Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are a valuable tool for students to reinforce their understanding of complex subjects, such as the structures and functions of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Designed for biology students at high school or introductory college level, these worksheets provide a concise and organized way to review key concepts and demonstrate mastery of the topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
- POGIL Biology Answer Key Meiosis
- Biology Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
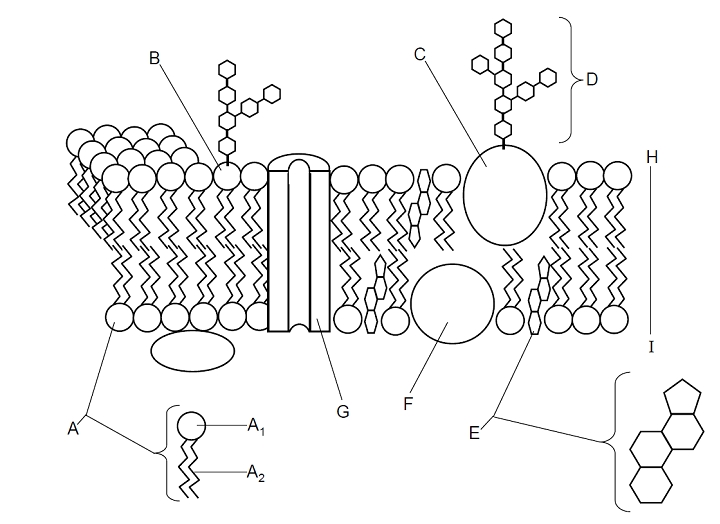
- Cell Membrane Diagram Labeled
- Unlabeled Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet
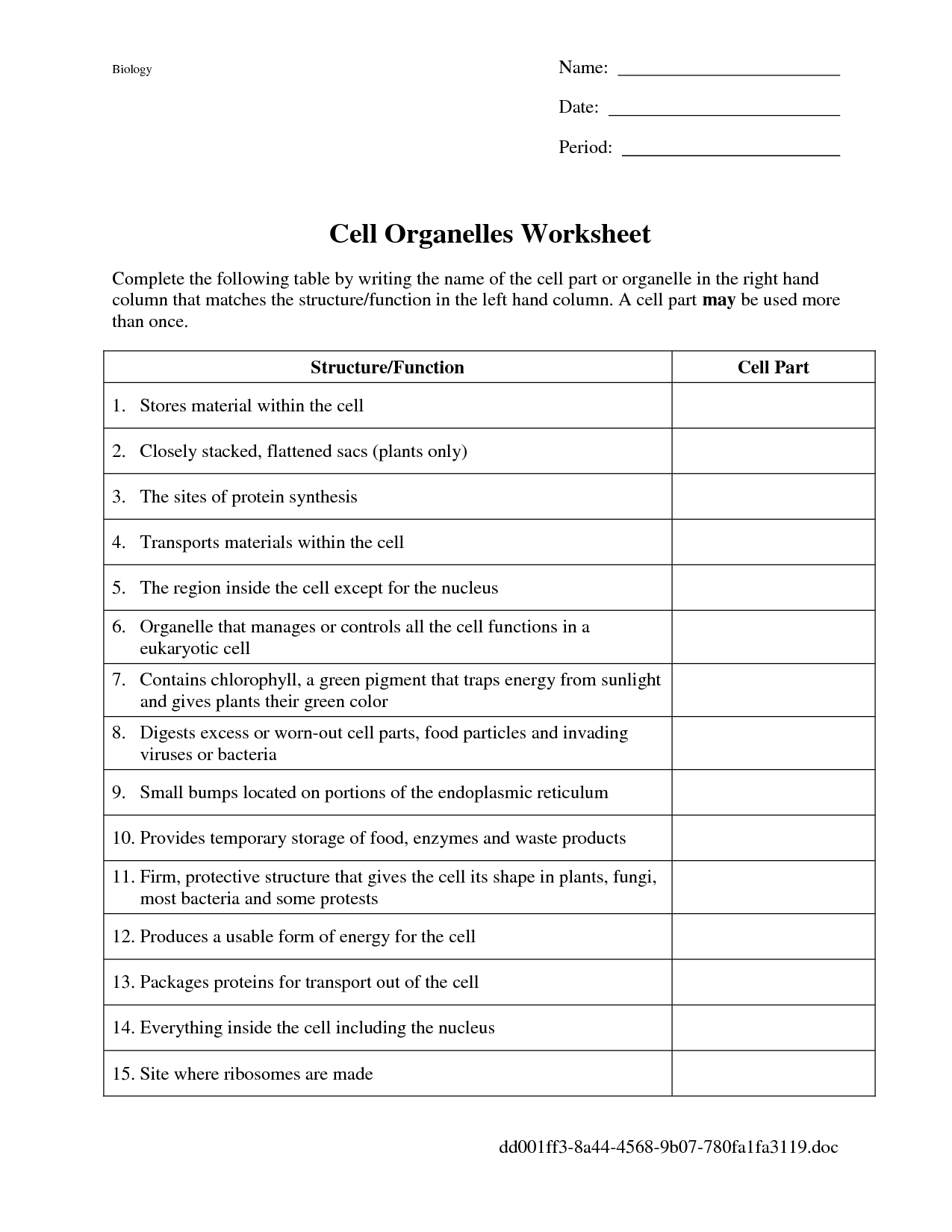
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
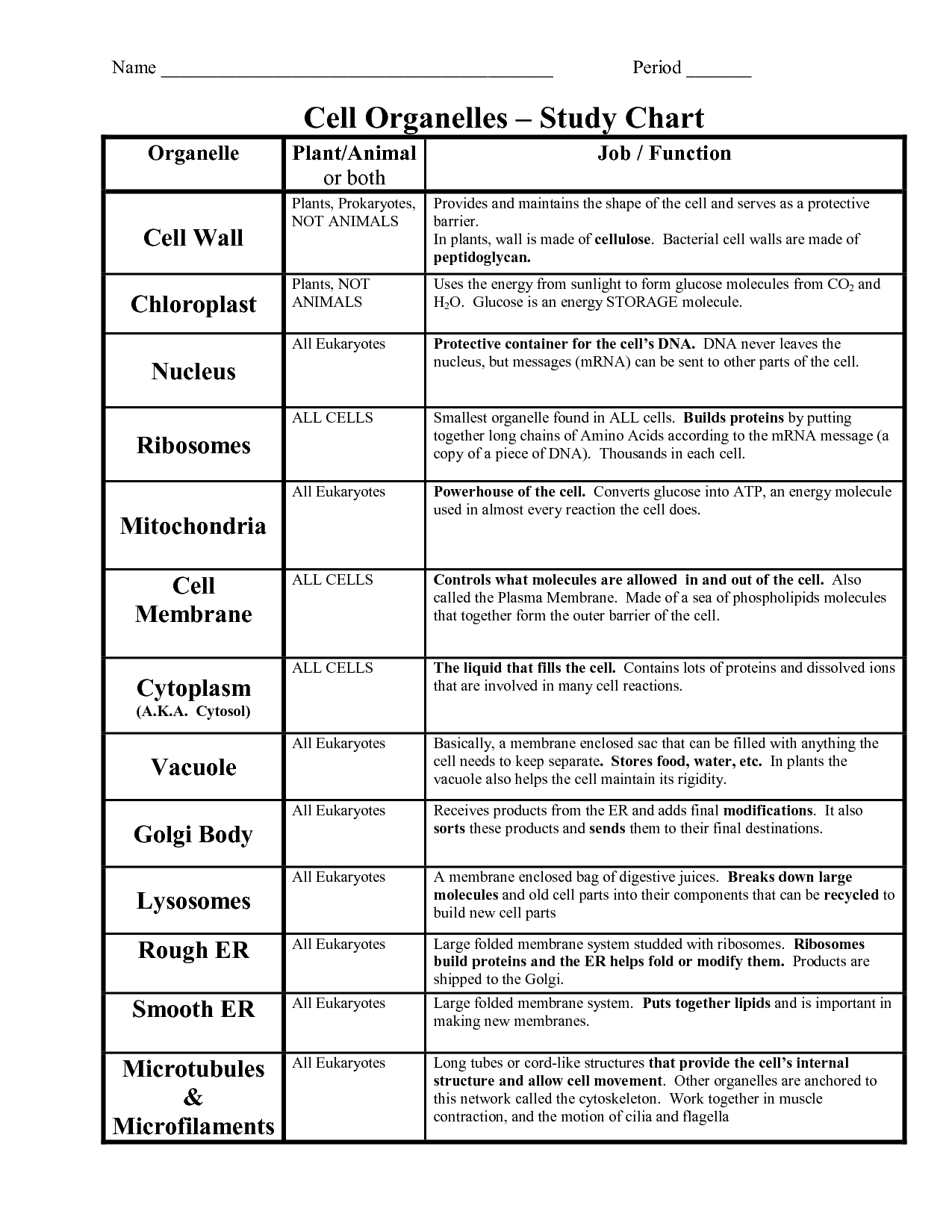
- Cell Organelles and Their Functions Chart
- Ancient Egypt
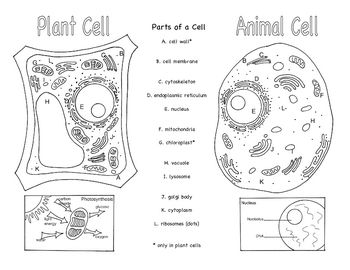
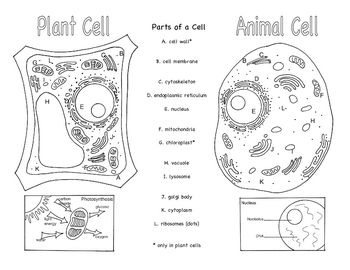
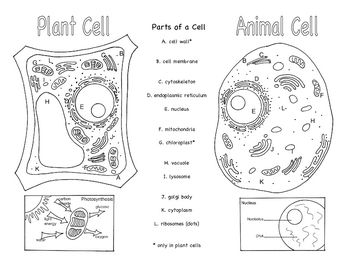
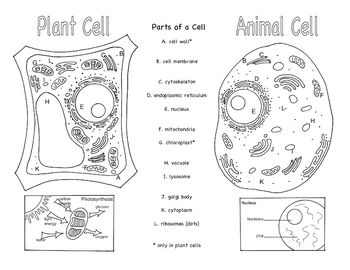
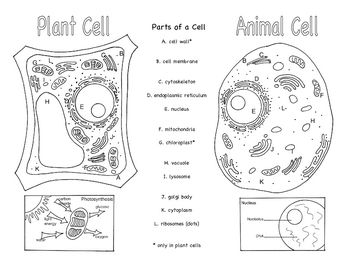
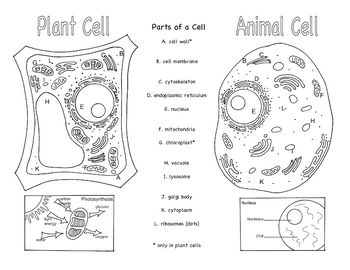
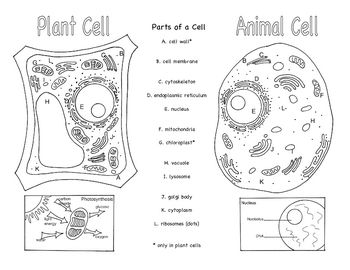
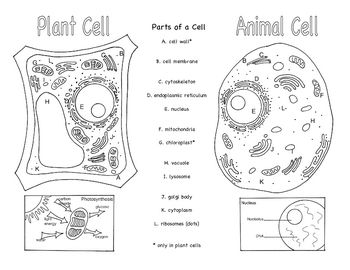
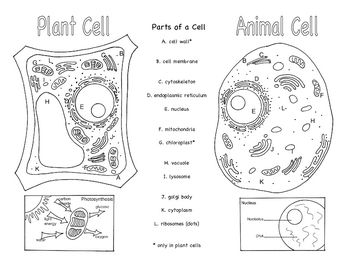
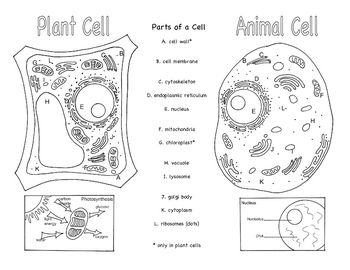
- Animal and Plant Cells Brochure
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
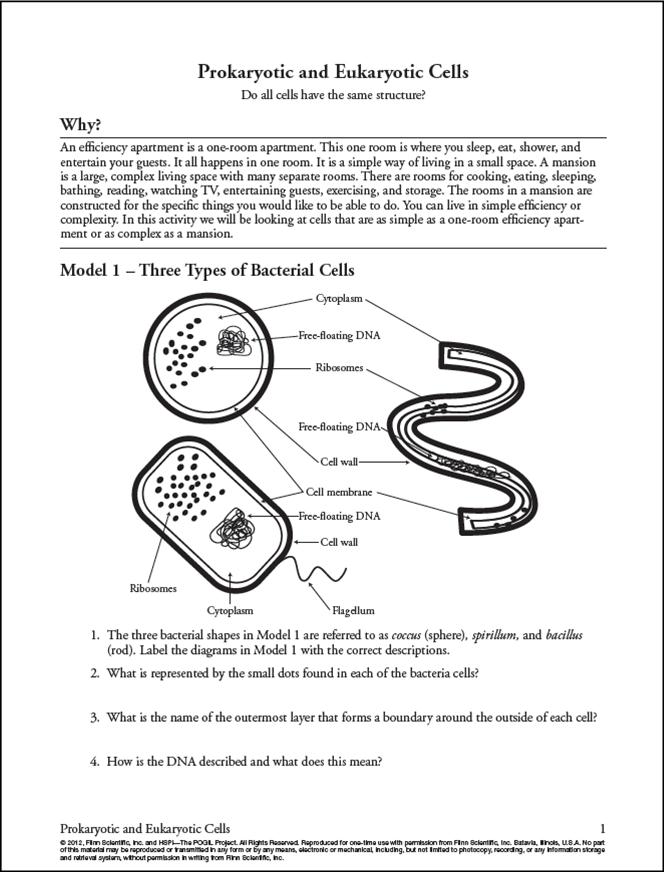
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence of a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus that separates the genetic material from the rest of the cell, while prokaryotic cells do not have a distinct nucleus and their genetic material is located in the cytoplasm. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more structurally complex than prokaryotic cells.
What is the structure that is present in eukaryotic cells but absent in prokaryotic cells?
One structure that is present in eukaryotic cells but absent in prokaryotic cells is the nucleus. The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that houses the cell's genetic material (DNA) in the form of chromosomes. It serves as the control center of the cell, regulating gene expression and coordinating cellular activities. In prokaryotic cells, the genetic material is located in the nucleoid region, a region within the cytoplasm where the DNA is not enclosed by a membrane.
Name two examples of prokaryotic cells.
Two examples of prokaryotic cells are bacteria and archaea.
Can prokaryotic cells carry out organelle-specific functions?
Prokaryotic cells do not contain organelles like eukaryotic cells do, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts, therefore they are not capable of carrying out organelle-specific functions. Instead, prokaryotic cells have a simpler structure without membrane-bound organelles, and their metabolic processes occur within the cytoplasm or on the cell membrane.
What is the size range of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells typically range in size from 0.2 to 2.0 micrometers in diameter.
Do prokaryotic cells have a nucleus?
No, prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is located in a region of the cell called the nucleoid, which is not enclosed by a membrane like the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
Name two examples of eukaryotic cells.
Animal cells and plant cells are two examples of eukaryotic cells.
List three organelles that are unique to eukaryotic cells.
Three organelles that are unique to eukaryotic cells are the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The nucleus houses the genetic material of the cell, the mitochondria are responsible for energy production through cellular respiration, and the endoplasmic reticulum plays a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis.
Can eukaryotic cells carry out photosynthesis?
Yes, eukaryotic cells can carry out photosynthesis. This process occurs in organelles called chloroplasts, which are found in plant cells and some protists. Chloroplasts contain pigments like chlorophyll that absorb sunlight and convert it into energy through photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide and water are used to produce glucose and oxygen.
What is the size range of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells typically range in size from about 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments