Organic Chemistry Review Worksheets
For students seeking a comprehensive review and practice in Organic Chemistry, look into using organic chemistry review worksheets. These worksheets serve as valuable tools to reinforce concepts, practice problem-solving, and solidify understanding of key topics. Designed specifically for those studying Organic Chemistry, these worksheets provide a focused and structured approach to aid in exam preparation and overall subject mastery.
Table of Images 👆
More Chemistry Worksheets
What is the definition of organic chemistry?
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that focuses on the study of carbon-based compounds, which are commonly found in living organisms. It involves the understanding of the structure, properties, and reactions of these compounds, as well as the synthesis and design of new organic molecules for various applications in medicine, industry, and materials science.
What are the main elements found in organic compounds?
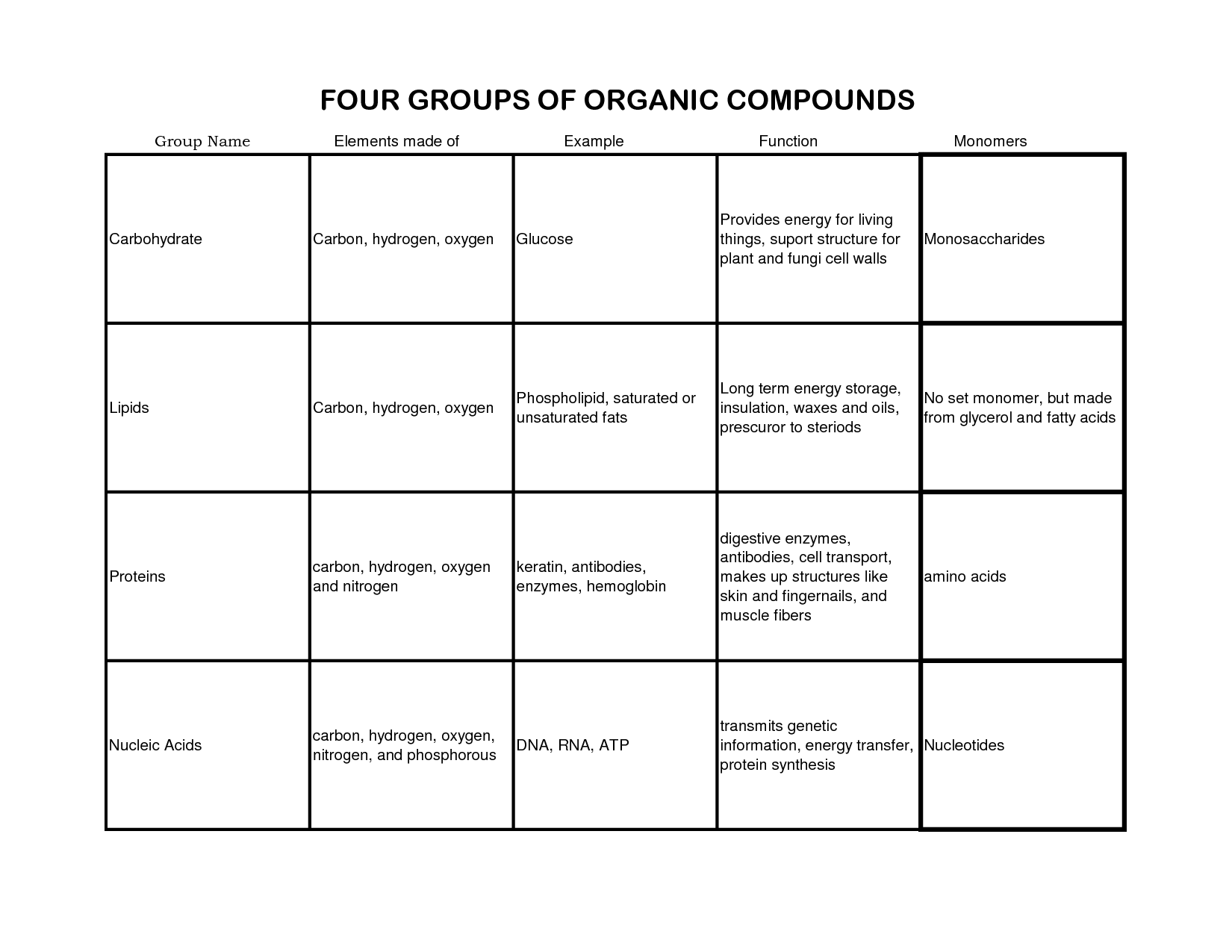
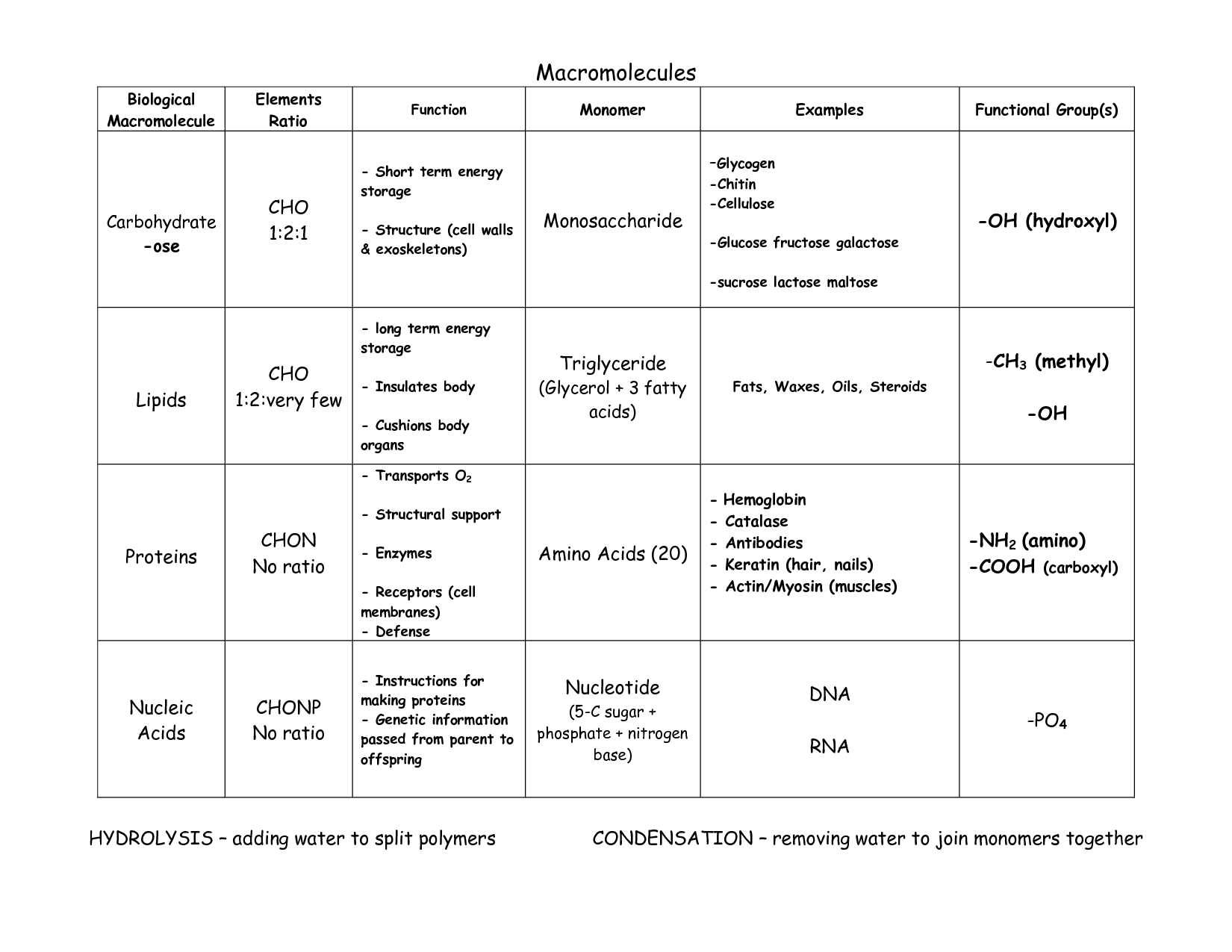
The main elements found in organic compounds are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur and phosphorus. Carbon is the central element in organic compounds, forming the backbone of molecules, while hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus are frequently involved in bonds and functional groups that give organic molecules their diverse properties and functions.
How do you determine the empirical formula of a compound?
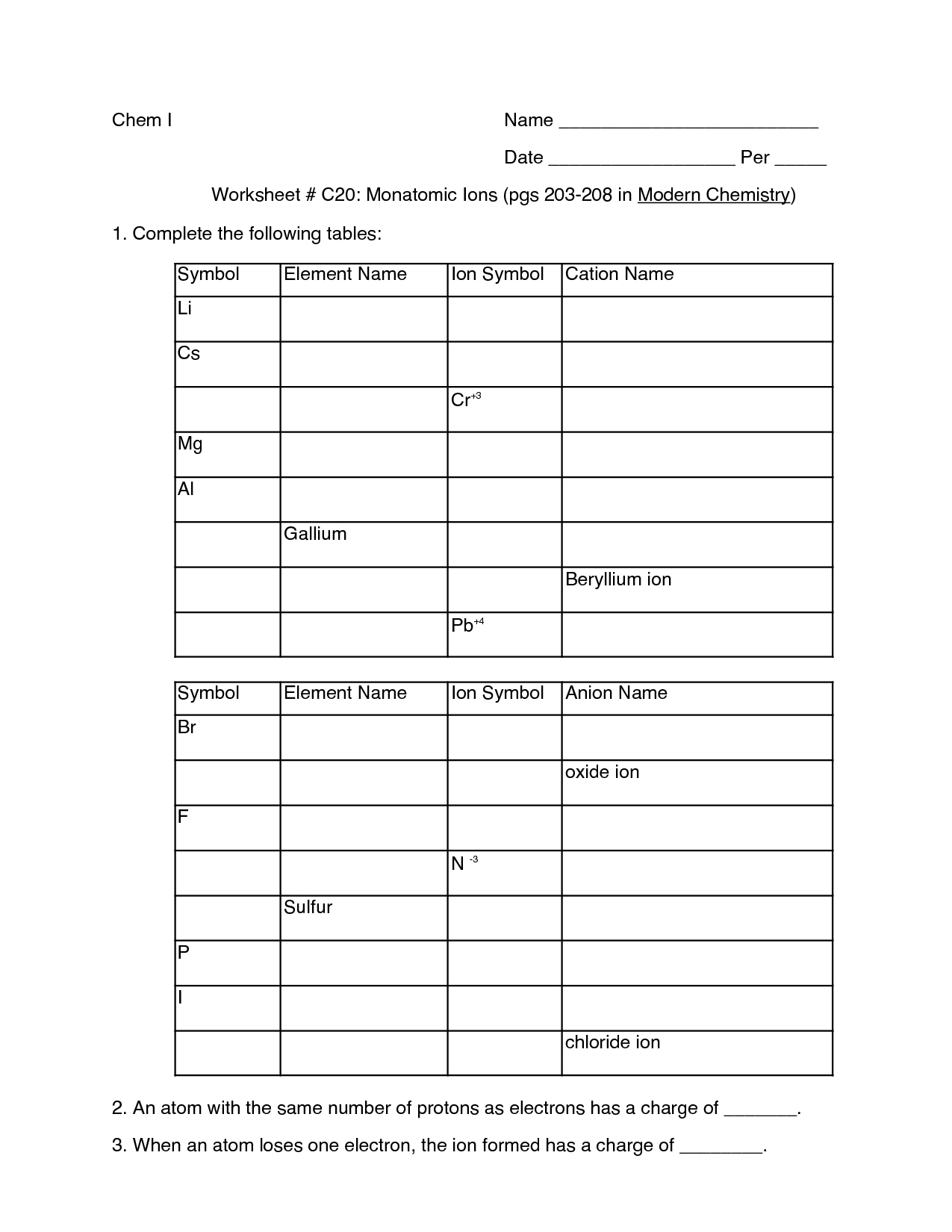
To determine the empirical formula of a compound, you need to determine the ratio of atoms present in the compound. This can be done by finding the mass of the elements present in the compound and converting them into moles. Then, divide the moles of each element by the smallest number of moles calculated to determine the simplest ratio of atoms in the compound, which represents the empirical formula.
What is the concept of isomerism in organic chemistry?
Isomerism in organic chemistry refers to the phenomenon where compounds with the same molecular formula have different structural arrangements or spatial orientations of atoms, resulting in distinct chemical and physical properties. There are different types of isomerism, including structural (constitutional) isomerism, stereoisomerism (geometric and optical), and tautomeric isomerism, each arising from specific differences in the connectivity or spatial arrangement of atoms within the molecules. Isomerism plays a crucial role in understanding the diversity and complexity of organic compounds and their behavior in chemical reactions.
Explain the difference between alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes.
Alkanes are hydrocarbons with single bonds between carbon atoms, alkenes have at least one double bond between carbon atoms, and alkynes have at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. These differences in bonding affect the physical properties and reactivity of each group of hydrocarbons, with alkenes and alkynes being more reactive due to the presence of multiple bonds.
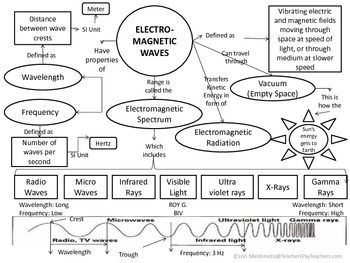
How does electronegativity affect organic compound reactions?
Electronegativity plays a significant role in organic compound reactions by influencing the polarity of bonds and the distribution of electrons in molecules. In reactions involving covalent bonds, differences in electronegativity between atoms determine the direction of electron movement and can affect the stability of reaction intermediates. Higher electronegativity of certain atoms can lead to stronger bonds and increased reactivity in organic compounds. Additionally, electronegativity influences the overall reactivity and behavior of functional groups in organic molecules, impacting how they interact with other compounds in chemical reactions.
What is the role of functional groups in organic compounds?
Functional groups in organic compounds determine the chemical reactivity and properties of the molecule. They define the specific chemical behavior of the compound, such as its acidity, basicity, polarity, and solubility. Functional groups also play a crucial role in identifying and categorizing organic molecules, as they are responsible for the characteristic reactions and functions of each compound. By understanding the functional groups present in a molecule, chemists can predict its behavior in various chemical reactions.
Describe the concept of chirality in organic chemistry.
Chirality in organic chemistry refers to the property of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, known as enantiomers. These enantiomers have the same chemical and physical properties, except for their interaction with other chiral molecules or polarized light. Chirality arises from having four different substituents around a central carbon atom, creating a unique three-dimensional arrangement. The two enantiomers are denoted as R and S configurations, based on their spatial orientation of substituents. Chirality plays a crucial role in drug design, asymmetric synthesis, and in biological systems.
How does resonance affect the stability of organic molecules?
Resonance in organic molecules stabilizes them by delocalizing electrons across multiple atoms, decreasing overall energy and making the molecule more stable. This occurs when a molecule can exhibit multiple electron structures due to the ability of electrons to move freely. The resulting stabilization helps prevent the molecule from easily reacting with other substances, contributing to its overall stability.
Explain the significance of aromatic compounds in organic chemistry.
Aromatic compounds are crucial in organic chemistry because they exhibit unique stability and reactivity patterns due to their delocalized pi electron system. This aromaticity is central to understanding the behavior of many organic molecules, influencing their chemical properties, reactions, and applications in various industries like pharmaceuticals, materials science, and agrochemicals. Additionally, aromatic compounds serve as building blocks for constructing complex organic molecules in synthesis, making them a cornerstone in the field of organic chemistry.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.















Comments