Refraction and Lenses Worksheet
This blog post will provide an in-depth analysis of refraction and lenses through a comprehensive worksheet. If you are a student or educator seeking a practical and engaging resource to reinforce your understanding of these concepts, this worksheet is designed to meet your needs.
Table of Images 👆
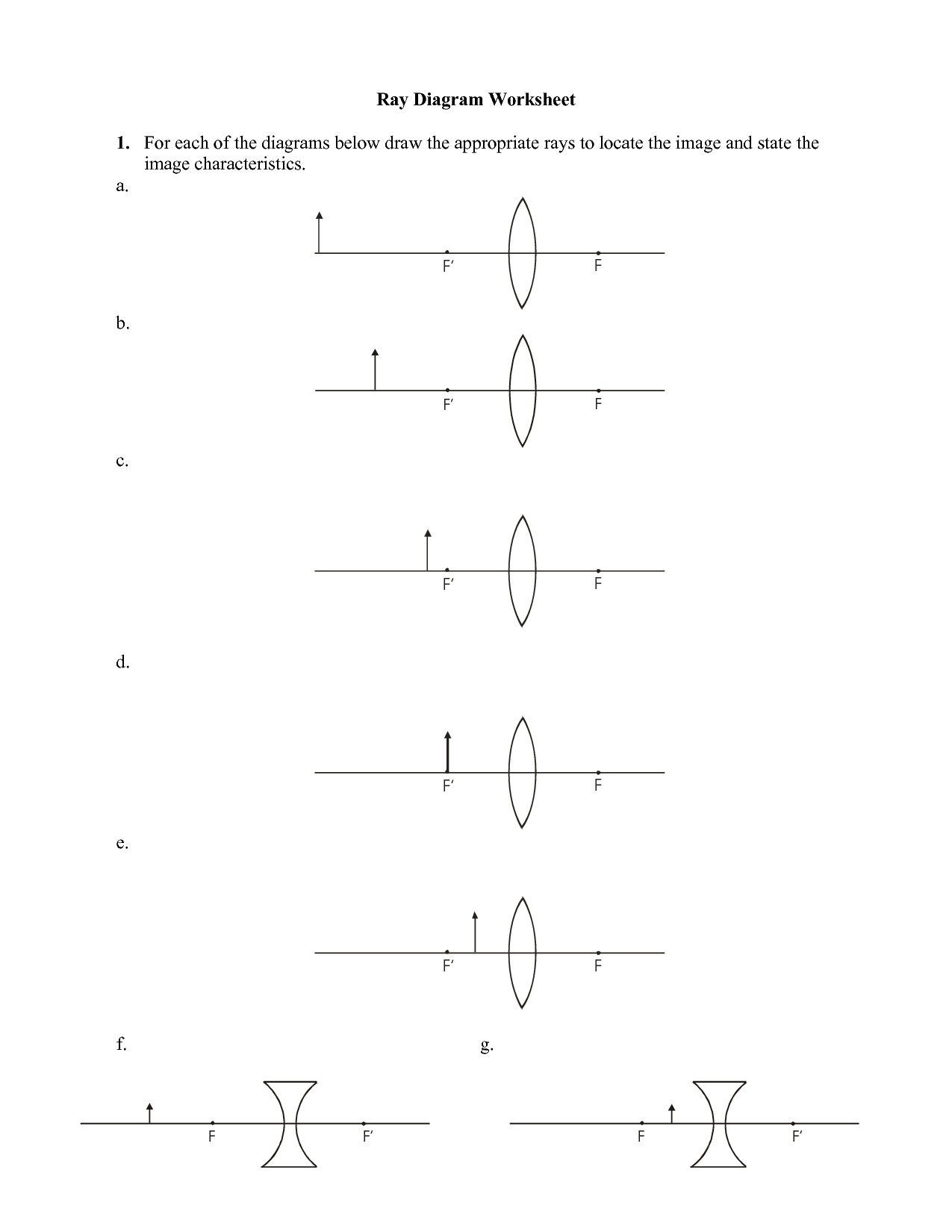
- Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Worksheet
- Impulse-Momentum Worksheet with Answer Key
- Mirrors and Reflection Worksheet Answers
- Light Reflection Refraction Worksheets
- Light and Atoms Worksheet 2 Answers
- Potential Energy Worksheets
- Reflection Refraction Worksheet
- Reflection Refraction Physics Cheat Sheet
- The New Testament
- Reflection Refraction and Diffraction
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is refraction?
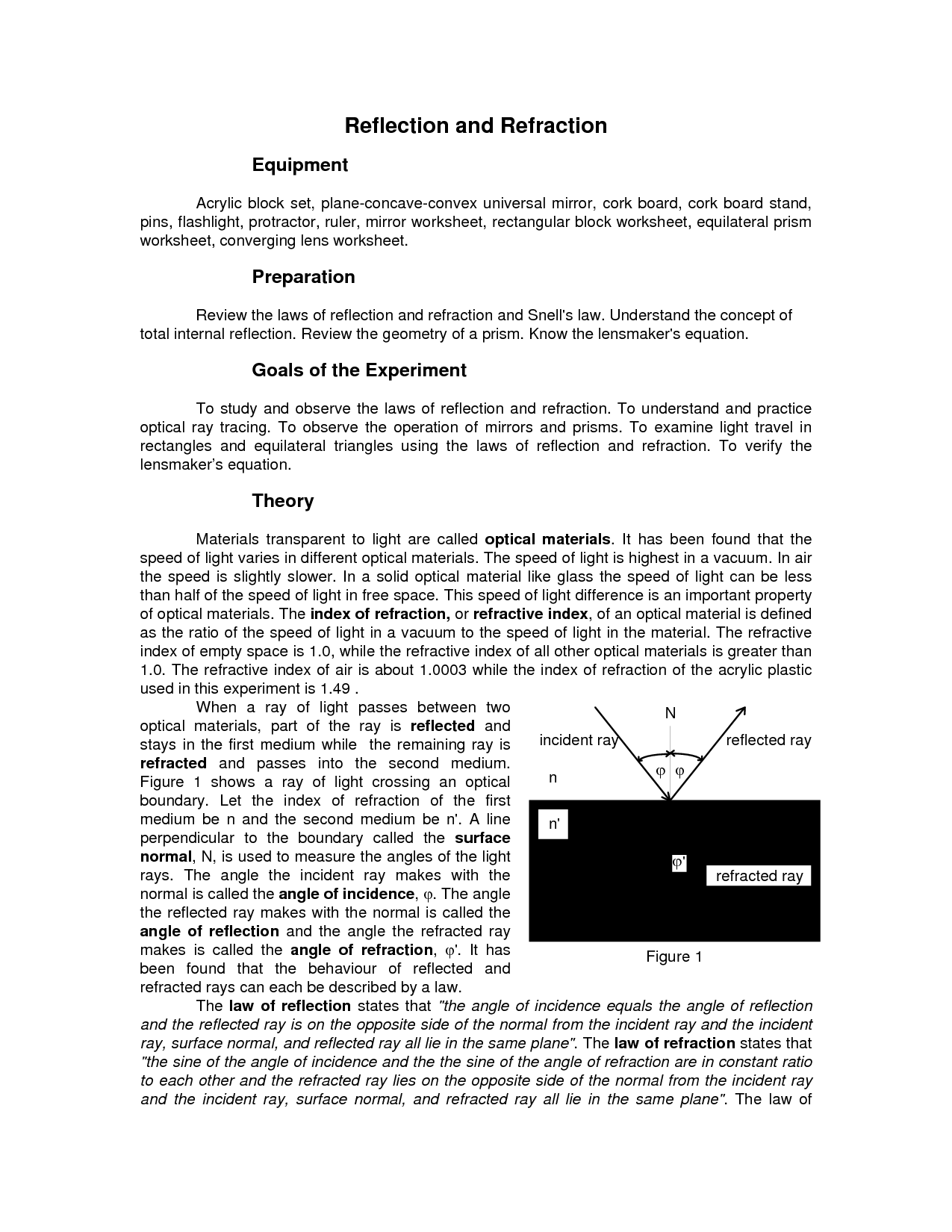
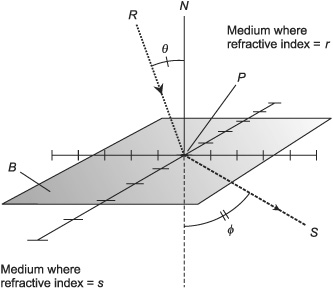
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave, such as light or sound, as it passes from one medium to another medium with a different density. This change in direction occurs because the wave travels at different speeds in each medium, causing it to bend.
How does refraction occur?
Refraction occurs when a wave changes direction as it travels from one medium to another due to a change in its speed. This change in speed results in the wave bending at the boundary between the two mediums, causing it to travel in a different direction. The amount of bending depends on the difference in the refractive indexes of the two materials and the angle at which the wave enters the new medium.
What is the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction?
The relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction is governed by Snell's Law, which states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is equal to the ratio of the velocities of light in the two different media. This relationship describes how light bends or refracts as it passes from one medium to another with different optical densities.
How do lenses refract light?
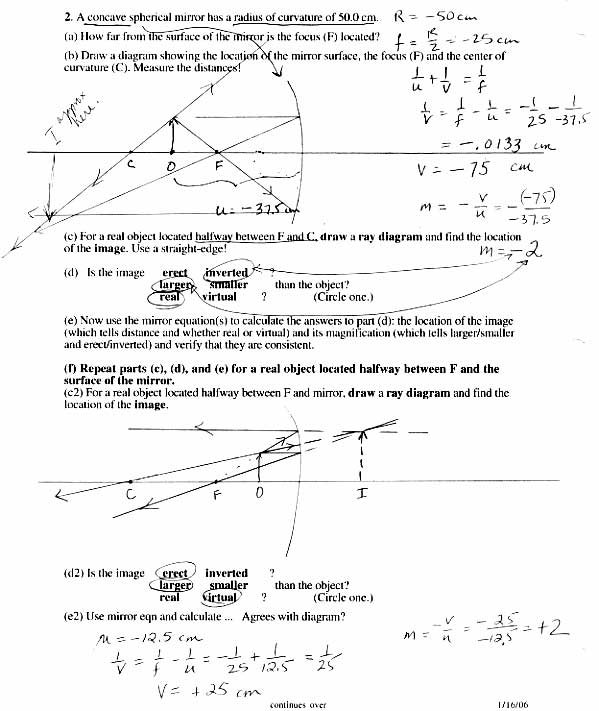
Lenses refract light by bending and focusing light rays as they pass through the lens. When light enters the lens, it changes speed and direction, causing the light rays to converge or diverge depending on the shape of the lens. Convex lenses, or converging lenses, focus incoming light rays to a single point called the focal point, while concave lenses, or diverging lenses, spread out the incoming light rays. This refraction process allows lenses to magnify or reduce the size of objects, correct vision, and create images in cameras and microscopes.
What are the two types of lenses?
The two types of lenses are convex lenses and concave lenses. Convex lenses bulge outwards in the middle and converge light rays to a focal point, creating real or virtual images, while concave lenses curve inward and diverge light rays, causing the rays to spread out and creating only virtual images.
What is the difference between concave and convex lenses?
Concave lenses are thinner in the center and cause light rays to diverge, creating virtual images that are smaller than the object. Conversely, convex lenses are thicker in the center and converge light rays to create real images that are magnified. Concave lenses are used in correcting nearsightedness, while convex lenses are used to correct farsightedness and for magnification purposes in devices such as cameras and glasses.
How does the shape of a lens affect the refraction of light?
The shape of a lens affects the refraction of light by determining how the light rays converge or diverge as they pass through the lens. Convex lenses, which are thicker in the center than at the edges, converge light rays and focus them to a point called the focal point. This type of lens is used in magnifying glasses and cameras. On the other hand, concave lenses, which are thinner in the center than at the edges, cause light rays to diverge and spread out. This type of lens is used in correcting conditions like myopia (nearsightedness). The curvature of the lens also plays a role in determining the amount of bending that occurs when light passes through it.
What is the focal point of a lens?
The focal point of a lens is the point where light rays parallel to the optical axis converge or appear to diverge from after passing through the lens. It is a key characteristic used to describe the ability of a lens to converge or diverge light, and is essential in understanding the behavior of lenses in optics and image formation.
How is the focal length of a lens determined?
The focal length of a lens is determined by measuring the distance between the lens and the point where parallel light rays converge (the focal point) when the lens is used to focus light. This can be done by placing a distant object in front of the lens and measuring the distance from the lens to the image plane when the object is in focus. Another method involves using a lens equation that relates the object distance, image distance, and focal length to determine the focal length of the lens.
How are lenses used in everyday applications?
Lenses are used in everyday applications in various ways, such as in eyeglasses to correct vision, in cameras to focus and capture images, in microscopes and telescopes to magnify objects, and in projectors to display images on screens. Additionally, lenses are used in devices like smartphones, binoculars, and car headlights to help users see more clearly or focus on objects at different distances.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments