Periodic Table Trends Worksheet
Are you a student or teacher interested in exploring the fascinating world of chemistry? Look no further! This blog post is dedicated to introducing you to a useful resource called the Periodic Table Trends Worksheet. Designed to help you understand the periodic trends of elements, this worksheet provides a structured approach to studying and visualizing how atomic properties change across the periodic table. Whether you're a high school student aiming to excel in chemistry or a teacher seeking supplementary materials for your lessons, this worksheet is a valuable tool for learning and reinforcing the concept of periodic trends.
Table of Images 👆
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers
- Electron Configuration Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Puns Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Chapter 6 Worksheet
- Cell Energy Crossword Puzzle Answers
- Electron Orbital Diagram
- Unit Conversion Factors Table
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
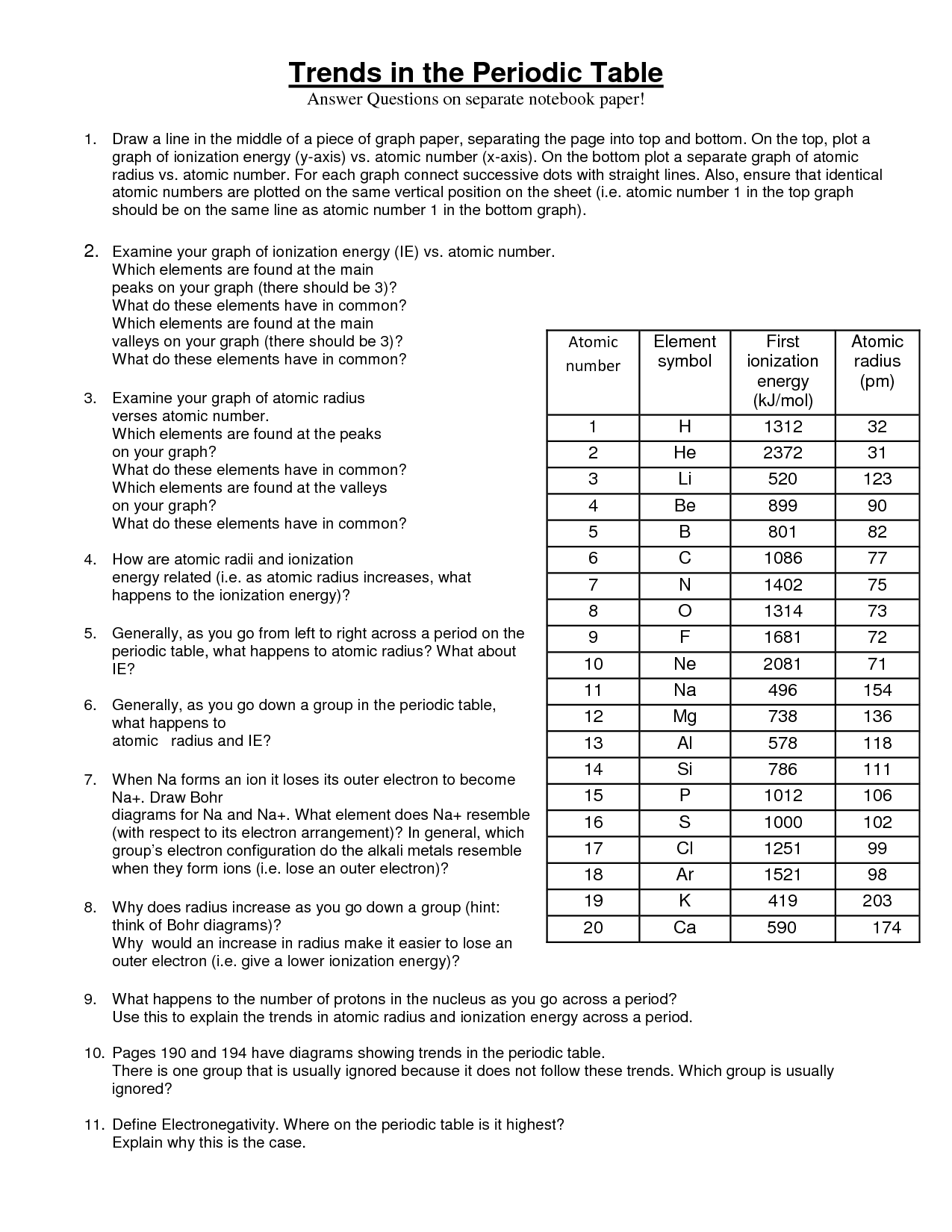
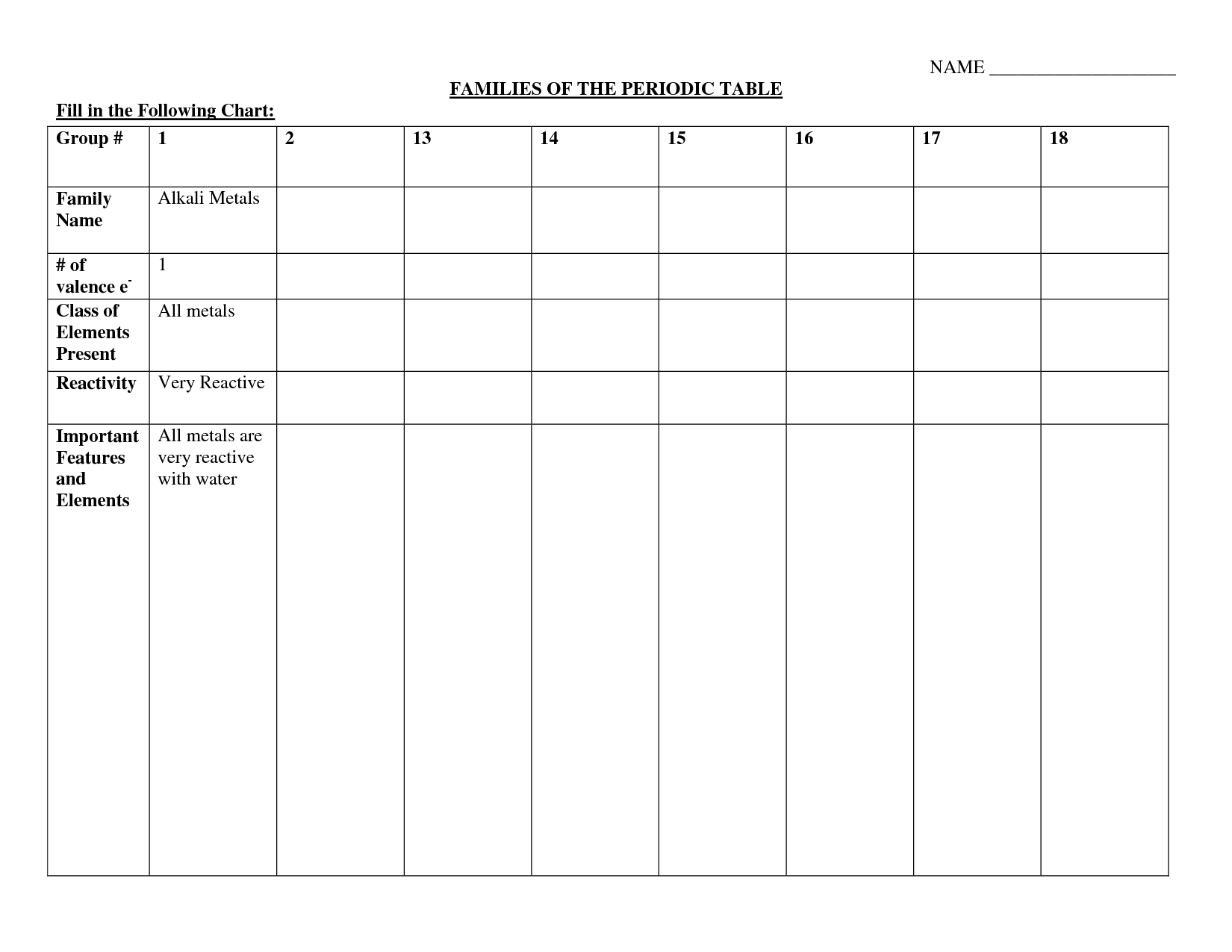
What is the periodic trend for atomic radius?
The periodic trend for atomic radius is that it generally decreases from left to right across a period on the periodic table, due to increasing nuclear charge and stronger attraction between electrons and nucleus. Conversely, atomic radius increases down a group on the periodic table, as electrons occupy higher energy levels farther from the nucleus, leading to a larger atomic radius.
How does ionization energy change across a period?
Ionization energy generally increases across a period from left to right. This is because as you move from left to right across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases while the shielding effect remains relatively constant, resulting in a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons in the outer shell. As a result, more energy is required to remove an electron from an atom, leading to an increase in ionization energy.
Describe the trend for electronegativity as you move down a group.
Electronegativity decreases as you move down a group in the periodic table. This is because the distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons increases with each energy level, reducing the attraction for electrons and resulting in a lower electronegativity value.
What happens to the first ionization energy as you move from left to right across a period?
The first ionization energy generally increases as you move from left to right across a period in the periodic table. This is because as you move towards the right, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons in the outer shell. As a result, it becomes harder to remove an electron and ionization energy increases.
Explain the trend in electronegativity as you move from left to right across a period.
Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right across a period on the periodic table. This trend occurs because the effective nuclear charge, or the positive charge experienced by an electron, increases as the number of protons in the nucleus increases. This stronger positive charge attracts electrons more strongly, resulting in higher electronegativity values and a greater ability to attract electrons towards themselves.
How does atomic radius change as you move down a group?
As you move down a group in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally increases. This is due to the addition of energy levels as you move down the group, which leads to the increase in size of the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. The increased distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell results in a larger atomic radius for elements lower in a group compared to those higher up the group.
Describe the trend in melting and boiling points down a group.
The melting and boiling points generally increase down a group in the periodic table. This trend is primarily influenced by the increase in atomic size and the number of electron shells as you move down the group. With larger atoms and more electron shells, the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals forces) between molecules become stronger, requiring more energy to break the bonds and transition from solid to liquid or liquid to gas.
What happens to the atomic size of cations compared to the parent atom?
When an atom loses one or more electrons to become a cation, it loses its outermost electron shells, resulting in a decrease in the atomic size of the cation compared to the parent atom. This is because the removal of electrons reduces the electron-electron repulsion in the outermost shell, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the remaining electrons, causing the atomic size to decrease.
Explain the trend in ionization energy as you move down a group.
Ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group on the periodic table. This is because the atomic size increases down a group, leading to a larger distance between the outermost electron and the nucleus. As a result, the electron is less tightly held and therefore requires less energy to remove, resulting in a lower ionization energy.
How does electron affinity change across a period?
Electron affinity generally increases across a period from left to right due to the increasing nuclear charge which attracts electrons more strongly. As you move across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, resulting in a greater positive charge that attracts electrons more strongly, leading to higher electron affinity values.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments