Nucleic Acid Worksheet
If you're a student or educator seeking a valuable resource to enhance your understanding of nucleic acids, look no further than a nucleic acid worksheet. This educational tool serves as an essential aid in comprehending the critical role nucleic acids play in our bodies and the field of genetics. Whether you're studying biology, biochemistry, or genetics, a nucleic acid worksheet provides a structured and organized way to delve into this complex subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- DNA Double Helix Coloring Worksheet Answers
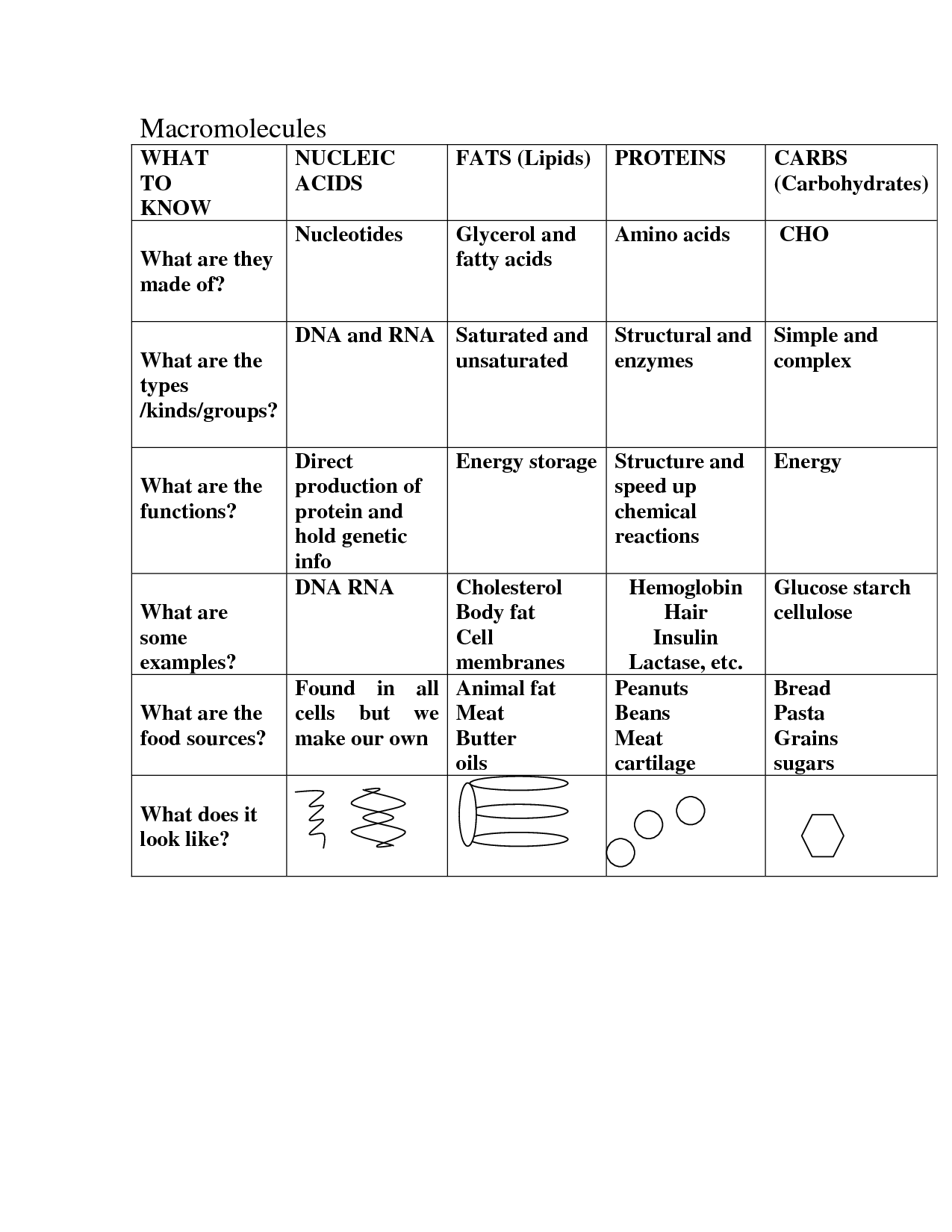
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
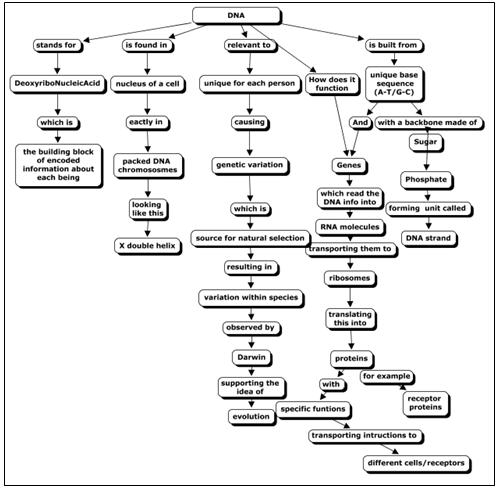
- DNA Structure Concept Map
- Carbohydrates Lipids and Proteins Worksheet
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Acids Bases and Salts Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are essential biomolecules that store, transmit, and express genetic information in living organisms. They are made up of nucleotide monomers, consisting of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are two main types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which carries genetic information for the synthesis of proteins, and ribonucleic acid (RNA), which plays a key role in protein synthesis and gene regulation.
What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries the genetic information necessary for the growth, development, and functioning of all living organisms, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and gene expression.
What is the primary function of DNA?
The primary function of DNA is to store and transmit genetic information that determines an organism's traits and characteristics, such as its physical features, behavior, and physiological processes.
What is the primary function of RNA?
The primary function of RNA is to serve as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes, carrying the genetic information encoded in DNA to guide the synthesis of proteins. This process, known as protein synthesis or translation, is essential for the functioning and development of living organisms. Additionally, RNA also plays roles in regulating gene expression, catalyzing biochemical reactions, and helping to modify other molecules in the cell.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA has a double helix structure composed of two long chains of nucleotides twisted around each other. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). These bases form complementary base pairs, with adenine pairing with thymine and cytosine pairing with guanine, holding the two strands together. The sequence of these base pairs along the DNA strands encodes genetic information.
What is the structure of RNA?
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a single-stranded nucleic acid made up of a long chain of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (ribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil). The sugar-phosphate backbones form the structural framework of the RNA molecule, with the nitrogenous bases extending from this backbone.
How is genetic information stored in DNA?
Genetic information is stored in DNA through a series of nucleotide base pairs, which form a double helix structure. The four types of nitrogenous bases – adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine – are arranged in specific sequences along the DNA molecule. These base pairs provide the genetic code that determines an organism's traits and characteristics. The sequence of these base pairs serves as the instructions for building proteins and carrying out various biological functions within an organism.
What is the process of DNA replication?
DNA replication is a complex process where a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to create two identical DNA molecules. The process involves unwinding the DNA double helix, separation of the two strands by helicase enzymes, and then synthesis of new strands by DNA polymerase enzymes using the existing strands as templates. The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in the form of Okazaki fragments. Finally, the RNA primers are removed, and the gaps between Okazaki fragments are filled in, resulting in two identical DNA molecules.
How is RNA involved in protein synthesis?
RNA is involved in protein synthesis as it serves as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs. Specifically, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from DNA in the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosomes according to the instructions on the mRNA, while ribosomal RNA (rRNA) helps to assemble the amino acids into a protein chain. Overall, RNA plays a crucial role in translating the genetic code from DNA into proteins during the process of protein synthesis.
How do mutations in nucleic acids affect biological processes?
Mutations in nucleic acids can affect biological processes by altering the sequence of the DNA or RNA, leading to changes in the corresponding proteins produced. These changes can result in disruptions to normal cellular functions, affecting processes such as growth, development, and metabolism. Some mutations may be neutral or even beneficial, while others can be harmful and lead to diseases or genetic disorders. Ultimately, mutations play a crucial role in evolution by providing genetic variability that drives adaptation and natural selection in populations.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments