Physical Science Worksheets for Science
Physical science worksheets are an invaluable resource for students seeking to deepen their understanding of key scientific concepts. These worksheets provide a wide range of engaging and thought-provoking exercises that cover topics such as matter, energy, forces, and motion. With their comprehensive approach to exploring the foundations of physical science, these worksheets cater specifically to students in middle and high school levels.
Table of Images 👆
- Physical Science Matter Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets Answer Key
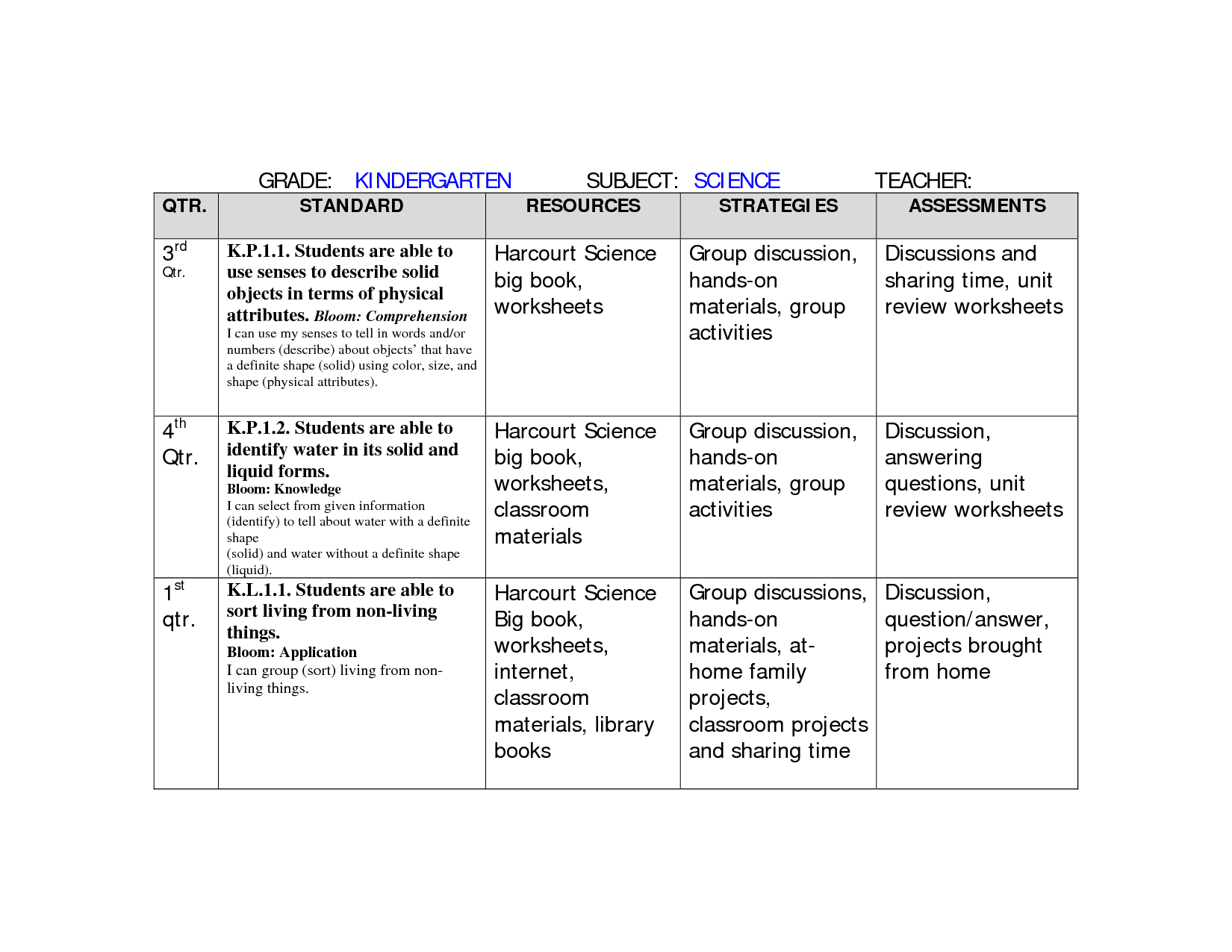
- Physical Science Worksheets
- 8th Grade Physical Science Worksheets
- 10 Grade Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Vocabulary Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheet 1
- Newtons Laws Worksheet
- Free Kindergarten Grade Science Worksheets
- Physical Evidence Forensic Science Worksheet
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is the stored energy an object has due to its position or state, such as gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy. On the other hand, kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. In simpler terms, potential energy is potential for movement, while kinetic energy is actual movement.
How does Newton's first law of motion relate to objects at rest and in motion?
Newton's first law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. This law relates to both objects at rest and in motion by describing their tendency to maintain their state of motion or rest unless an external force causes a change. It explains the concept of inertia, where objects resist changes in their motion or rest unless a force is applied to them.
What is the difference between a solid, liquid, and gas in terms of particle arrangement and movement?
In a solid, particles are tightly packed together in a fixed, organized structure with little movement besides vibrating in place. In a liquid, particles are close together but can move around each other, allowing the substance to take the shape of its container. In a gas, particles are far apart and have a high degree of freedom of movement, constantly moving at high speeds and filling the entire volume of the container they are in.
How does the law of conservation of mass apply to chemical reactions?
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, only rearranged. This means that the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products in any chemical reaction. In other words, the number of atoms of each element present in the reactants must be equal to the number of atoms of each element in the products. This fundamental principle is crucial in balancing chemical equations and understanding the stoichiometry of reactions.
What is the difference between an exothermic and endothermic reaction?
An exothermic reaction releases heat energy to the surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature, while an endothermic reaction absorbs heat energy from the surroundings, causing a decrease in temperature. In exothermic reactions, the products have less energy than the reactants, while in endothermic reactions, the products have more energy than the reactants.
How do elements in the periodic table differ in terms of atomic number, mass number, and valence electrons?
Elements in the periodic table differ in terms of atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus and determines the element's identity. Mass number varies due to the differing numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Valence electrons, on the other hand, are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom and are crucial in determining the element's chemical properties, with elements in the same group having the same number of valence electrons.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum?
The relationship between wavelength and frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum is inverse. This means that as wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is defined by the equation: speed of light = wavelength x frequency. The different types of electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays, all have varying wavelengths and frequencies that are related by this inverse relationship.
How does surface area affect the rate of reaction in a chemical reaction?
Surface area affects the rate of reaction in a chemical reaction by increasing the contact area between reactant particles, leading to more frequent and effective collisions. A greater surface area means more reactant particles are exposed to each other, allowing for a higher rate of successful collisions and ultimately resulting in a faster reaction. This is why finely divided or powdered substances react more quickly than larger, bulkier ones.
What are the different types of electromagnetic waves and their respective uses?
There are several types of electromagnetic waves, including radio waves (used in communication and broadcasting), microwaves (used in cooking and communication), infrared radiation (used in heating and night vision technologies), visible light (used for vision and optical communications), ultraviolet radiation (used in sterilization and fluorescence), X-rays (used in medical imaging and security screening), and gamma rays (used in cancer treatment and sterilization). Each type of electromagnetic wave has unique properties and applications across various industries and technologies.
How does the greenhouse effect contribute to global warming?
The greenhouse effect contributes to global warming by trapping heat from the sun in the Earth's atmosphere. Gases like carbon dioxide and methane act as a barrier, allowing sunlight to enter and warm the Earth's surface, but trapping heat as it tries to escape back into space. This buildup of heat leads to the overall warming of the planet, resulting in global warming.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments