Neuron Diagram Worksheet
Are you a biology student or educator trying to reinforce your understanding of neuron structures? Look no further than our Neuron Diagram Worksheet. This worksheet provides a detailed and informative diagram of a neuron, allowing you to study and review its different components. Whether you are preparing for an exam or simply seeking to expand your knowledge, this worksheet is a valuable resource for anyone interested in the workings of the brain and nervous system.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the function of the cell body in a neuron?
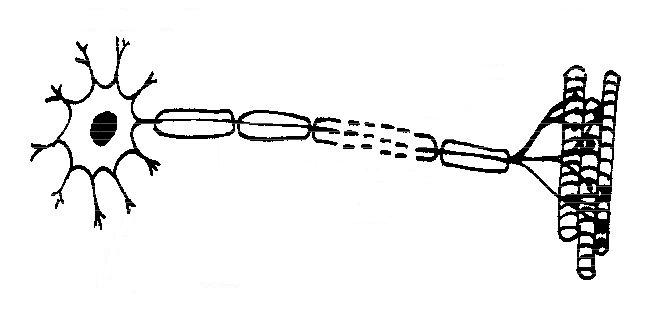
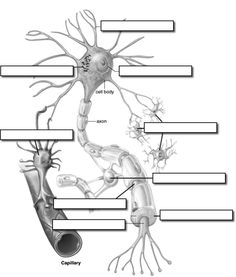
The cell body of a neuron, also known as the soma, contains the nucleus and other organelles responsible for carrying out the basic functions of the cell, such as protein synthesis and metabolism. It integrates the signals received from dendrites and, based on the input it receives, decides whether to generate a nerve impulse that is then sent down the axon to communicate with other neurons. Essentially, the cell body plays a crucial role in the overall functioning and regulation of the neuron.
What do dendrites do in a neuron?
Dendrites receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body of the neuron. They play a crucial role in integrating and processing these incoming signals, which ultimately determine whether the neuron will generate an action potential and pass the signal on to other neurons.
What is the role of the axon in transmitting nerve impulses?
The axon functions as the main conducting pathway for transmitting nerve impulses from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands. Its long structure allows for rapid transmission of electrical signals in the form of action potentials, enabling efficient communication between different parts of the nervous system. The axon is covered by a fatty sheath called myelin, which helps to speed up the transmission of impulses by insulating the electrical signal.
What are myelin sheaths and what is their purpose?
Myelin sheaths are protective coverings made of protein and fatty substances that surround and insulate the axons of nerve cells. Their purpose is to increase the speed and efficiency of nerve impulse transmission along the axon. By providing insulation, myelin sheaths help prevent electrical signals from leaking out and ensure that they travel quickly and smoothly along the nerve fiber, allowing for rapid communication between different parts of the nervous system.
What is the function of the synapse in a neuron?
The function of a synapse in a neuron is to transmit electrical or chemical signals from one neuron to another. This communication allows neurons to communicate and pass on information throughout the nervous system, ultimately influencing various processes such as sensory perception, motor function, and cognitive functions.
How do neurotransmitters facilitate communication between neurons?
Neurotransmitters facilitate communication between neurons by being released from the axon terminals of one neuron in response to an action potential. These chemical messengers then cross the synaptic gap and bind to specific receptors on the dendrites or cell bodies of the receiving neuron. This binding either excites or inhibits the receiving neuron, influencing whether an action potential will be generated. This process allows for the transmission of signals from one neuron to another, enabling communication within the nervous system.
What are sensory neurons and what is their role in the nervous system?
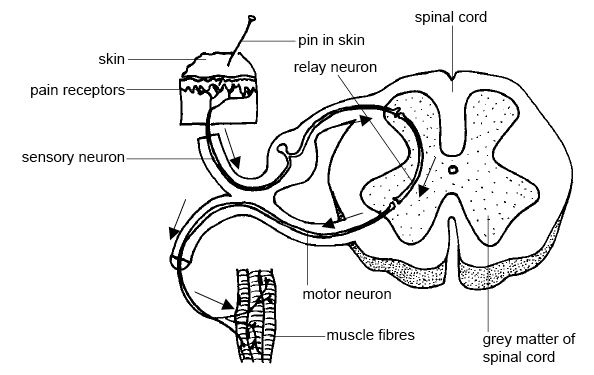
Sensory neurons are specialized nerve cells responsible for transmitting sensory information from the body to the central nervous system. They are equipped with receptors that detect various stimuli such as light, pressure, temperature, and chemicals. Once activated, sensory neurons generate electrical signals that are then relayed to the brain for processing and interpretation. This fundamental role of sensory neurons allows the body to sense and respond to its external environment, maintaining homeostasis and facilitating various bodily functions.
What do motor neurons control in the body?
Motor neurons are responsible for controlling muscle movements in the body. They transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, enabling voluntary movements such as walking, talking, and grasping objects. Additionally, motor neurons play a crucial role in maintaining involuntary functions like breathing and heartbeat.
What is the purpose of interneurons?
Interneurons serve as bridges between sensory and motor neurons in the central nervous system, allowing for the processing and integration of information. They play a crucial role in regulating and coordinating communication between different parts of the nervous system to generate appropriate responses to stimuli, helping to control complex behaviors and cognitive functions.
How does the structure of a neuron allow for efficient transmission of electrical signals?
The structure of a neuron, with its long, branching extensions known as dendrites and axons, allows for efficient transmission of electrical signals through the nervous system. Dendrites receive electrical signals from other neurons and transmit them towards the cell body, where they are integrated and processed. The axon then carries the electrical signal away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles. The myelin sheath that surrounds some axons insulates and speeds up the transmission of electrical impulses, while the gaps in the myelin sheath, known as nodes of Ranvier, help to regenerate and amplify the signals as they travel along the axon. These specialized structures and pathways enable neurons to rapidly and efficiently communicate and coordinate functions throughout the body.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments