Protein Group Worksheets
Protein group worksheets are a valuable tool for individuals and educators who are interested in learning more about the essential macronutrient. These worksheets provide a comprehensive and organized way to explore the different sources of protein, their nutritional content, and their benefits for the body.
Table of Images 👆
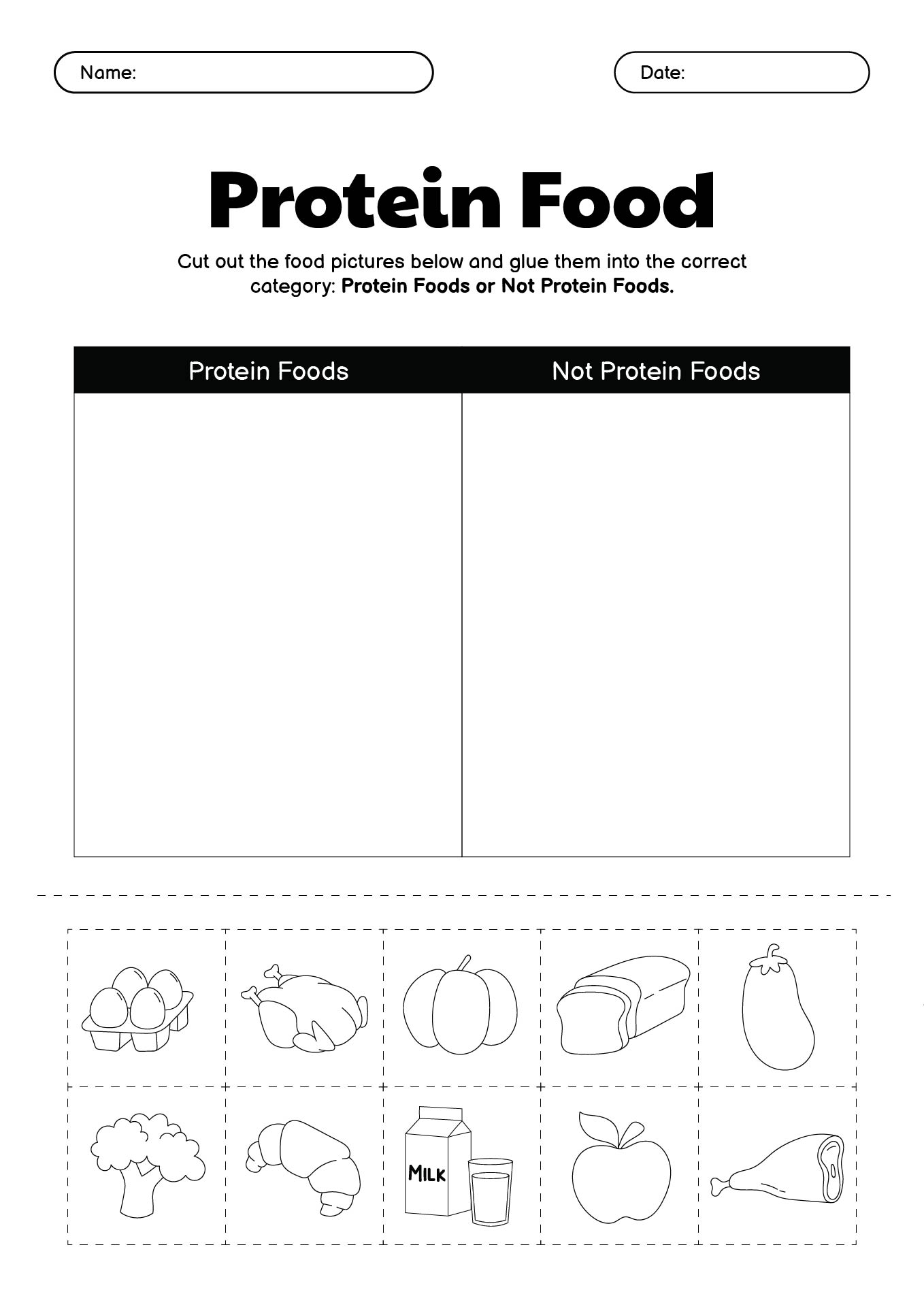
- Protein Food Group Coloring Pages Kids
- Food Groups Worksheets
- Grain Food Group Coloring
- Food Groups Colouring Pages
- Eat the Rainbow Preschool Worksheets
- Healthy Food Coloring
- Dairy Food Group Coloring Page
- Carbohydrates Food Coloring Page
- Preschool Food Group Activities
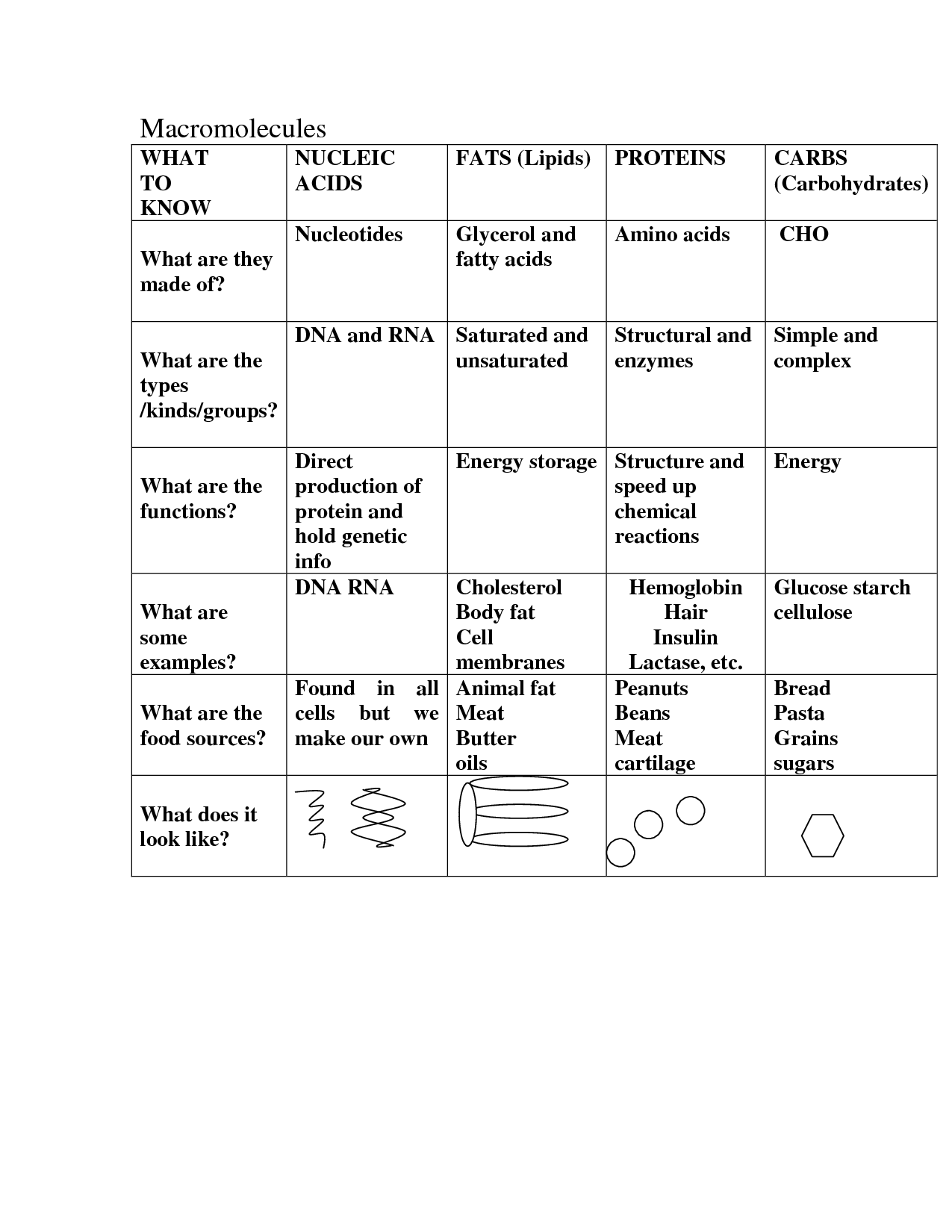
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Protein Food Group Coloring Page
- Healthy Food Pyramid Coloring Pages
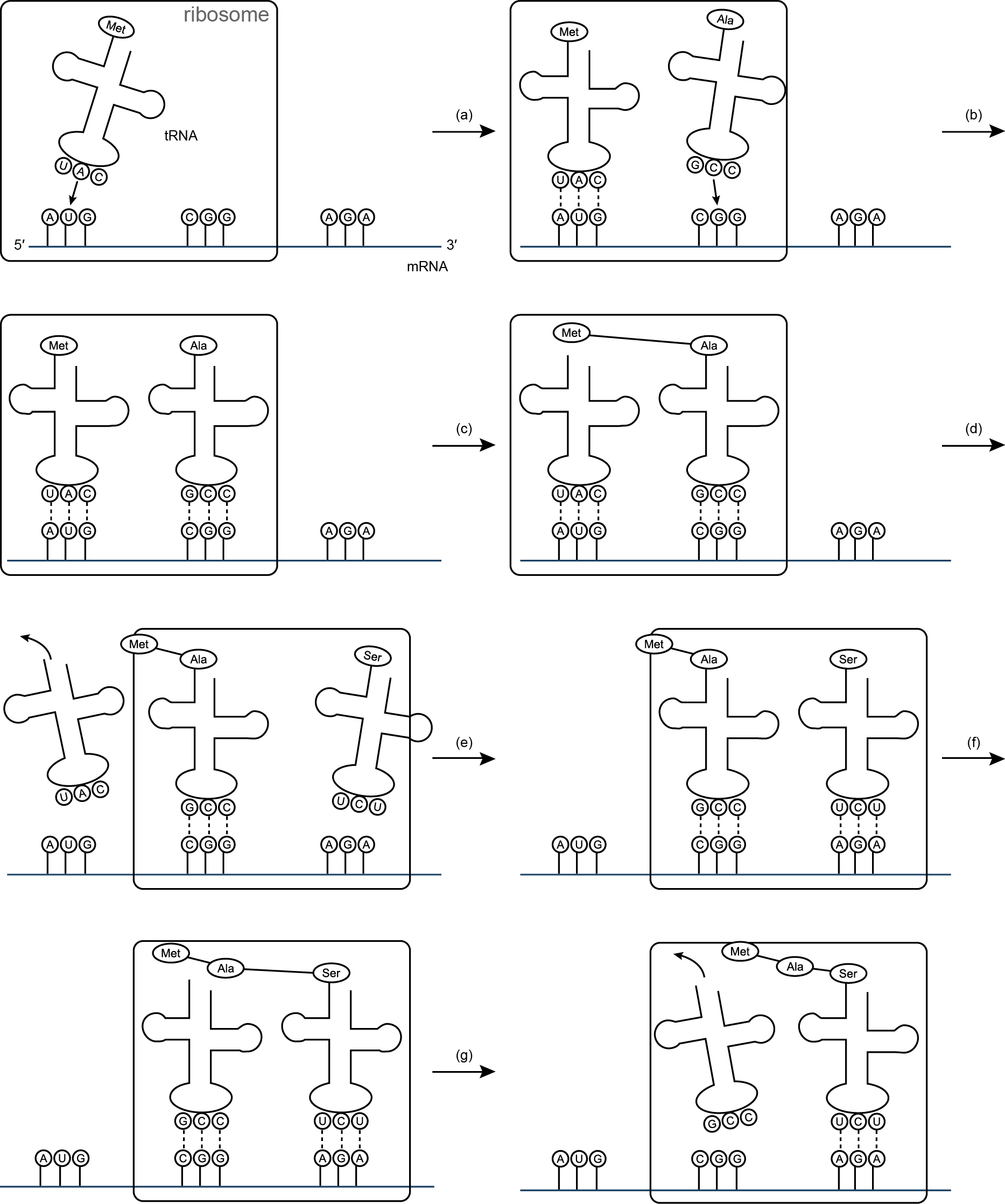
- Transcription Worksheet DNA mRNA Amino Acid
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the main function of proteins?
Proteins play a variety of critical roles in the body, but their main function is to serve as the building blocks of tissues and organs, as well as act as enzymes to facilitate chemical reactions, transport molecules in and out of cells, and support the immune system by recognizing and defending against foreign substances. Ultimately, proteins are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's cells and tissues.
How are proteins made in the body?
Proteins are made in the body through a process called protein synthesis. It involves two main steps: transcription and translation. During transcription, the information encoded in a gene is copied into a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA then exits the cell's nucleus and serves as a template for translation, where ribosomes read the mRNA and use transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a specific protein. This process occurs in all cells and is essential for various functions in the body.
What are the building blocks of proteins?
The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are organic compounds that contain an amino group and a carboxyl group. There are 20 different amino acids that can combine in various sequences to form different proteins, each with its own unique structure and function.
How are proteins classified?
Proteins are classified based on their structure, function, and composition. Structurally, proteins can be classified as fibrous or globular. In terms of function, proteins can be enzymes, structural proteins, transport proteins, signaling proteins, or regulatory proteins. Compositional classification of proteins is based on their amino acid sequence and the presence of specific functional domains. These different classification systems help to categorize and understand the diverse roles and properties of proteins in living organisms.
What are some examples of dietary sources of protein?
Some examples of dietary sources of protein include chicken, fish, eggs, dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, legumes like beans and lentils, nuts, seeds, tofu, tempeh, and whole grains like quinoa and oats.
What is the recommended daily intake of protein?
The recommended daily intake of protein varies depending on factors such as age, sex, weight, and activity level. On average, it is recommended that adults consume around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. However, athletes or individuals who are more physically active may require more protein to support muscle growth and repair. It is best to consult with a healthcare provider or a nutritionist to determine the right amount of protein for your specific needs.
What happens if we don't consume enough protein?
Not consuming enough protein can lead to a variety of health issues, including muscle loss, weakened immune system, slower wound healing, fatigue, and hair loss. Protein is essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in the body, so a deficiency can have serious consequences on overall health and wellbeing. It is important to ensure adequate protein intake through a balanced diet to support proper bodily functions.
How does protein contribute to muscle growth and repair?
Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair as it provides the necessary building blocks, known as amino acids, needed for the synthesis of new muscle proteins. Specifically, protein consumption following exercise helps to stimulate muscle protein synthesis, supporting muscle recovery and adaptation to the stress of exercise, ultimately leading to muscle growth. Additionally, proteins play a crucial role in repairing damaged muscle tissue after intense physical activity, aiding in the recovery process and promoting overall muscle health and strength.
How do proteins regulate biochemical processes in the body?
Proteins regulate biochemical processes in the body by acting as enzymes, receptors, transporters, and signaling molecules. Enzymes, which are specialized proteins, catalyze biochemical reactions and help facilitate the conversion of substrates into products. Receptors are proteins that bind to specific molecules, such as hormones or neurotransmitters, and initiate a cellular response. Transport proteins facilitate the movement of molecules across cell membranes or within cells. Signaling proteins transmit signals within cells or between cells to regulate processes like growth, metabolism, and gene expression. Overall, proteins play a crucial role in maintaining cellular functions and homeostasis in the body.
Can protein be used as a source of energy?
Yes, protein can be used as a source of energy. When carbohydrates and fats are not available, the body can break down protein into amino acids, convert them into glucose, and use them for energy. However, using protein as an energy source is not ideal as proteins are primarily needed for building and repairing tissues in the body. It is more efficient for the body to rely on carbohydrates and fats for energy.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments