Physical Science Worksheets and Answers
Physical science worksheets are a valuable educational tool for students who want to strengthen their understanding of key concepts in subjects such as chemistry and physics. Designed to engage and challenge learners, these worksheets provide ample opportunities to enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills while reinforcing core knowledge. Whether you’re a high school student looking to ace your science exams or a homeschool parent searching for additional resources, physical science worksheets offer a structured and engaging approach to learning.
Table of Images 👆
- Physical and Chemical Properties Worksheet Answer Key
- Holt Science Spectrum Worksheets Answers
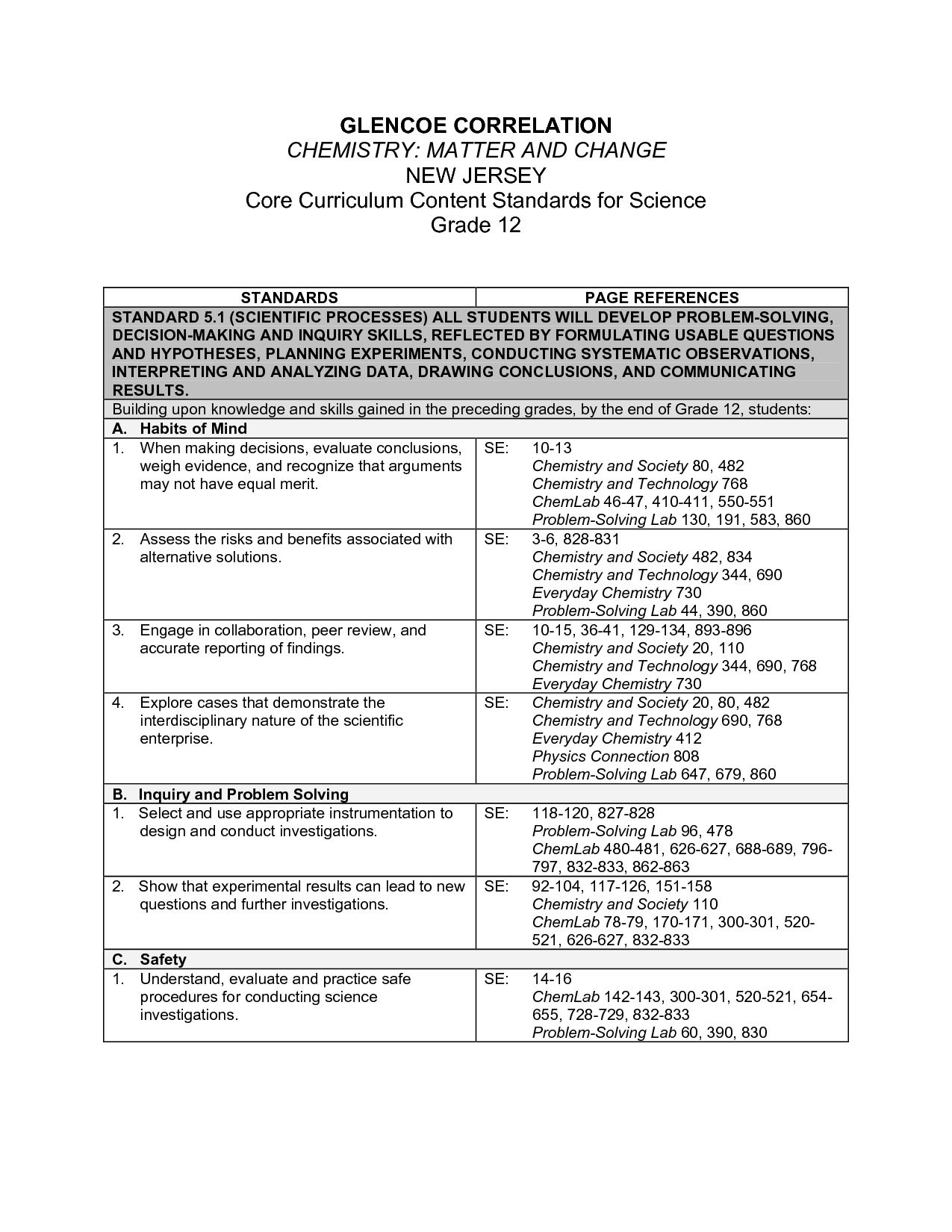
- Glencoe Chemistry Chapter Assessment Answers
- Study Guide Science Chapter 6 2 Grade
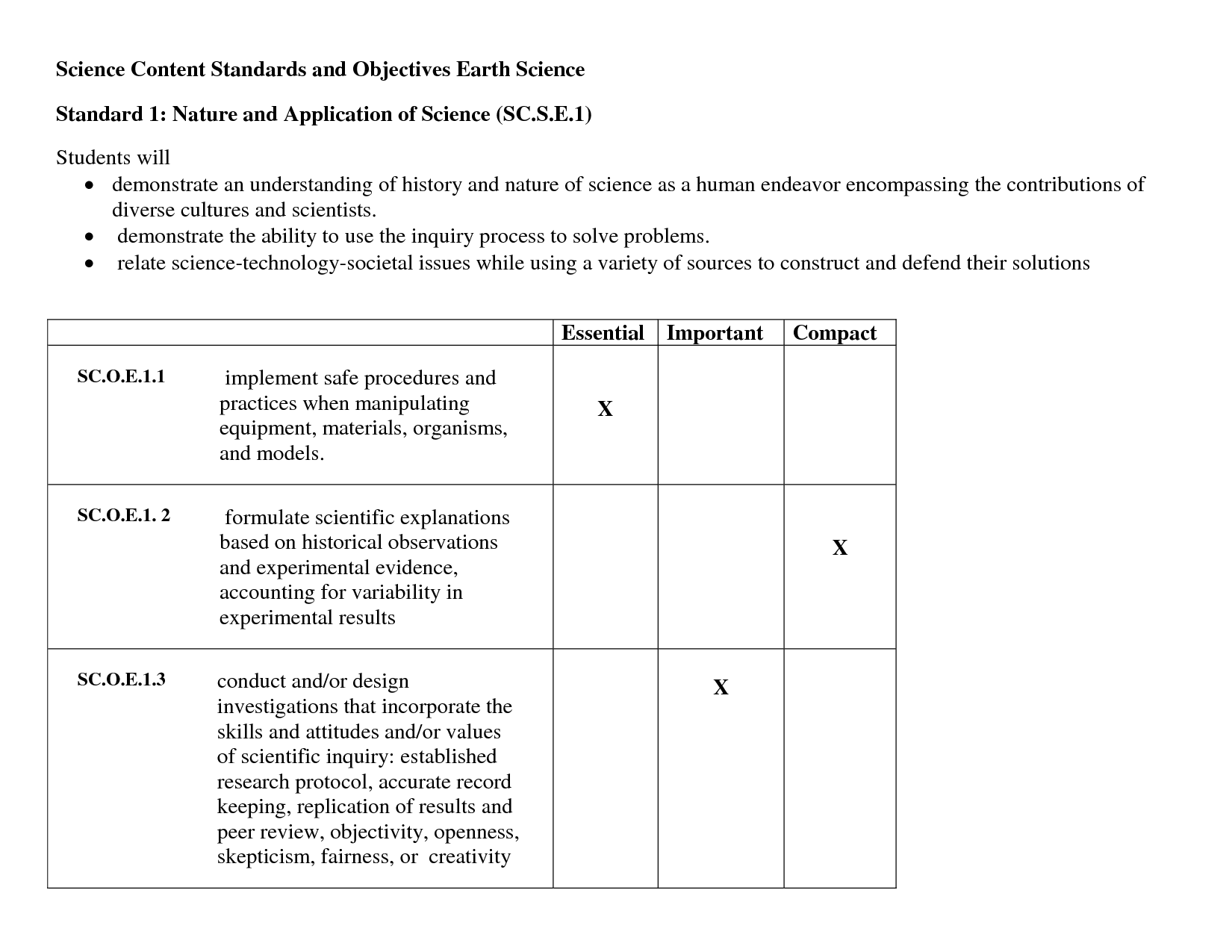
- Holt Physical Science Chapter Review Answers
- Physical vs Chemical Change Worksheet
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers
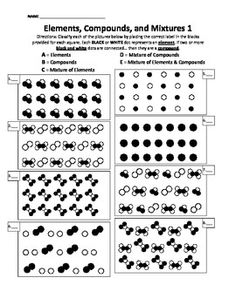
- Elements Compounds and Mixtures Worksheet Answers
- Potential Kinetic Energy Worksheet
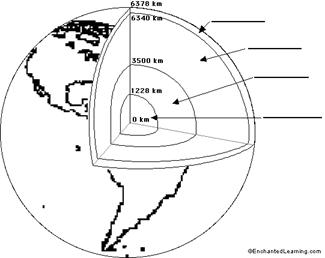
- Earth Layers Diagram Worksheet
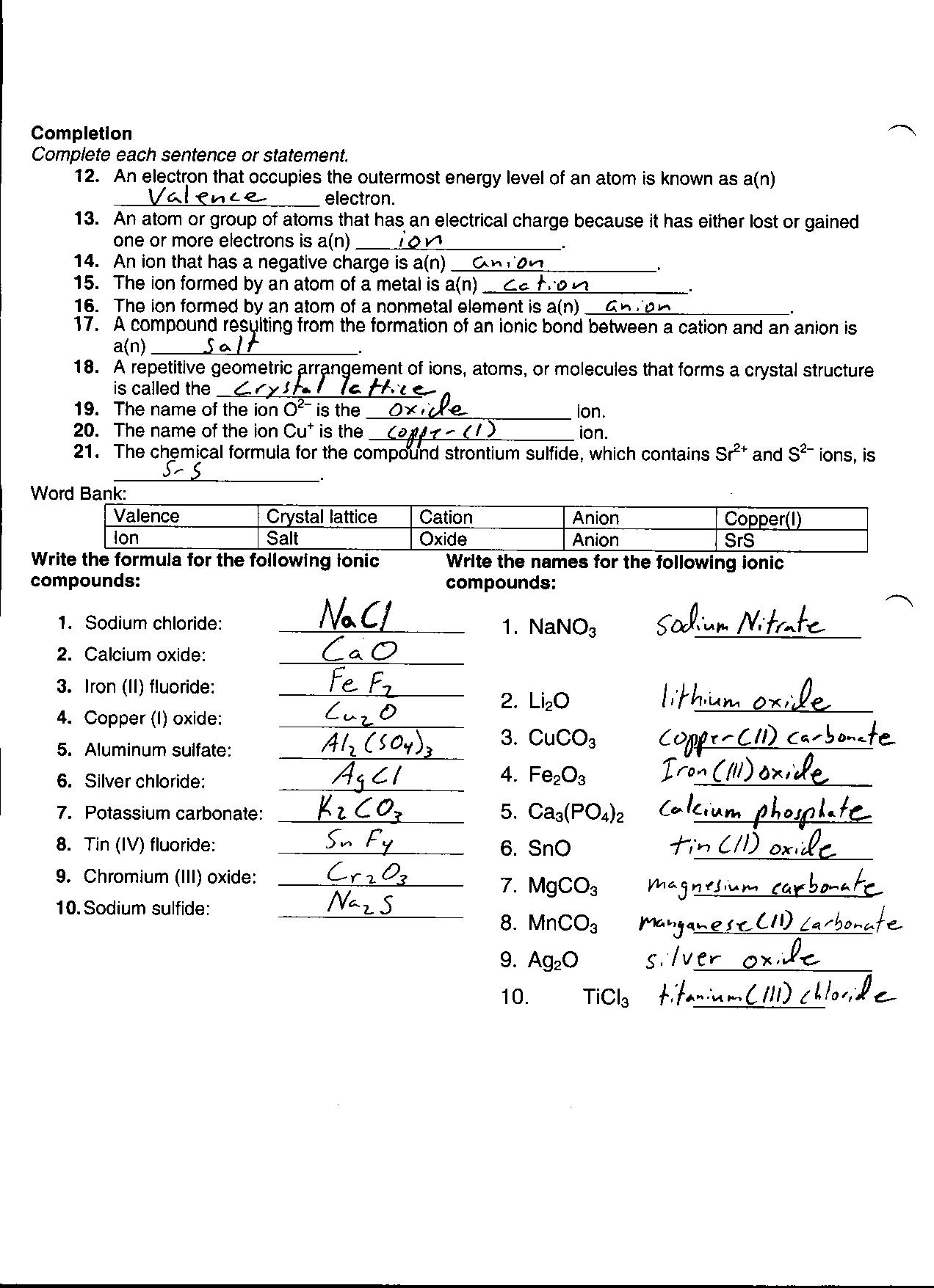
- Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
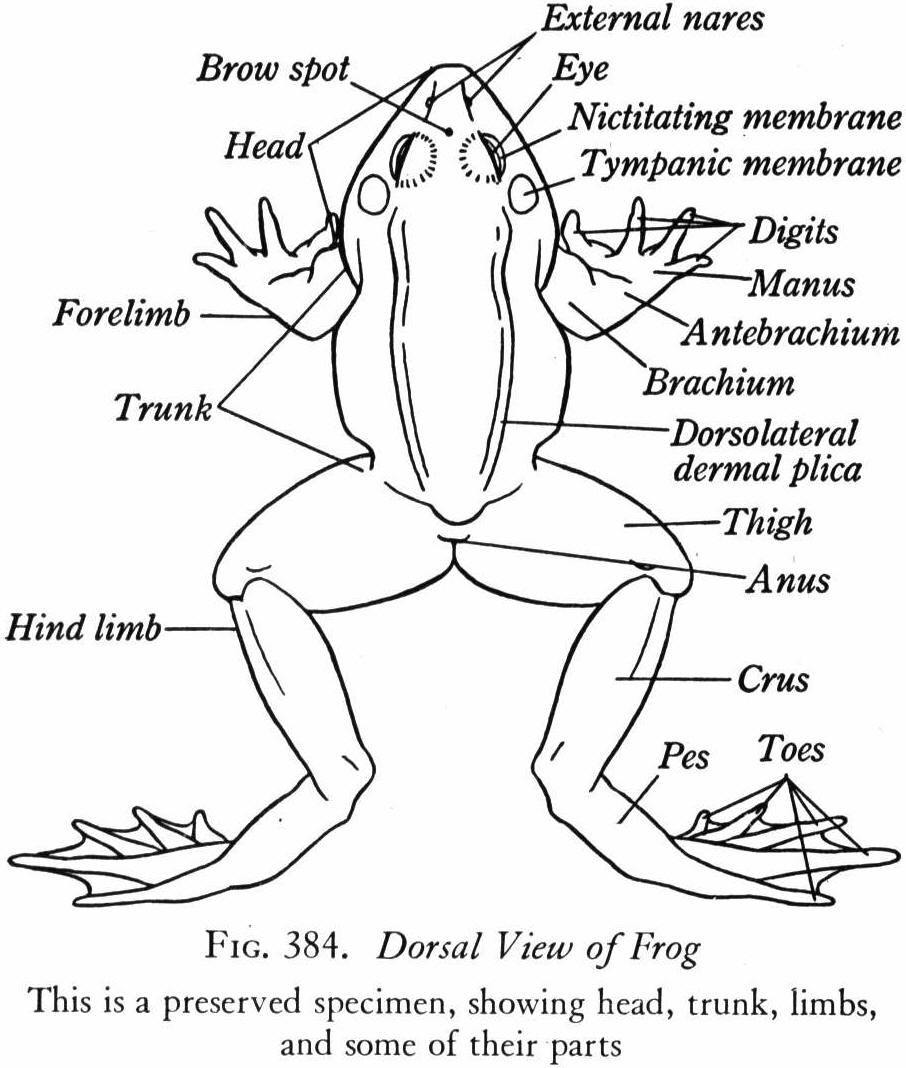
- Frog External Anatomy Diagram
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the law of conservation of energy?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time, regardless of the changes that may occur within that system. All forms of energy, whether potential, kinetic, thermal, or any other type, are subject to this fundamental principle of conservation.
Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy.
Potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its position or state, such as gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy. Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is the energy of motion possessed by an object. It is determined by the object's mass and velocity. Potential energy is converted into kinetic energy when an object moves, and vice versa, as seen in the swinging of a pendulum or a roller coaster moving up and down hills.
What are the basic properties of matter?
The basic properties of matter include mass, volume, density, and physical state (solid, liquid, gas). Additionally, matter can exhibit properties such as color, texture, shape, odor, conductivity, and magnetism. These properties help define the characteristics of different substances and how they interact with each other in the physical world.
Describe the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a complex metabolic process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. It takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves several steps: 1) Light absorption by chlorophyll molecules in the chloroplasts; 2) Conversion of light energy into chemical energy, splitting water molecules to release oxygen as a byproduct; 3) Utilization of the energy to synthesize ATP and NADPH; 4) Carbon dioxide fixation through the Calvin cycle, where ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose; and 5) Release of excess oxygen back into the atmosphere. Photosynthesis is vital for sustaining life on Earth as it produces oxygen and serves as the foundation of the food web.
What is Newton's first law of motion?
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force. This means that an object will not change its state of motion unless a force is applied to it.
Explain the difference between conductors and insulators.
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electrical current easily, due to the presence of free electrons that can move around. In contrast, insulators are materials that do not allow the flow of electrical current easily, as they have tightly bound electrons that do not move easily. Conductors, such as metals, have low resistance to electricity, while insulators, like rubber or plastic, have high resistance. This difference in conductivity is crucial for various applications in electrical engineering and technology.
What is the chemical formula for water?
The chemical formula for water is H2O.
Describe the process of cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells generate energy from the breakdown of glucose molecules. It consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. During glycolysis, glucose is converted into pyruvate and a small amount of ATP is produced. The citric acid cycle then metabolizes pyruvate into carbon dioxide, generating more ATP and electron carriers. Finally, in oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from the electron carriers are used to create a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which drives the production of a large amount of ATP. Overall, cellular respiration produces energy in the form of ATP that cells can use for various metabolic processes.
What are the three states of matter and their characteristics?
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, with particles tightly packed and vibrating in place. Liquids have a fixed volume but take the shape of their container, with particles still close together but able to move around. Gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume, as particles are far apart and move freely.
Explain the difference between a physical and chemical change.
A physical change involves a reversible alteration in the physical properties of a substance without changing its chemical composition, such as melting, freezing, or dissolving. In contrast, a chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties due to the rearrangement of atoms and the breaking or forming of chemical bonds, such as burning wood or rusting iron.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments