Nucleic Acids Worksheet Key
Are you a teacher or a student in need of a reliable and comprehensive resource to reinforce your understanding of nucleic acids? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with a valuable resource - the Nucleic Acids Worksheet Key - designed to aid your learning journey. Whether you are a high school student studying biology or a college-level student specializing in genetics, this worksheet will provide you with a solid foundation on the structure and function of nucleic acids. So, let's dive in and explore the essential aspects of this important topic!
Table of Images 👆
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- Amino Acid Codon Chart Worksheets
- Macromolecules Worksheet 2 Answer Key
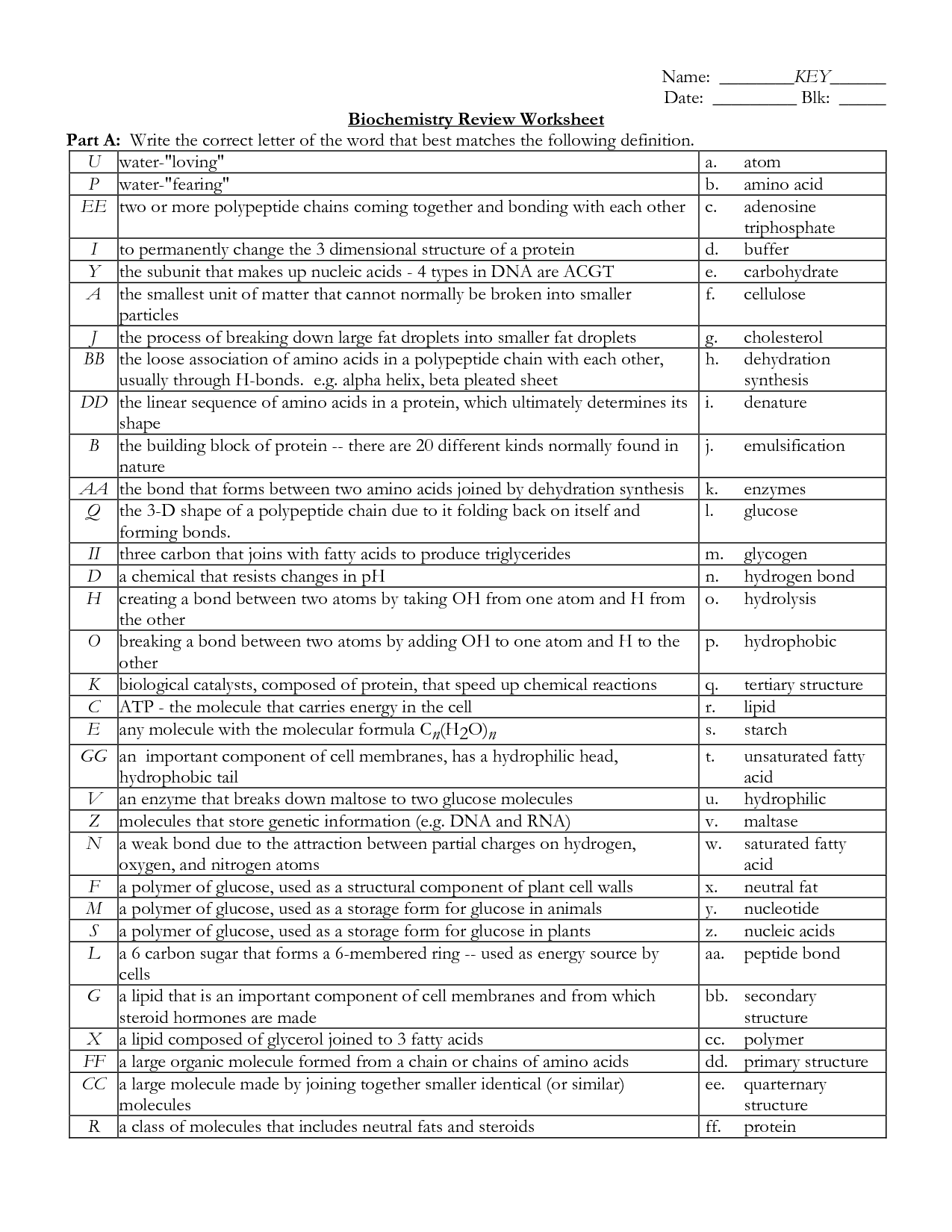
- Biochemistry Review Worksheet
- Worksheets Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are biopolymers that serve as the building blocks of genetic material in living organisms. They are composed of nucleotide monomers, each consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The two main types of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), which play essential roles in storing, transmitting, and expressing genetic information in cells.
What is the primary function of nucleic acids?
The primary function of nucleic acids is to store and transmit genetic information. They carry the instructions for making proteins, which are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of cells in living organisms. Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are crucial for the inheritance of traits and the overall functioning of an organism's cells.
What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries genetic information in cells and is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic instructions from one generation to the next. RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and gene expression by translating the genetic code stored in DNA into functional proteins.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double helix structure made up of two long chains of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), or thymine (T). The nucleotide chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, with adenine pairing with thymine and guanine pairing with cytosine. This structure allows DNA to store and transmit genetic information in the form of a genetic code.
What is the structure of RNA?
RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid that consists of a long chain of nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), or cytosine (C). These bases can form complementary base pairs with each other, allowing RNA molecules to fold into specific 3D structures essential for their function in processes such as protein synthesis and gene regulation.
How is information encoded in nucleic acids?
Information is encoded in nucleic acids through the arrangement of nucleotide bases along the molecule's backbone. In DNA, the order of the four bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) forms a genetic code that carries instructions for protein synthesis. This information is transcribed into messenger RNA, which then directs the assembly of specific amino acids into proteins. The sequence of bases in the nucleic acid determines the specific order of amino acids in the protein, thus encoding genetic information.
How are nucleic acids replicated?
Nucleic acids are replicated through the process of DNA replication. In this process, the DNA double helix unwinds and separates into two strands. Each original strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand, resulting in two identical molecules of DNA. The enzyme DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing strand following the base-pairing rules (A with T, C with G) to ensure accuracy and fidelity in the replication process.
What is transcription?
Transcription is the process of copying genetic information from DNA into RNA. It involves the enzyme RNA polymerase binding to a specific region of the DNA molecule and creating a complementary RNA strand using the nucleotide bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil. This process is essential for gene expression and protein synthesis in cells.
What is translation?
Translation is the process of converting a text or spoken language from one language to another while maintaining the original meaning, nuance, and style of the source content. A translator aims to convey the message accurately and effectively to the target audience in the new language while taking cultural context, idiomatic expressions, and linguistic nuances into consideration.
What are some examples of nucleic acids in living organisms?
Examples of nucleic acids in living organisms include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA carries genetic information in the form of genes, and RNA is involved in protein synthesis and gene expression. Both nucleic acids play crucial roles in the functioning and reproduction of living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments