Physical Science Motion Worksheet
If you're an educator in need of engaging and informative resources for teaching your students about motion, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we'll explore the benefits of using worksheets as a valuable tool to reinforce the concept of motion in physical science. Whether you're a science teacher looking to enhance your lesson plans or a homeschooling parent seeking supplemental materials, worksheets can provide a structured format for your students to practice and apply their knowledge.
Table of Images 👆
- Potential Kinetic Energy Worksheet
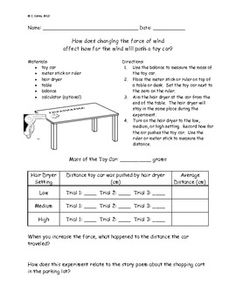
- Science Force and Motion Worksheets
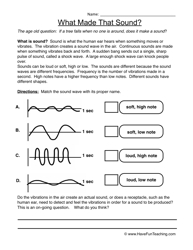
- First Grade Worksheets Science Sound Energy
- Science Worksheets Heat Energy
- How to Make a Paper Airplane Worksheet
- 9th Grade Physical Science Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Science Worksheets Force
- Scientific Method Worksheet
- Science Worksheets with Answer Key
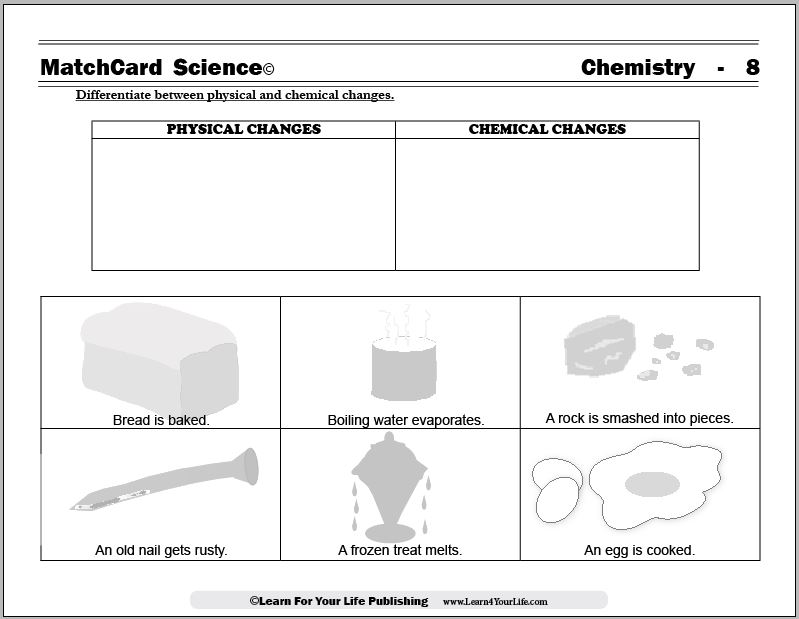
- Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheets
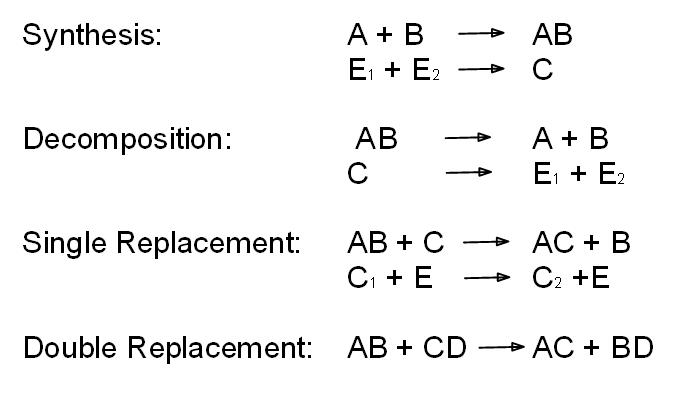
- Chemical Reaction Types Worksheet
- Soil Worksheets Grade 2
- How to Make a Paper Helicopter Fly
- Science 8th Grade Substance Compound
- Calvin and Hobbes Loopholes
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is motion?
Motion is the change in position of an object over time in relation to a reference point. It can be described in terms of speed, direction, and acceleration, with different forms such as linear motion, circular motion, and oscillatory motion. Motion is a fundamental concept in physics that helps us understand the behavior of objects in the world around us.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that represents how fast an object is moving, regardless of direction, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the speed of an object and its direction of motion. In other words, velocity not only tells you how fast something is moving but also the direction in which it is moving, whereas speed only tells you how fast something is moving.
What is the relationship between distance, time, and speed?
The relationship between distance, time, and speed is determined by the formula: Speed = Distance / Time. This formula shows that speed is equal to the distance covered divided by the time taken to cover that distance. In essence, speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving, which is determined by the distance it has traveled in a given amount of time.
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of an object's velocity with respect to time. It measures how quickly the velocity of an object is changing, either increasing or decreasing. It can be thought of as the change in velocity over a specific period of time, and is typically expressed in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
How is acceleration different from velocity?
Acceleration and velocity are both related to an object's motion, but they are different concepts. Velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position. It has a magnitude and a direction. Acceleration, on the other hand, is the rate at which an object's velocity changes. It can be a change in speed, direction, or both. In simpler terms, velocity tells us an object's speed and direction of motion, while acceleration tells us how quickly that speed or direction is changing.
What is the difference between positive and negative acceleration?
Positive acceleration refers to an increase in the speed of an object, while negative acceleration (also known as deceleration or retardation) refers to a decrease in speed. Positive acceleration causes an object to move faster, while negative acceleration causes an object to slow down.
What is Newton's first law of motion?
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This means that an object will continue to stay still if it is already at rest, or it will keep moving at a constant velocity if no force is applied to change its state of motion.
What is Newton's second law of motion?
Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This law is represented by the equation F = ma, where F is the net force applied to an object, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration produced.
What is Newton's third law of motion?
Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object.
How do forces affect motion?
Forces affect motion by changing an object's speed, direction, or both. When a force is applied to an object, it can cause the object to accelerate, decelerate, or change direction. The magnitude and direction of the force determine how the object will move, following Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. Thus, forces play a crucial role in determining the motion of an object in a given environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments