to look at their composition and structure: minerals are composed of a single mineral compound, such as quartz or feldspar, while rocks contain a mixture of different minerals. Additionally, minerals have a characteristic crystal form and cleavage, whereas rocks do not exhibit distinct crystal shapes. Minerals also have unique physical properties like hardness and color that can be used for identification, while rocks are classified based on their texture and mineral content.
What is the Mohs scale used for?
The Mohs scale is used to measure the hardness of minerals based on their ability to scratch one another. It ranks minerals from 1 (talc, softest) to 10 (diamond, hardest), helping geologists and jewelers identify and classify different minerals based on their hardness characteristics.
Define the term crystal structure.
A crystal structure is the specific arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material, exhibiting a regular, repeating three-dimensional pattern. It includes the positions of the constituent particles and the distances between them, providing a unique geometric framework that gives crystals their distinctive physical and chemical properties.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments