Muscle Contraction Worksheet
Are you a fitness enthusiast or a biology student looking to enhance your understanding of muscle contraction? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore a variety of worksheets that can help you grasp the concepts and dynamics of muscle contraction. Whether you're trying to memorize the different types of muscle fibers or understand the process of sliding filament theory, these worksheets will provide you with the necessary entity and subject-specific exercises to solidify your knowledge.
Table of Images 👆
- Muscle Contraction Worksheet Answers
- Muscle Tissue Worksheet
- Muscle Coloring Worksheet
- Free Printable Muscular System Worksheets
- Endocrine System Worksheets with Answers
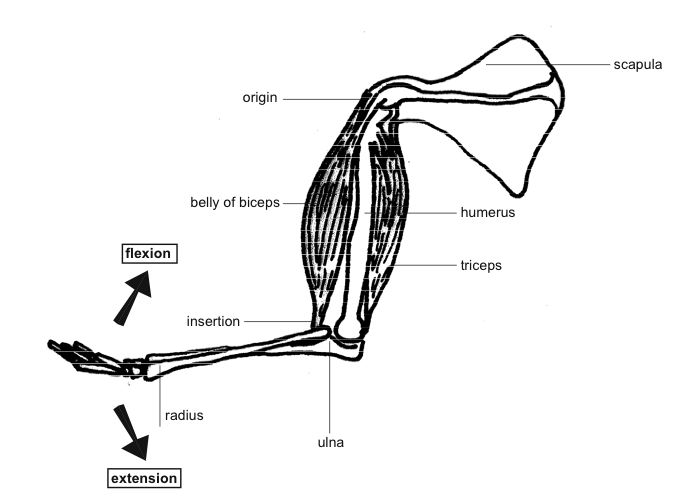
- Antagonistic Muscles Diagram
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology Exercise 2 Answers
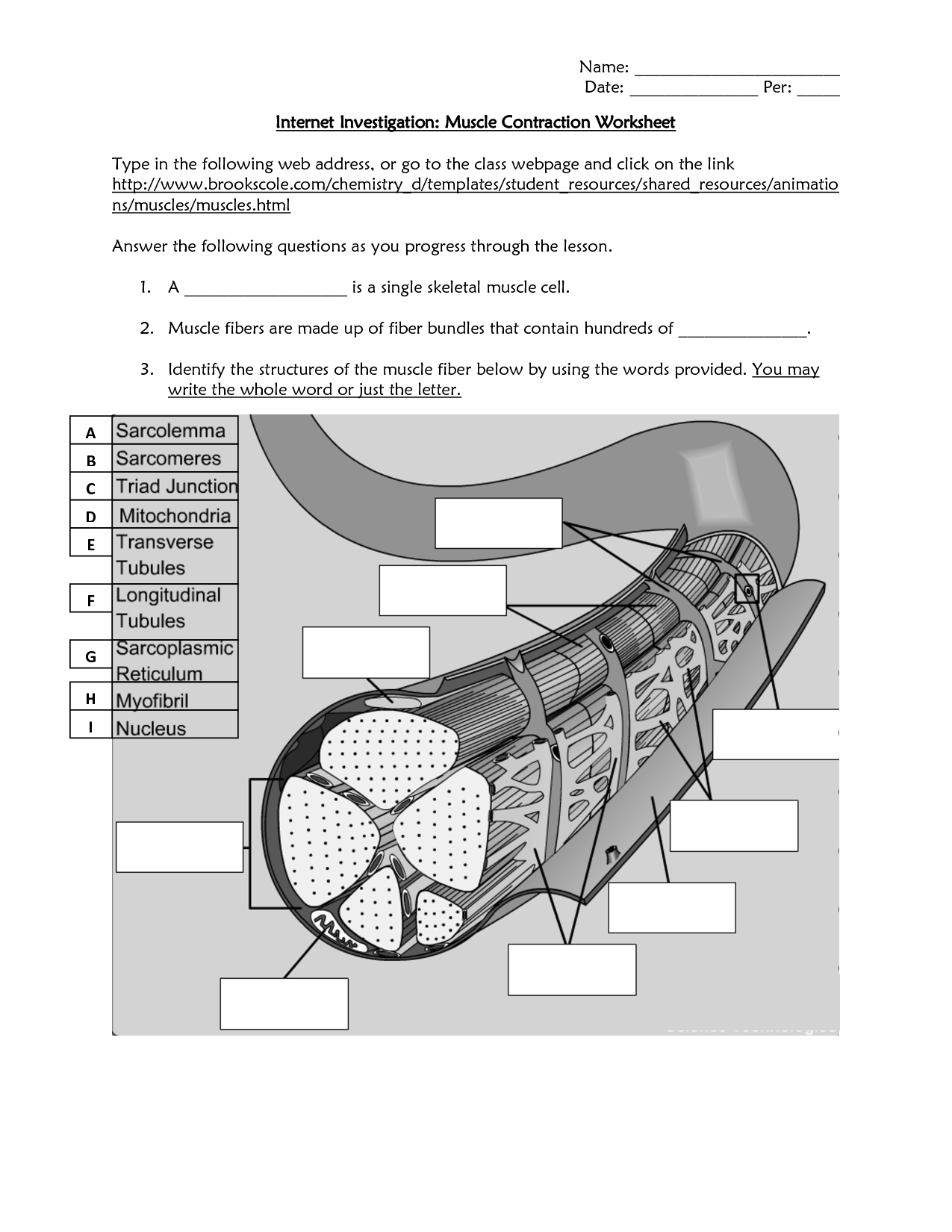
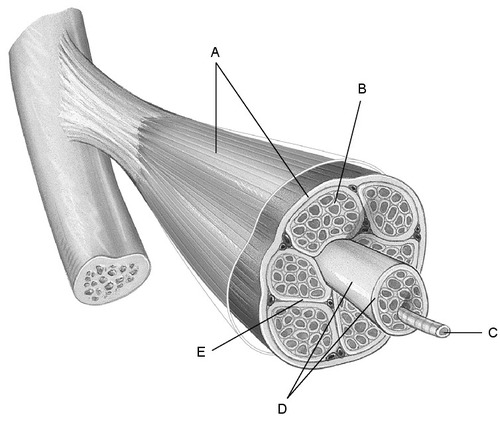
- Connective Tissue Surrounding Muscle Fiber Bundles
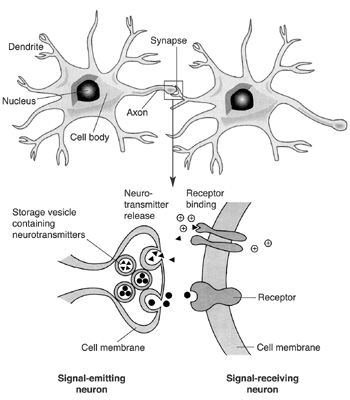
- Nerve Cell Neuron with Synapse
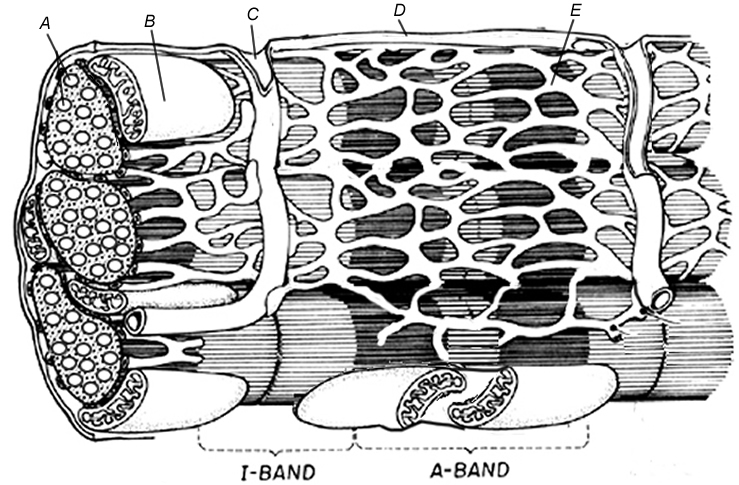
- Label a Sarcomere Worksheet
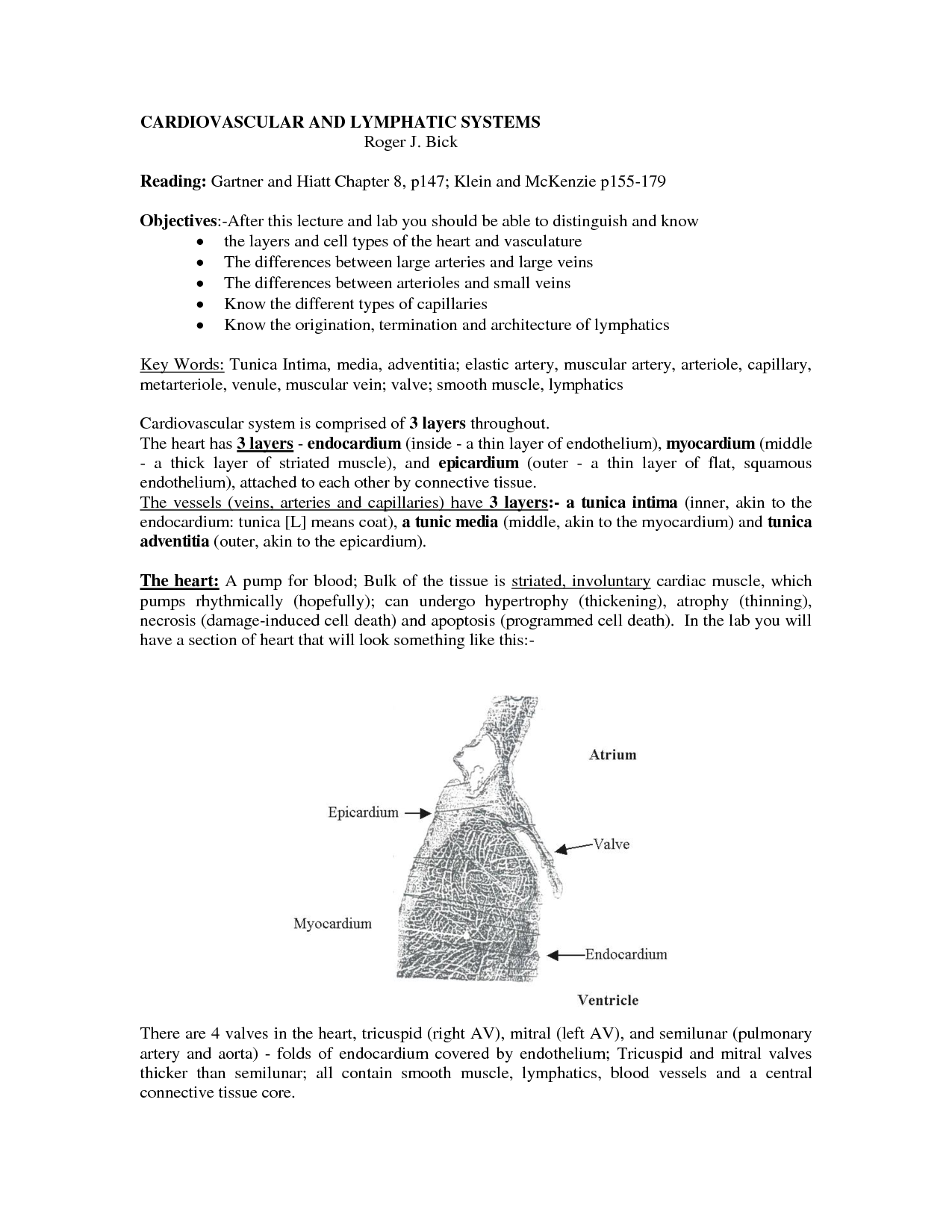
- Human Heart Coloring Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is muscle contraction?
Muscle contraction is the process through which muscle fibers generate force and shorten in length, leading to movement of body parts. This process is controlled by the nervous system and involves the sliding of actin and myosin filaments within muscle fibers. When a muscle is stimulated by a motor neuron, calcium ions are released, triggering the cross-bridge cycle and causing the muscle fibers to contract.
How does a muscle contract?
A muscle contracts through a process called excitation-contraction coupling, where a nerve impulse triggers the release of calcium ions in the muscle cell. The presence of calcium allows the proteins actin and myosin to interact and create cross-bridges, which result in the shortening of the muscle fibers. This contraction allows the muscle to generate force and movement.
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
Calcium plays a crucial role in muscle contraction by binding to troponin, a protein in the muscle fibers. This allows the tropomyosin molecule to move and expose the active sites on actin, enabling myosin to form cross-bridges and initiate the sliding filament mechanism, leading to muscle contraction. Essentially, calcium acts as a trigger for the contraction process in muscle fibers.
How is ATP involved in muscle contraction?
ATP is utilized in muscle contraction as a source of energy. When a muscle is stimulated to contract, ATP molecules are broken down, releasing energy that is required for the myosin and actin filaments to slide past each other, resulting in muscle contraction. This energy allows for the cross-bridge cycling between myosin heads and actin filaments, ultimately leading to the shortening of the muscle fibers and generation of force.
What are the three types of muscle contractions?
The three types of muscle contractions are concentric, eccentric, and isometric. Concentric contractions occur when the muscle shortens while generating force, as in lifting a weight. Eccentric contractions happen when the muscle lengthens while under tension, such as lowering a weight. Isometric contractions occur when there is tension in the muscle but no movement, like holding a plank position.
What is the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction?
The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction states that muscle fibers contract by the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within the muscle cell. When a muscle is stimulated by a nerve impulse, calcium ions are released, leading to the binding of myosin heads to actin filaments and the subsequent formation of cross-bridges. This causes the actin filaments to slide towards the center of the sarcomere, resulting in muscle contraction. This theory explains the molecular mechanism behind muscle contraction at a cellular level.
What is the role of myosin in muscle contraction?
Myosin is a motor protein that plays a crucial role in muscle contraction by interacting with actin filaments to generate muscle movement. During contraction, myosin molecules use ATP energy to repeatedly bind to actin, pull on the filaments, release, and then reset to bind again. This cycle causes the muscle fibers to shorten and generate force, enabling movement and activity.
What is the role of actin in muscle contraction?
Actin is a protein that plays a crucial role in muscle contraction by interacting with myosin. During contraction, actin and myosin filaments slide past each other, causing the muscle to shorten. The interaction between actin and myosin allows for the generation of force and movement in muscle cells, enabling various bodily functions such as locomotion and organ function.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in muscle contraction?
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in muscle contraction by relaying signals from motor neurons to muscle fibers at the neuromuscular junction. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters (such as acetylcholine) into the synaptic cleft, further binding to receptors on the muscle cell membrane and initiating a series of events that result in muscle contraction. This process is essential for communication between the nervous system and muscles, ultimately allowing for coordinated movement and bodily functions.
How does muscle contraction contribute to movement in the body?
Muscle contraction is essential for movement in the body as it allows muscles to generate force and tension, resulting in the shortening of muscle fibers. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bones to which it is attached, creating movement at the joints. This process is key for actions like walking, running, lifting objects, and any other voluntary or involuntary movements. Additionally, muscle contractions help maintain posture, stabilize joints, and provide balance and coordination for various activities.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments