Probability Worksheet 7th Grade Practice
Are you a middle school student looking to sharpen your skills in probability? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with a comprehensive probability worksheet designed specifically for 7th graders. With carefully curated questions and step-by-step solutions, this worksheet will help you grasp the concepts of probability and gain confidence in solving related problems. So let's get started!
Table of Images 👆
- 6th Grade Math Probability Worksheets
- Order of Operations Math Worksheets Printable
- Statistics and Probability Worksheets 7th Grade
- 7th Grade Math Worksheets Printable
- 7th Grade Math Worksheets
- 8th Grade Math Probability Worksheets
- 7th Grade Math Problems Worksheets
- Probability Worksheet Grade 3
- Math Properties Worksheets 7th Grade
- 10th Grade Math Problems Worksheets
- Chance and Probability Worksheets
- 7th Grade Math Worksheets Algebra
- Basic Probability Worksheet
- 7th Grade Probability Questions
More 7th Grade Worksheets
7th Grade Vocabulary WorksheetsPre-Algebra 7th Grade Math Worksheets
7th Grade Math Worksheets Proportions
Complex Sentence Worksheets 7th Grade
Geometry Angles Worksheet 7th Grade Math
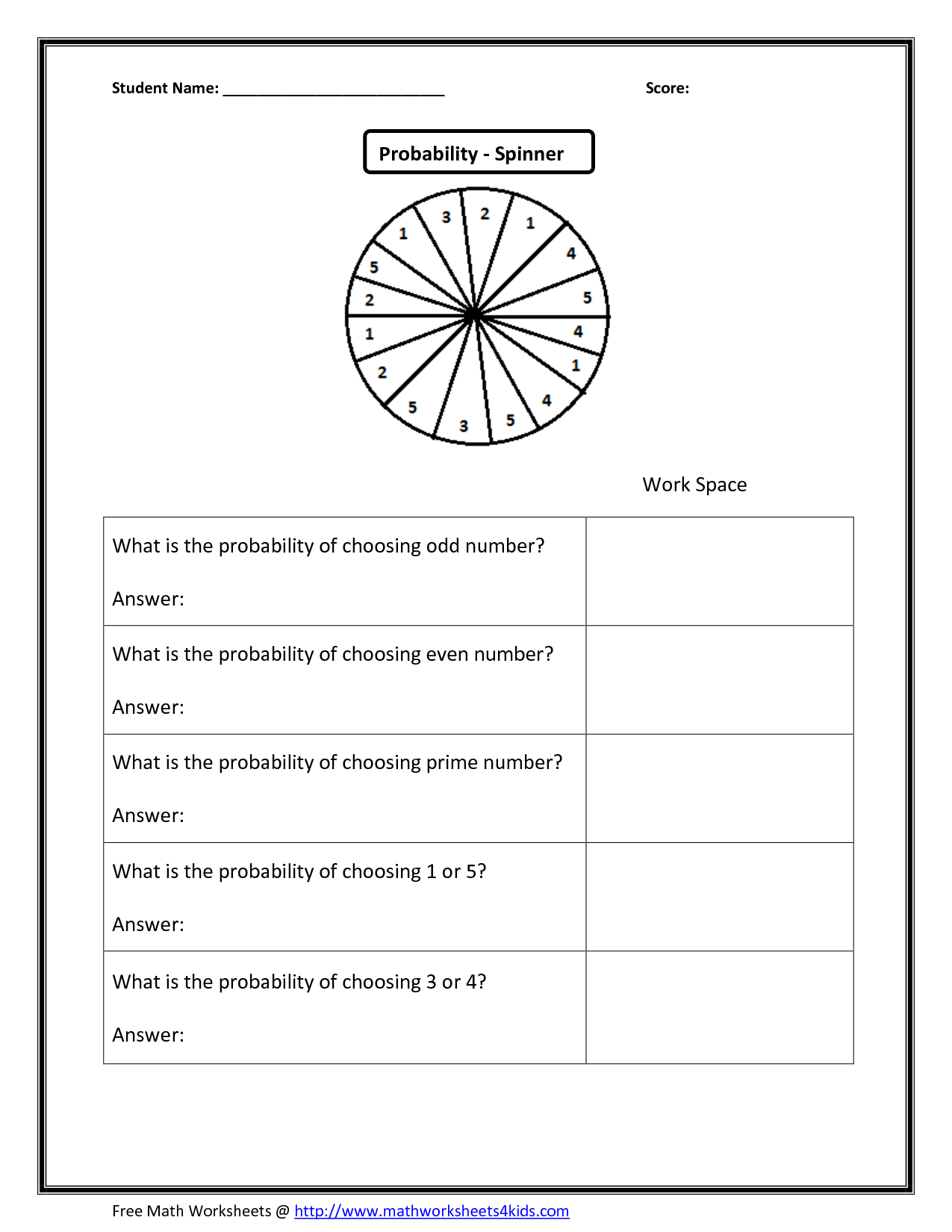
What is the definition of probability?
Probability is a mathematical concept that measures the likelihood of a specific event or outcome occurring within a given set of possibilities. It is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty, with higher probabilities suggesting a greater chance of the event happening.
What is the difference between experimental probability and theoretical probability?
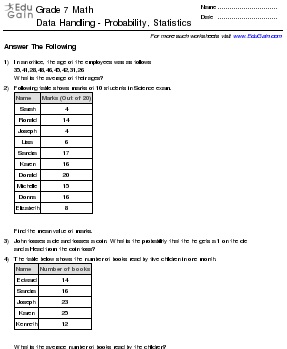
Experimental probability is based on outcomes obtained from conducting an actual experiment or observation, while theoretical probability is based on calculating the likelihood of an event occurring using mathematical principles and formulas. Experimental probability is determined by observing events in real-life situations, while theoretical probability is calculated based on the underlying probabilities of the outcomes in a given situation.
How is probability expressed as a fraction, decimal, and percentage?
Probability can be expressed as a fraction, decimal, and percentage. As a fraction, it is represented as a ratio of favorable outcomes to total outcomes, for example, 1/4. As a decimal, it is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total outcomes, such as 0.25. Lastly, as a percentage, it is obtained by multiplying the decimal probability by 100, giving a percentage representation like 25%.
What is a sample space in probability?
In probability theory, a sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment or process. It includes every possible outcome that could result from the experiment, and it serves as the foundation for assigning probabilities to events within the experiment. The sample space is a fundamental concept in probability theory and is crucial for determining the likelihood of various outcomes occurring.
What is the multiplication rule in probability?
The multiplication rule in probability states that the probability of the intersection of two independent events occurring is equal to the product of the probabilities of each event occurring separately. Mathematically, for two independent events A and B, the probability of both events happening is P(A ? B) = P(A) * P(B). This rule helps calculate the overall likelihood of multiple events occurring together.
What is the addition rule in probability?
The addition rule in probability states that the probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring is equal to the sum of their individual probabilities. This rule is represented as P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) when events A and B are mutually exclusive.
What is the difference between independent and dependent events in probability?
Independent events are events whose outcomes do not affect each other, meaning the outcome of one event does not impact the outcome of another event. On the other hand, dependent events are events where the outcome of one event affects the outcome of another event, indicating that the events are interrelated and the probability of the second event happening depends on the outcome of the first event.
What is the concept of complement in probability?
In probability, the complement of an event refers to the event that does not occur. It is the opposite outcome to the event of interest. The probability of the complement is equal to one minus the probability of the original event. For instance, if event A is the probability of getting a head when flipping a coin, the complement of event A would be the probability of getting a tail, and this can be calculated as one minus the probability of getting a head.
How do you calculate the probability of mutually exclusive events?
To calculate the probability of mutually exclusive events, you add the individual probabilities of each event. This is because if events are mutually exclusive, they cannot occur simultaneously. For example, if the probability of event A occurring is 0.4 and the probability of event B occurring is 0.6, and the events are mutually exclusive, then the probability of either event A or event B occurring is 0.4 + 0.6 = 1.
How do you solve problems involving probability using tree diagrams?
To solve problems involving probability using tree diagrams, first identify the possible outcomes at each stage of the event. Then, draw a tree diagram to represent the different branches of outcomes and their probabilities at each stage. Multiply the probabilities along each branch to find the overall probability of a specific outcome or event. By visually organizing the information in a tree diagram, you can easily calculate probabilities and make better decisions based on the likelihood of different outcomes occurring.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments