Nutrition Worksheets and Math
Are you someone who values both nutrition and math? If so, you're in luck! We have a collection of nutrition worksheets that combine the concepts of math and healthy eating. These worksheets are designed for students in grades 3-5 and aim to reinforce understanding of both subjects in an engaging and interactive way. Whether you're a teacher looking for additional resources for your classroom or a parent wanting to supplement your child's learning at home, these nutrition worksheets are a great tool to help reinforce important knowledge in both math and healthy eating habits.
Table of Images 👆
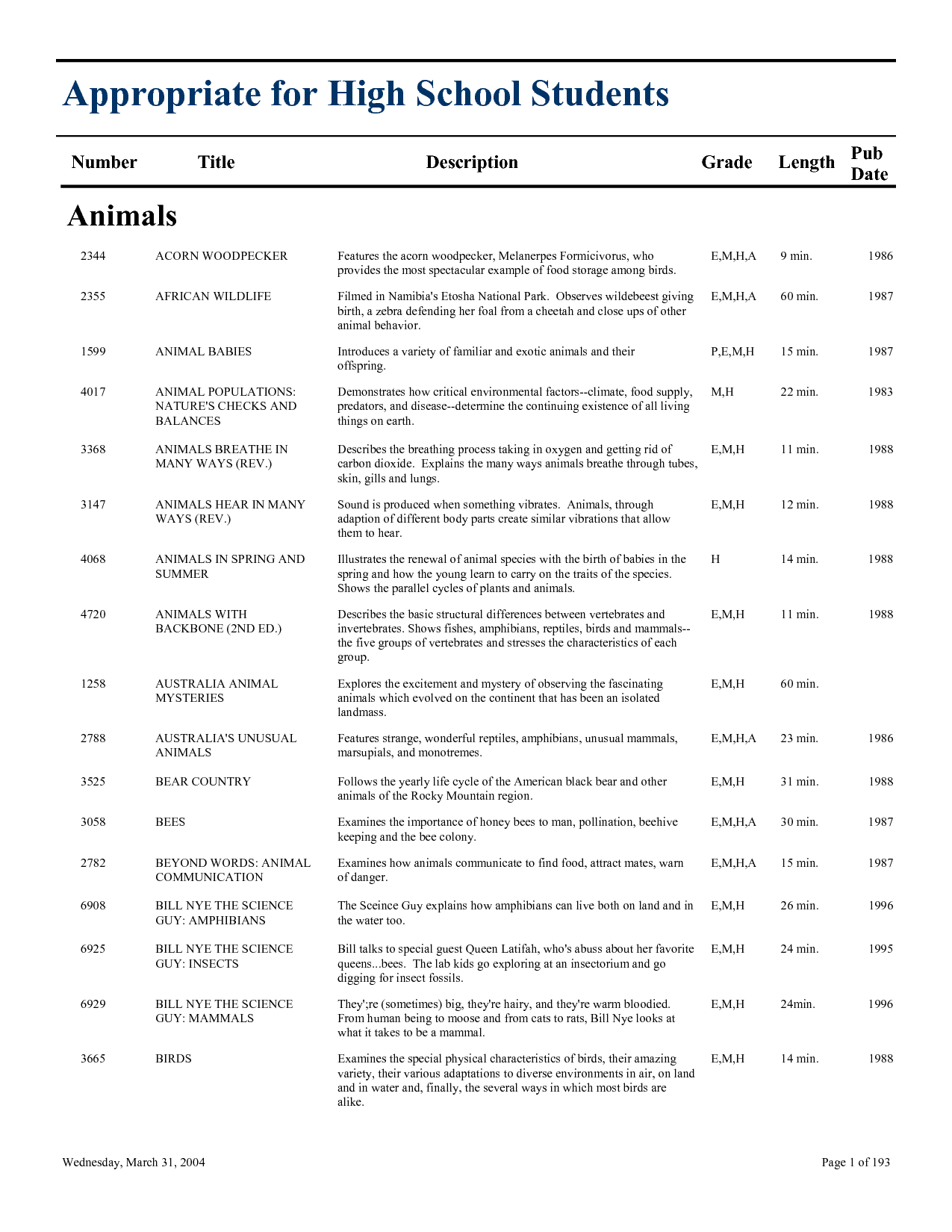
- Nutrition Worksheets for High School Students
- Free Printable Worksheets On Health
- School Science Worksheets
- Food Nutrition Labels Worksheet
- Health and Nutrition Worksheets
- Free Printable School Worksheets
- Reading Food Labels Worksheet
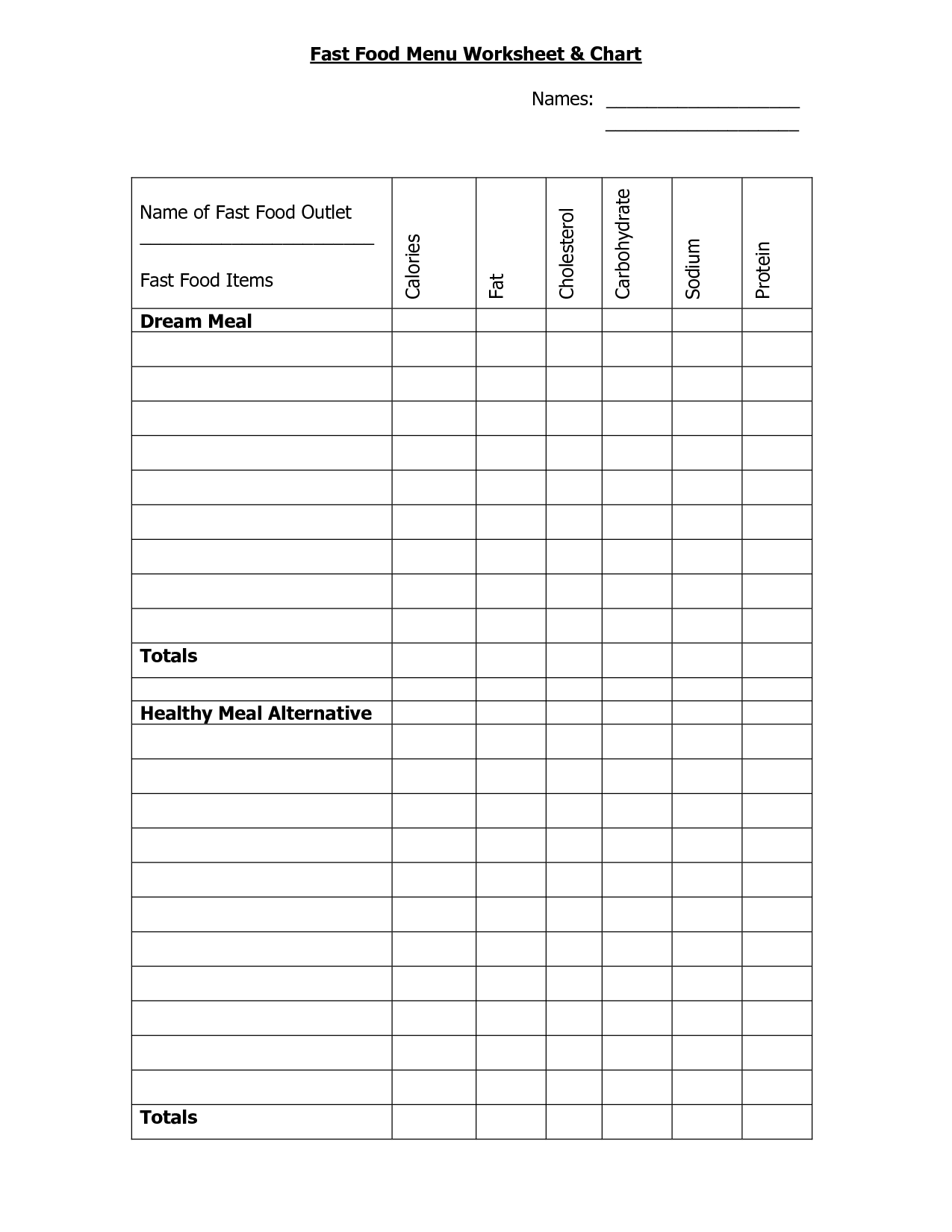
- Printable Restaurant Menu Worksheet
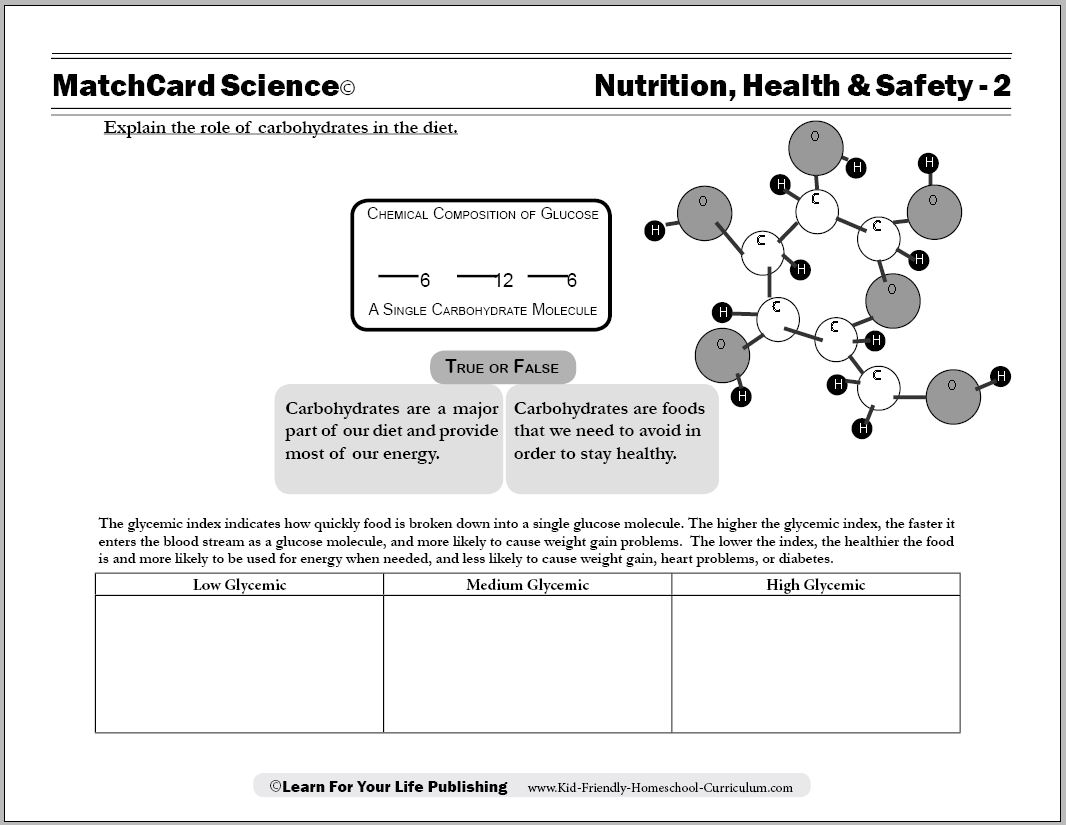
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Nutrition
- Nutrition Math Activities
- Digestion and Nutrition Worksheet
- Math and Food
More Math Worksheets
Printable Math WorksheetsMath Worksheets Printable
Printable Math Worksheets Multiplication
Math Worksheets for 2nd Graders
Math Multiplication Worksheets
First Grade Subtraction Math Worksheets Printable
Math Worksheets Integers
Middle School Math Coloring Worksheets
Hard Math Equations Worksheets
Valentine's Day Math Coloring Worksheets
What are macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the three main types of nutrients that provide energy for the body: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These nutrients are essential for proper growth, development, and overall health, and they make up the majority of our diet. Macronutrients are needed in larger quantities compared to micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, to support various bodily functions and activities.
What is the role of fiber in the diet?
Fiber plays a crucial role in the diet by promoting healthy digestion, aiding in weight management, regulating blood sugar levels, and lowering the risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer. Additionally, fiber helps to keep you feeling full and satisfied after meals, supports a healthy gut microbiome, and contributes to overall gut health by preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements.
How does the body process carbohydrates?
When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose during digestion. The glucose then enters the bloodstream, causing a rise in blood sugar levels. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps regulate this process by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy production or storage. Any excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen, which can be converted back into glucose when energy is needed.
What are antioxidants and how do they benefit our health?
Antioxidants are compounds that can help prevent or slow damage to cells caused by free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can harm cells. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. Additionally, antioxidants can also help support a healthy immune system and promote overall well-being by protecting cells from oxidative stress and inflammation.
What are the functions of vitamins in the body?
Vitamins play essential roles in the body by supporting various physiological functions such as metabolism, immune system function, cell growth, and development, maintaining healthy vision, skin, and bones, acting as antioxidants to protect against cell damage, and assisting in the production of hormones and enzymes involved in numerous bodily processes. Each vitamin has specific functions and deficiencies can lead to health problems, highlighting the crucial role these micronutrients play in overall health and well-being.
How does protein contribute to muscle growth and repair?
Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair as it provides the building blocks, amino acids, needed for muscle protein synthesis. During periods of exercise-induced muscle damage, consuming protein helps to repair and rebuild muscle fibers, leading to muscle growth and recovery. Protein also plays a crucial role in regulating muscle protein turnover, maintaining muscle mass, and supporting overall muscle health.
What is the importance of water in our diet?
Water is essential for human survival as it plays a vital role in various bodily functions. It helps in maintaining body temperature, transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells, removing waste and toxins, lubricating joints, and protecting organs and tissues. Adequate water intake is crucial for overall health and well-being, as it helps support digestion, metabolism, and energy levels. Dehydration can lead to serious health issues, so it is important to stay hydrated by consuming an adequate amount of water daily as part of a balanced diet.
How does the body metabolize fats?
When fats are consumed, they are broken down by enzymes in the digestive system into fatty acids and glycerol. These components are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells for energy production. In the cells, fatty acids are metabolized through a process called beta-oxidation, where they are broken down further into acetyl-CoA molecules. Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle in the mitochondria, where it is converted into ATP, the main energy source for the body. Unused fats are stored in adipose tissue for later energy use.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats have no double bonds between carbon atoms, making them solid at room temperature and typically found in animal products and some plant oils. On the other hand, unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms, making them liquid at room temperature and predominantly found in plant-based oils. Unsaturated fats are considered healthier than saturated fats as they can help lower bad cholesterol levels in the body when consumed in moderation.
What are the potential health risks associated with excessive sodium intake?
Excessive sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. It can also contribute to fluid retention, leading to swelling in the extremities and causing strain on the heart and blood vessels. Additionally, high sodium intake may increase the risk of osteoporosis, stomach cancer, and other health issues. It is important to be mindful of sodium consumption and aim to keep it within recommended limits to maintain good health.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments