Organic Compounds Worksheet Answers
If you're a student or an educator in need of accurate and reliable organic compounds worksheet answers, you've come to the right place. This blog post aims to provide you with a detailed breakdown of organic compounds and their corresponding answers, designed to assist learners in understanding and mastering the subject. Whether you're studying for an exam or seeking additional practice materials, this post will help you grasp the concept of organic compounds more effectively.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Chemistry Functional Groups
- Organic Compound Worksheet Answers Biology
- Alkane Nomenclature Worksheet with Answers
- Drawing Hydrocarbons Worksheet
- Blank Water Cycle Worksheet
- Chemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
- Elements and Compounds Worksheet 6th Grade
- Chemistry Colligative Properties Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Answer Key
- 6th Grade Science Classification Worksheets
- Le Chatelier Principle Worksheet Answers
- Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
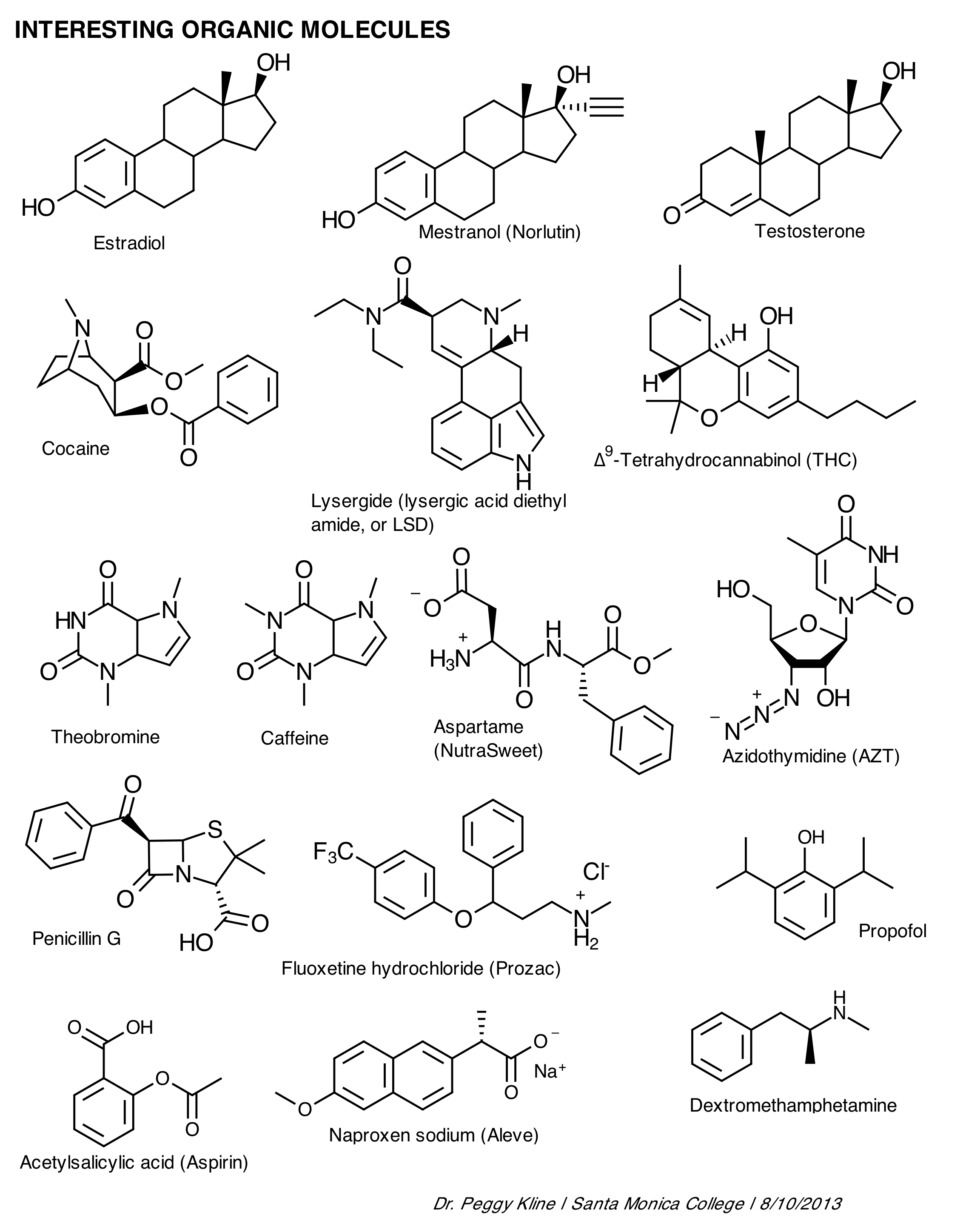
What are organic compounds?
Organic compounds are molecules that contain carbon atoms bonded together with other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and more. These compounds are the basis of life and are found in a wide range of substances including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and many other biological molecules.
How are organic compounds different from inorganic compounds?
Organic compounds are composed of carbon atoms that typically bond with hydrogen, oxygen, and other elements to form complex structures found in living organisms. In contrast, inorganic compounds do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and are generally simpler in structure. Additionally, organic compounds are typically associated with biological processes and organic matter, while inorganic compounds are often minerals or gases found in the Earth's crust.
What is the molecular structure of organic compounds?
Organic compounds are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen atoms, with other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and others sometimes present. The molecular structures of organic compounds can vary widely, with different arrangements and combinations of atoms leading to the diversity of organic molecules. These structures can include straight or branched chains, rings, or complex three-dimensional shapes, all connected by covalent bonds.
Give an example of a simple organic compound.
An example of a simple organic compound is methane (CH4), which consists of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.
How do organic compounds contribute to the formation of life?
Organic compounds are essential building blocks for life as they contain carbon and hydrogen atoms that can form complex molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These molecules provide the necessary structure, energy, and information storage for living organisms to grow, reproduce, and function. In the early Earth environment, organic compounds likely played a key role in the chemical reactions that eventually led to the formation of the first living cells. Today, organic compounds continue to drive the biochemical processes that sustain life on Earth.
What are the main elements found in organic compounds?
The main elements found in organic compounds are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. These elements are essential for forming the diverse range of molecules and compounds that make up living organisms, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Additionally, organic compounds can also contain trace amounts of other elements such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium.
How do carbon atoms contribute to the diversity of organic compounds?
Carbon atoms contribute to the diversity of organic compounds due to their unique ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms and with a variety of other elements. These bonds can be single, double, or triple, and can form complex branching chains, rings, and other structures. Additionally, carbon atoms can form functional groups such as hydroxyl, carbonyl, and amino groups, which greatly expand the types of compounds that can be created. The versatility of carbon in bonding and structure allows for a vast array of organic compounds with different properties and functions, leading to the immense diversity seen in the field of organic chemistry.
What are functional groups in organic compounds?
Functional groups in organic compounds are specific groups of atoms that are responsible for the chemical reactions and characteristics of molecules. They determine the type of reactions a compound can undergo and its physical and chemical properties. Examples of functional groups include hydroxyl (-OH), carbonyl (C=O), amino (-NH2), and carboxyl (-COOH).
How do organic compounds participate in chemical reactions?
Organic compounds participate in chemical reactions by either giving or receiving electrons, forming covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. This allows them to undergo various types of reactions such as oxidation, reduction, substitution, addition, and elimination reactions. The functional groups present in organic compounds play a crucial role in determining the types of chemical reactions they can participate in, ultimately influencing their reactivity and behavior in a wide range of chemical processes.
Provide an example of a complex organic compound and describe its function.
One example of a complex organic compound is hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. Hemoglobin consists of four subunits, each containing a heme group with an iron atom at its center. The iron atom binds to oxygen molecules, allowing hemoglobin to transport oxygen efficiently and facilitate cellular respiration.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments