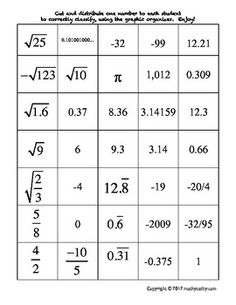
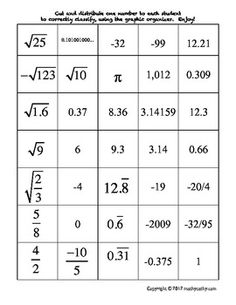
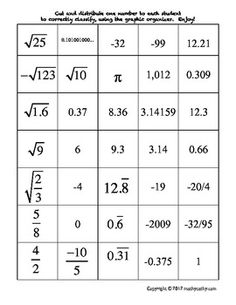
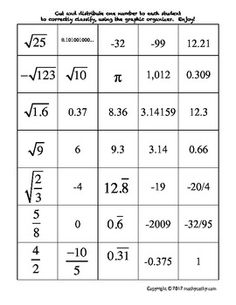
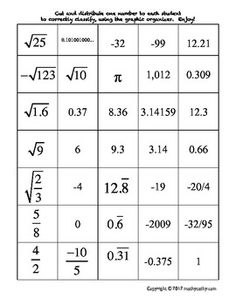
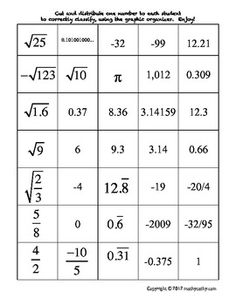
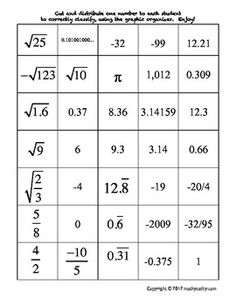
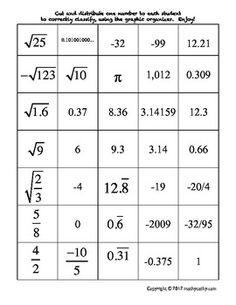
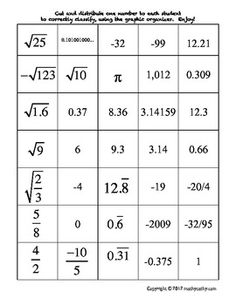
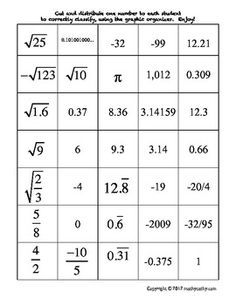
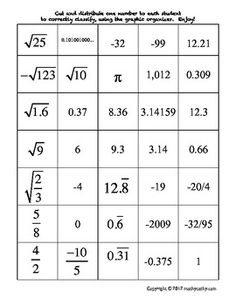
Ordering Rational and Irrational Numbers Worksheet
Are you seeking a practical and effective way to reinforce your understanding of ordering rational and irrational numbers? Look no further than this ordering rational and irrational numbers worksheet! This resource is designed to assist students in organizing and comparing different types of numbers, helping them sharpen their analytical and critical thinking skills. By providing clear instructions and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet is an excellent tool for middle and high school students who are studying mathematics.
Table of Images 👆
More Number Worksheets
Teen Number Practice WorksheetNumber Cut Out Worksheet
Kindergarten Number Worksheets 1 50
Thanksgiving Number Worksheets
Blank Kindergarten Numbers 1-100 Worksheets
Missing Number Multiplication Worksheets
Missing Teen Numbers Worksheet
6th Grade Color by Number Worksheets
Counting Numbers to 1000 Worksheets
What is a rational number?
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction where the numerator and denominator are both integers and the denominator is not zero. Rational numbers include integers, fractions, and terminating or repeating decimals.
How can you determine if a number is rational or irrational?
A number is rational if it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. On the other hand, a number is irrational if it cannot be written as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. To determine if a number is rational or irrational, one can try to express it as a fraction first. If this is not achievable and the decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating, then the number is irrational.
Can rational numbers be written in fraction form? Why or why not?
Yes, rational numbers can be written in fraction form because they are numbers that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. This means that any rational number can be written in the form a/b, where a and b are integers and b is not equal to zero. This fraction form allows us to represent any rational number accurately and precisely.
Give an example of a rational number that is not an integer.
An example of a rational number that is not an integer is 3/4. This fraction represents a number that is not a whole number but can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, 3 and 4.
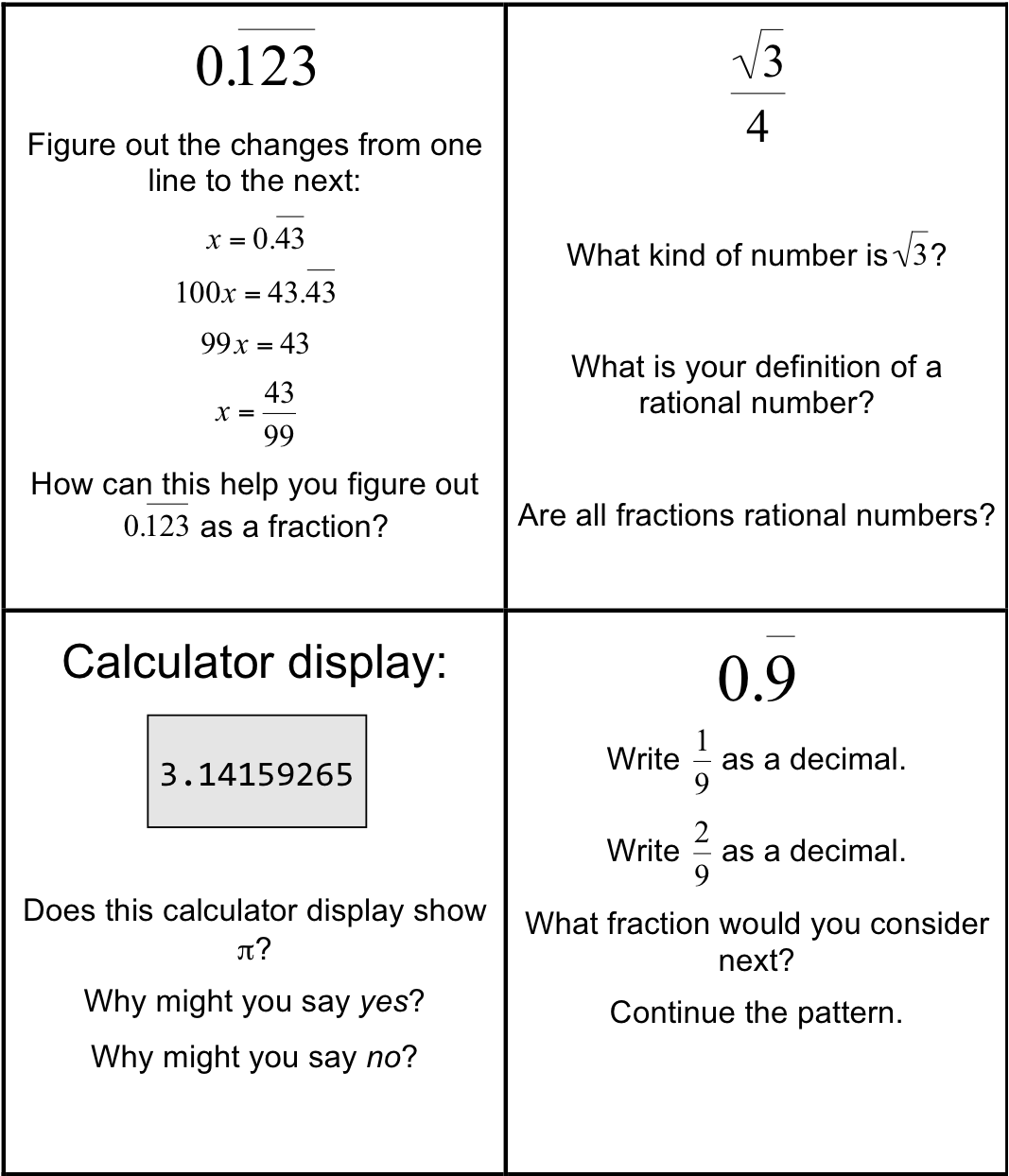
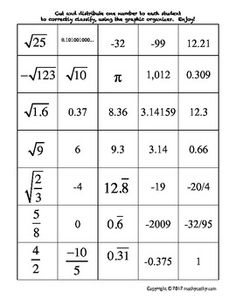
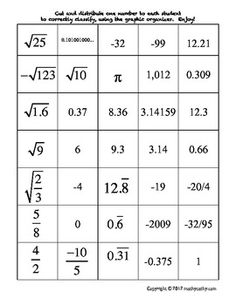
Explain the concept of ordering rational numbers.
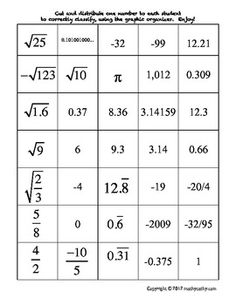
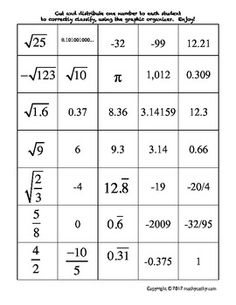
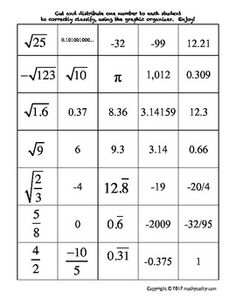
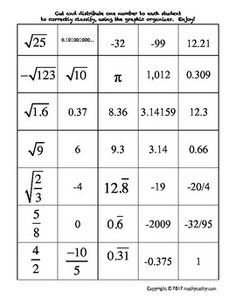
Ordering rational numbers involves arranging them from least to greatest or greatest to least on a number line or in a list based on their numerical value. When ordering rational numbers, you can compare them using their numerical value, fractions can be converted to common denominators, and decimals can be compared by looking at the place value of digits. In essence, ordering rational numbers allows us to establish a clear hierarchy and understand their relative magnitudes in relation to one another.
How do you compare two rational numbers with different denominators?
To compare two rational numbers with different denominators, you first need to find a common denominator for both numbers. To do this, you can find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators. Once you have converted both rational numbers to have the same denominator, you can then compare them by looking at the numerators. The rational number with the greater numerator is the larger number. If the numerators are equal, then you can compare the denominators to determine the larger number.
Provide an example of ordering rational numbers using a number line.
Sure! Let's order the rational numbers -3, 4/3, 0, -1/2, and 2 on a number line. Starting from the left, -3 is the smallest, followed by -1/2, then 0, then 4/3, and finally, 2 is the largest. So, the order from smallest to largest is -3, -1/2, 0, 4/3, and 2.
Define an irrational number.
An irrational number is a real number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, but rather as an infinite, non-repeating decimal. These numbers have decimal expansions that neither terminate nor repeat, making them impossible to represent accurately with a finite number of decimal places. Examples of irrational numbers include the square root of 2 (?2), ? (pi), and e (Euler's number).
Give an example of an irrational number.
An example of an irrational number is the square root of 2 (?2), which cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has an infinite non-repeating decimal expansion.
Can irrational numbers be expressed as fractions? Why or why not?
No, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions because they cannot be written as a ratio of two integers. Irrational numbers have non-repeating and non-terminating decimal expansions, which means they cannot be accurately represented by a fraction. Fractions represent rational numbers, which are numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. Examples of irrational numbers include the square root of 2 and pi.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments