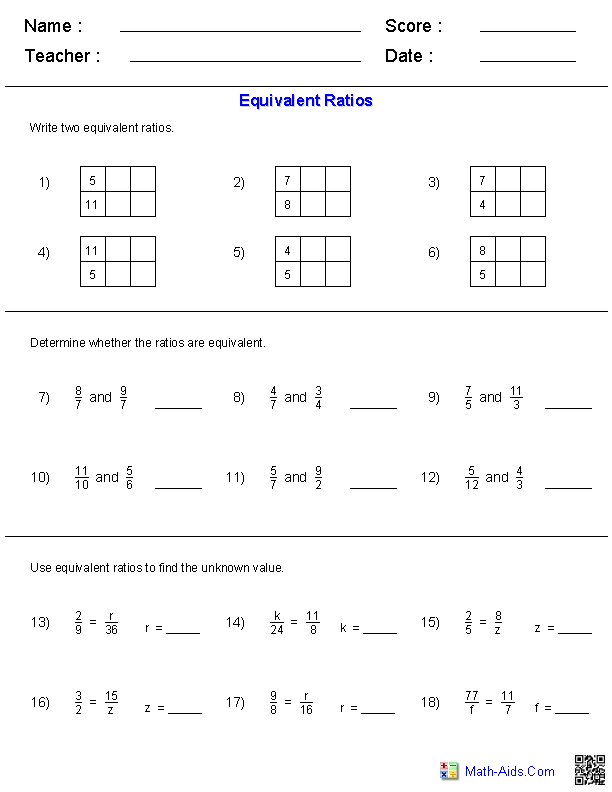
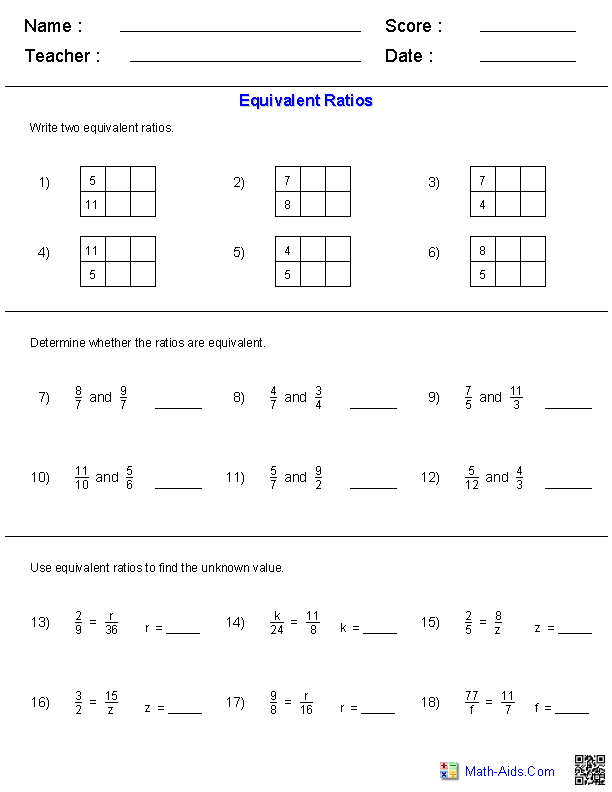
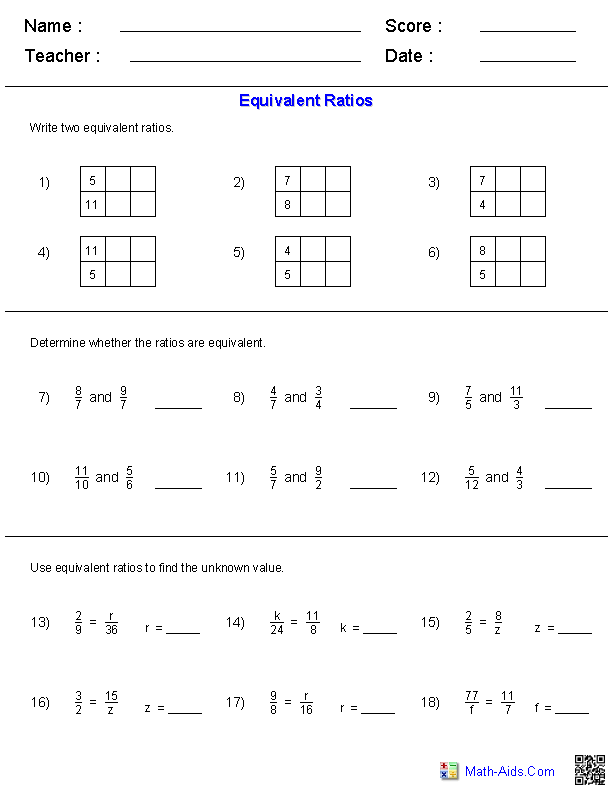
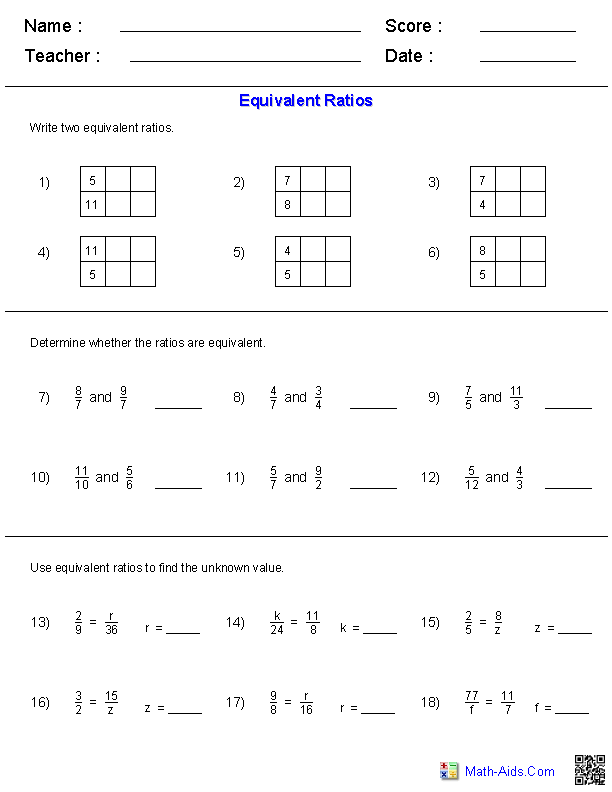
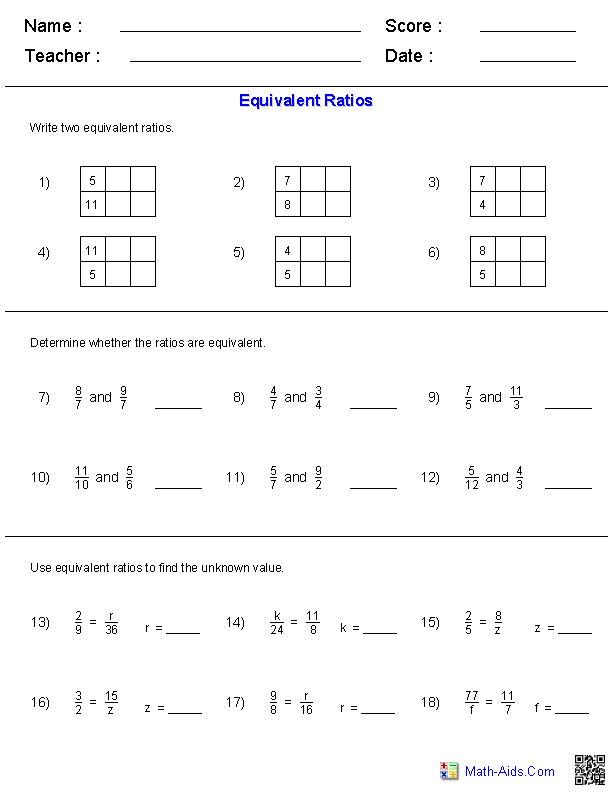
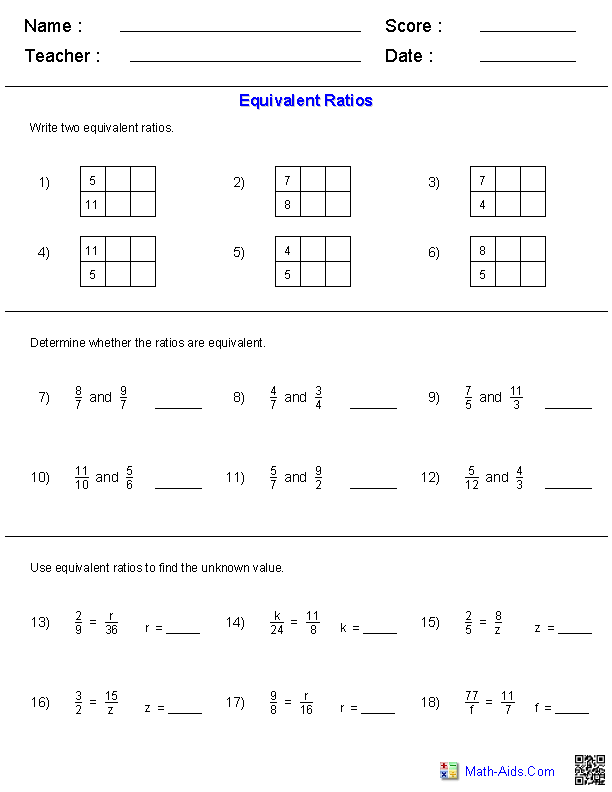
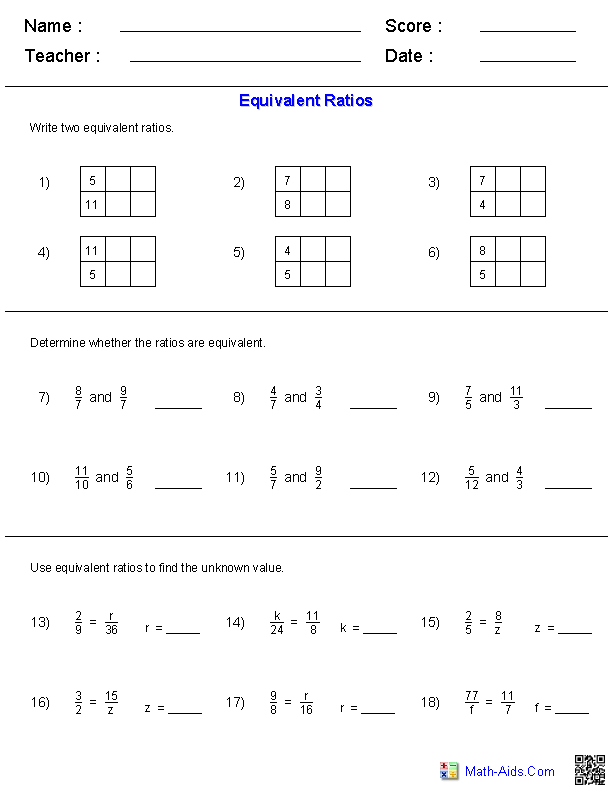
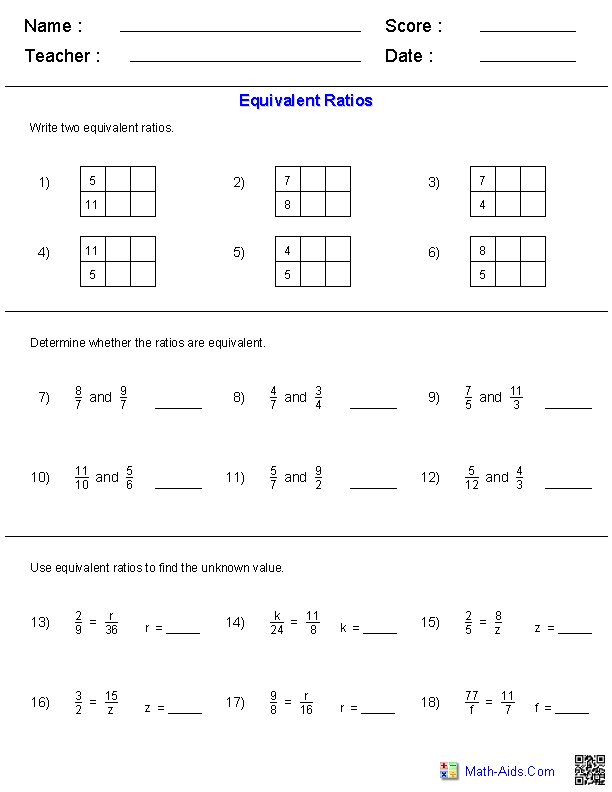
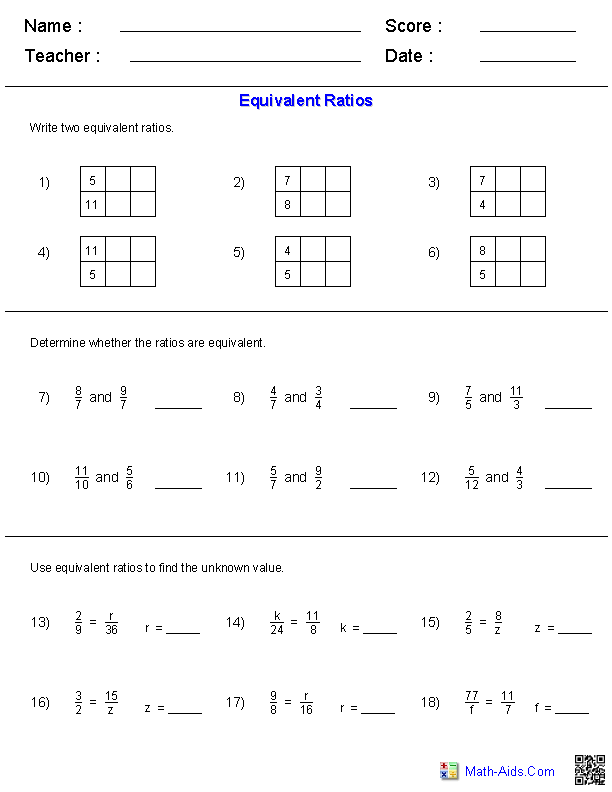
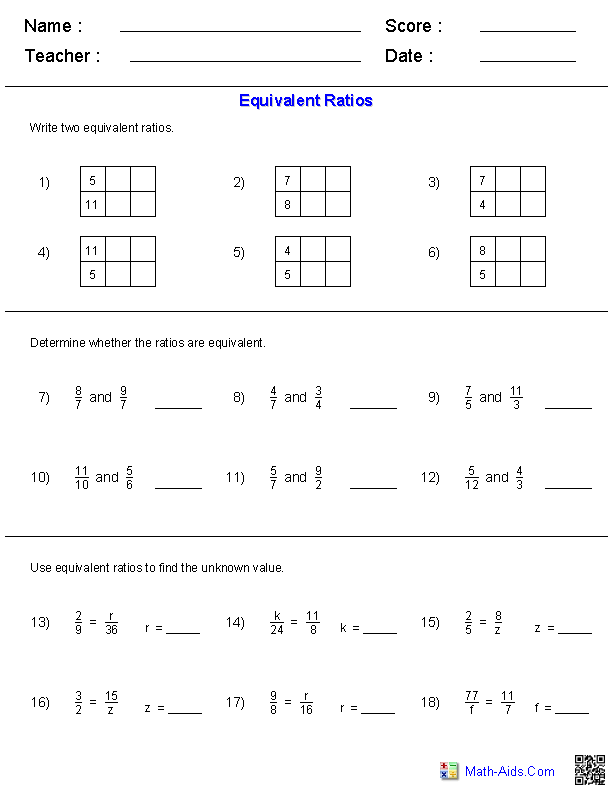
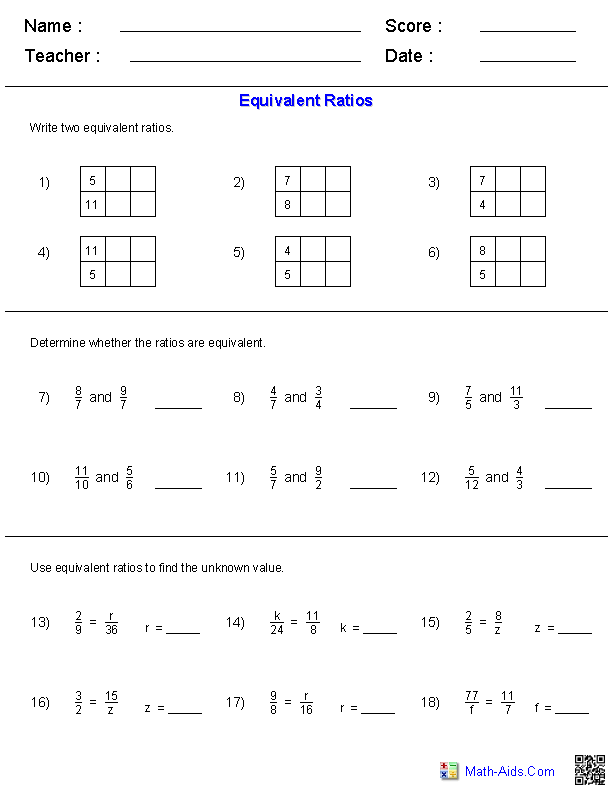
Quadratic Equation Practice Problem Worksheet
If you're a high school student struggling with quadratic equations or a teacher looking for extra practice materials for your students, this quadratic equation practice problem worksheet is just what you need.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
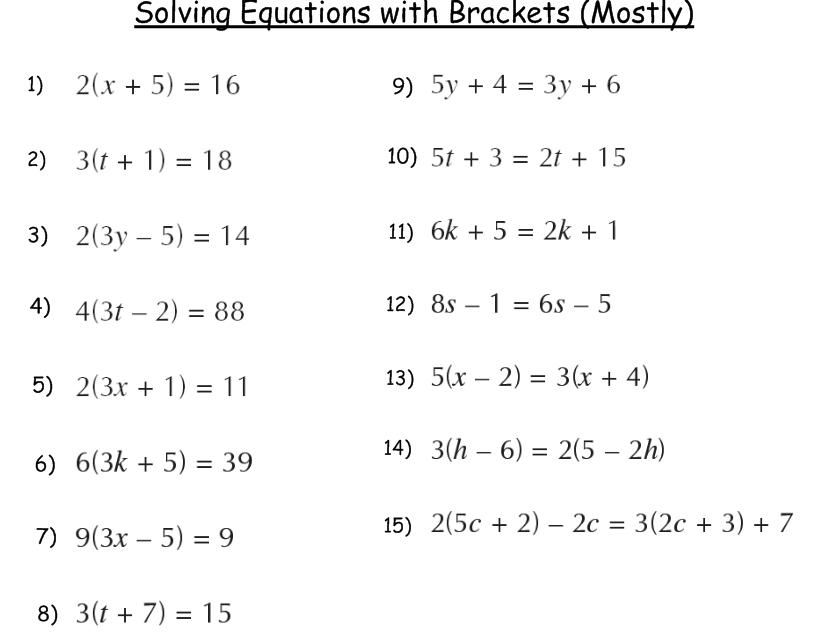
What is the general form of a quadratic equation?
The general form of a quadratic equation is written as ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and x represents the variable.
How many solutions does a quadratic equation have at most?
A quadratic equation can have at most two solutions, which can be real or complex, based on the discriminant (b^2 - 4ac) of the equation. If the discriminant is positive, the quadratic equation will have two distinct real solutions. If the discriminant is zero, the equation will have one real solution. If the discriminant is negative, the equation will have two complex (or imaginary) solutions.
What is the vertex form of a quadratic equation?
The vertex form of a quadratic equation is given as \( y = a(x-h)^2 + k \), where \( (h,k) \) represents the coordinates of the vertex of the parabolic curve. This form is useful for easily identifying the vertex of the parabola and understanding how changes in the values of \( a \), \( h \), and \( k \) affect the shape and position of the graph.
How do you find the vertex of a quadratic equation?
To find the vertex of a quadratic equation in the form of y = ax^2 + bx + c, you can use the formula x = -b/(2a) to find the x-coordinate of the vertex. Then, substitute this x-value into the original equation to find the y-coordinate of the vertex. The vertex will be the point where the parabola changes direction and is either at the minimum (for a positive value of a) or maximum (for a negative value of a) point of the graph.
What is the discriminant of a quadratic equation used for?
The discriminant of a quadratic equation is used to determine the nature of the roots of the equation. By calculating the discriminant (b^2 - 4ac), one can find out if the quadratic equation has two real and distinct roots, two real and equal roots, or two complex roots. This information is helpful in solving the equation and understanding the geometry of its graph.
How do you determine the nature of the solutions using the discriminant?
You can determine the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation using the discriminant, which is given by the formula ? = bē - 4ac. If the discriminant is greater than 0, the equation has two distinct real solutions. If the discriminant is equal to 0, the equation has one real solution (or two identical real solutions). If the discriminant is less than 0, the equation has two complex conjugate solutions. Overall, the discriminant helps to classify the nature of the solutions of a quadratic equation based on the value obtained through the formula.
What is the quadratic formula used for?
The quadratic formula is used to solve quadratic equations, which are equations of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0. By using the quadratic formula, one can find the roots or solutions of the equation, which are the values of x that satisfy the equation. This formula is particularly useful in algebra and mathematics for solving various problems involving quadratic equations.
How do you graph a quadratic equation?
To graph a quadratic equation, you first need to rearrange it into the standard form y = ax^2 + bx + c. Plot the vertex point at (-b/2a, f(-b/2a)), where f(-b/2a) is the value of y obtained by substituting -b/2a into the equation. Next, find the x-intercepts by solving the equation for y = 0 using the quadratic formula. Lastly, draw a symmetrical parabola using the vertex point and x-intercepts. Remember to label the axes and any key points to create a clear and accurate graph of the quadratic equation.
How can you determine if a quadratic equation opens upwards or downwards?
To determine if a quadratic equation opens upwards or downwards, look at the coefficient of the squared term (the term with the variable raised to the power of 2). If the coefficient is positive, the parabola opens upwards. If the coefficient is negative, the parabola opens downwards. The coefficient influences the direction of the opening of the quadratic equation.
What are the key properties of a quadratic equation?
A quadratic equation is a second-degree polynomial equation that can be written in the standard form \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are constants with \( a \neq 0 \). The key properties of a quadratic equation include having a U-shaped graph (parabola), having a maximum or minimum point, having one or two real roots or complex roots depending on the discriminant (\( b^2 - 4ac \)), and the symmetry of the graph about the axis of symmetry, which is given by \( x = -b/(2a) \).
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




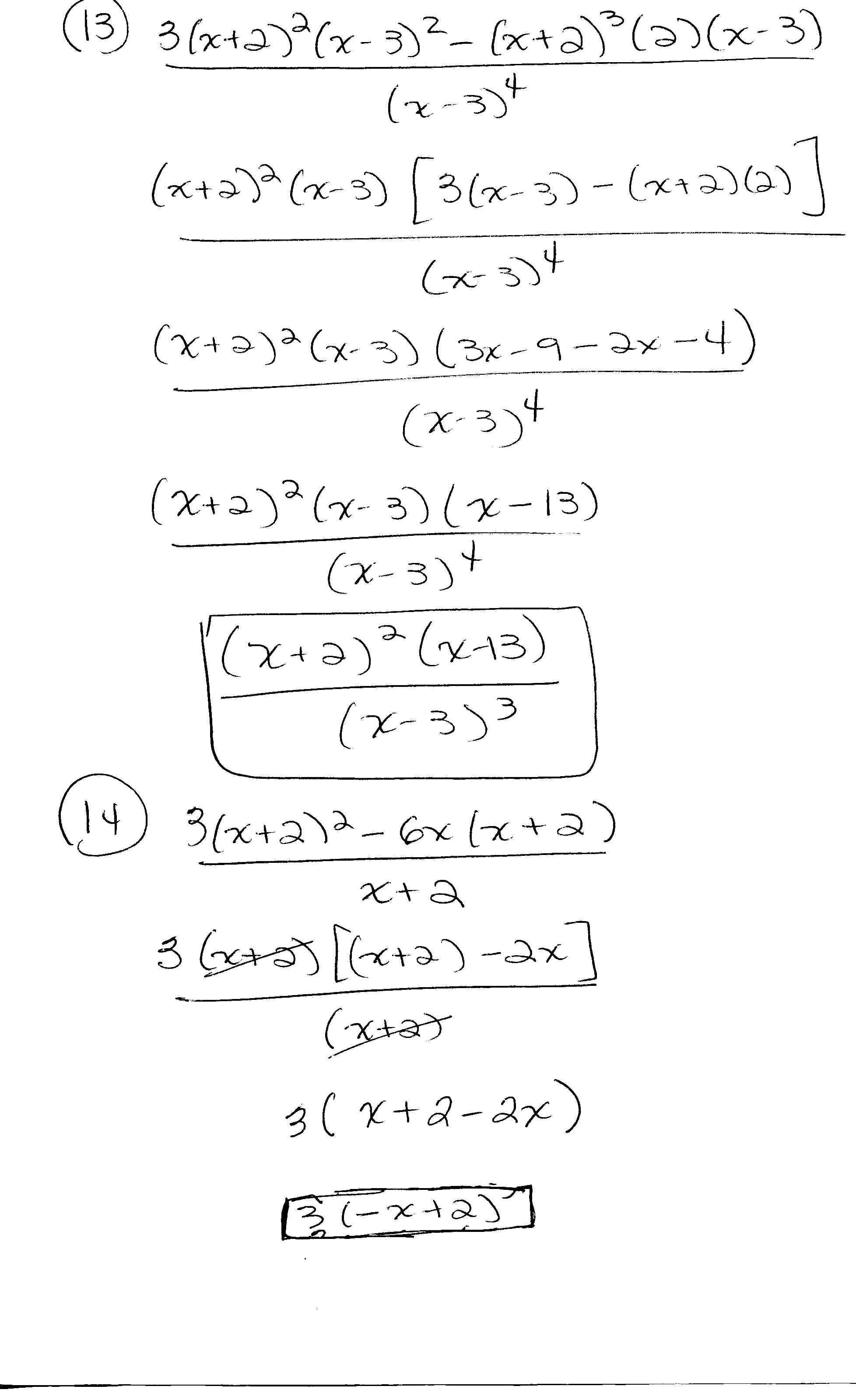


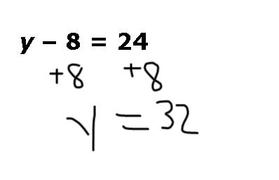















Comments