Real Number System Worksheet PDF
Are you a math teacher or parent searching for a reliable resource to test your students' knowledge of the real number system? If so, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we will discuss the benefits of using worksheets to reinforce understanding of this foundational mathematical concept. By providing targeted practice problems, worksheets offer an effective tool to engage students and help them grasp the intricacies of the real number system. Whether you're looking for supplementary materials for your classroom or additional assignments for independent study, worksheets can be a valuable asset for both educators and learners alike.
Table of Images 👆
More Number Worksheets
Teen Number Practice WorksheetNumber Cut Out Worksheet
Kindergarten Number Worksheets 1 50
Thanksgiving Number Worksheets
Blank Kindergarten Numbers 1-100 Worksheets
Missing Number Multiplication Worksheets
Missing Teen Numbers Worksheet
6th Grade Color by Number Worksheets
Counting Numbers to 1000 Worksheets
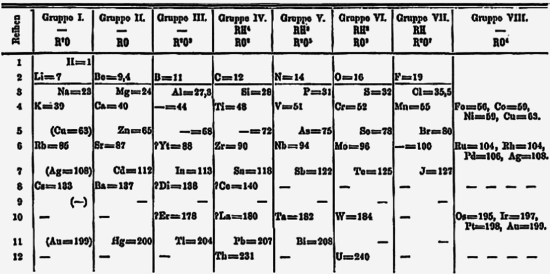
What is the Real Number System?
The Real Number System is a system that includes all rational and irrational numbers. It encompasses all numbers that can be represented on a number line, including integers, fractions, decimals, and square roots. The set of real numbers is continuous and infinite, allowing for the representation of any quantity or measurement on a mathematical scale.
What are the main subsets of the Real Number System?
The main subsets of the Real Number System include the Natural Numbers (positive integers), Whole Numbers (non-negative integers), Integers (positive and negative whole numbers including zero), Rational Numbers (numbers that can be expressed as fractions), and Irrational Numbers (numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions). These subsets collectively make up the Real Number System, which encompasses all numbers that can be represented on the number line.
How are rational numbers defined?
Rational numbers are defined as any number that can be expressed as a fraction where the numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero. In other words, rational numbers are numbers that can be written in the form a/b, where a and b are integers and b is not equal to zero.
What are the characteristics of irrational numbers?
Irrational numbers are real numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions with integer numerator and denominator. They are non-repeating and non-terminating decimals, making them infinitely long and non-repeating sequences of digits. Irrational numbers have an infinite decimal expansion in which the digits do not follow a predictable pattern. Additionally, they are not roots of any non-zero polynomial equation with integer coefficients.
Explain the concept of repeating decimals.
Repeating decimals are decimal numbers that have a repeating pattern of one or more digits that goes on infinitely. These patterns are typically denoted by placing a vinculum (a bar) over the repeating digits, such as in the decimal representation 0.333... where the "3" repeats infinitely. The pattern in a repeating decimal can be one or more digits in length and usually indicates that the decimal form cannot be fully expressed as a fraction with a finite number of digits.
How can you differentiate between a terminating and a non-terminating decimal?
A terminating decimal is a decimal number that ends (terminates) and has a finite number of digits after the decimal point, such as 0.75 or 3.2. In contrast, a non-terminating decimal is a decimal number that continues indefinitely without repeating, such as ? (pi) or ?2. This means that a non-terminating decimal has an infinite number of digits after the decimal point.
Describe the process of ordering real numbers on a number line.
To order real numbers on a number line, you start by placing the numbers from left to right in increasing order. The number line has zero at the center, with negative numbers to the left and positive numbers to the right. You then place smaller numbers to the left of larger numbers in accordance with their values. For decimal numbers, you compare the whole numbers before the decimal point first and then the numbers after the decimal point. Decimals can be converted to fractions to simplify the comparison process. Finally, you can compare irrational numbers by approximating them to a certain level of precision and placing them accordingly on the number line.
What is the significance of the number zero in the Real Number System?
In the Real Number System, zero is significant because it serves as the additive identity element, meaning that when zero is added to any real number, the result is that real number itself. It also acts as the multiplicative identity, such that when any real number is multiplied by zero, the product is zero. Additionally, zero is the only integer that is neither positive nor negative, impacting calculations and equations involving positive and negative values.
How does the concept of absolute value apply to real numbers?
The concept of absolute value applies to real numbers by giving the distance of a number from zero on the number line. It is always a non-negative value, representing the magnitude of a number regardless of its sign. Absolute value can be calculated by dropping the negative sign if present, making it a useful tool for finding the distance between two points or determining the size of a number without considering its direction.
Briefly discuss the concept of complex numbers within the Real Number System.
Complex numbers extend the Real Number System by introducing the imaginary unit "i," where i^2 = -1. A complex number is then expressed as a sum of a real part and an imaginary part, taking the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers. This representation allows for solutions to equations with no real roots, enabling a deeper understanding and analysis of mathematical problems. Complex numbers play a crucial role in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics, as they provide a powerful tool for modeling and solving a wide range of problems.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments