Pythagorean Theorem Worksheets and Answers
Are you a math teacher or a student learning about the Pythagorean Theorem? If so, you may be looking for worksheets that can help reinforce your understanding of this important concept. Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with a variety of Pythagorean Theorem worksheets and their corresponding answers, allowing you to practice and master this mathematical entity.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
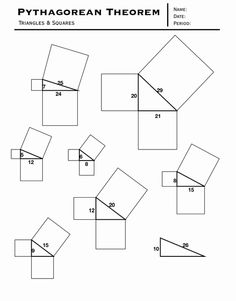
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Mathematically, it can be expressed as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where c represents the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides.
How is the Pythagorean Theorem represented mathematically?
The Pythagorean Theorem is represented mathematically as \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \), where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the two shorter sides of a right triangle, and \(c\) is the length of the hypotenuse. This equation shows the relationship between the sides of a right triangle and is fundamental in geometry and trigonometry.
What are the three sides of a right triangle?
The three sides of a right triangle are the hypotenuse, which is the side opposite the right angle and is the longest side; the adjacent side, which is the side next to the angle of interest; and the opposite side, which is the side across from the angle of interest.
How can the Pythagorean Theorem be used to find the length of one side of a right triangle?
To find the length of one side of a right triangle using the Pythagorean Theorem, you would first identify the two sides of the triangle that are known. Let's call the unknown side "c" and the other two sides "a" and "b". Then, you can use the formula a² + b² = c², where a and b are the lengths of the two known sides. Substitute the known values into the equation to solve for the unknown side, c.
Can the Pythagorean Theorem be used for all triangles or just right triangles?
The Pythagorean Theorem can only be used for right triangles, as it specifically relates to the relationship between the squares of the lengths of the sides in a right triangle. For other types of triangles, different formulas and theorems must be used to determine their properties and relationships.
What is the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem?
The converse of the Pythagorean Theorem states that if the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle.
How can the Pythagorean Theorem be applied in real-life situations?
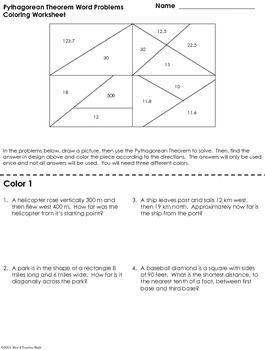
The Pythagorean Theorem can be applied in a variety of real-life situations, such as measuring distances, calculating areas, and designing structures. For example, it can be used in construction to ensure that buildings are built with stable right angles, determining the length of cables required for a zip line, or calculating the distance a person needs to walk to get from one point to another. Ultimately, the Pythagorean Theorem provides a fundamental tool for solving many geometric problems in everyday scenarios.
What are some common misconceptions or mistakes students make when using the Pythagorean Theorem?
One common misconception students make when using the Pythagorean Theorem is incorrectly identifying the hypotenuse in a right triangle. This can lead to using the wrong side lengths in the formula a² + b² = c², resulting in inaccurate calculations. Another mistake is forgetting to square the side lengths before adding them together or omitting a squared term altogether. Additionally, students sometimes incorrectly apply the Pythagorean Theorem to non-right triangles, which only works for right triangles.
How can the Pythagorean Theorem be extended to higher dimensions?
The Pythagorean Theorem can be extended to higher dimensions through the concept of the distance formula in n-dimensional space, where the distance between two points is calculated by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the differences in each coordinate direction. This generalized form allows for the calculation of distance and relationships between points in spaces of any dimension, maintaining the essence of the Pythagorean relationship but expanding it beyond the confines of 2-dimensional space.
Are there any alternative methods to the Pythagorean Theorem for finding the length of the sides of a right triangle?
Yes, there are alternative methods for finding the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. Some examples include trigonometric ratios (such as sine, cosine, and tangent) and special right triangle properties (like 30-60-90 and 45-45-90 triangles). These methods can be used in specific cases to calculate the side lengths without relying on the Pythagorean Theorem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments