mRNA and Transcription Worksheet
Are you a biology student searching for a helpful resource on mRNA and transcription? Look no further! In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of worksheets in facilitating understanding of these complex concepts. Worksheets provide an interactive and structured approach to learning, allowing you to grasp the key entities and subjects involved in mRNA and transcription processes.
Table of Images 👆
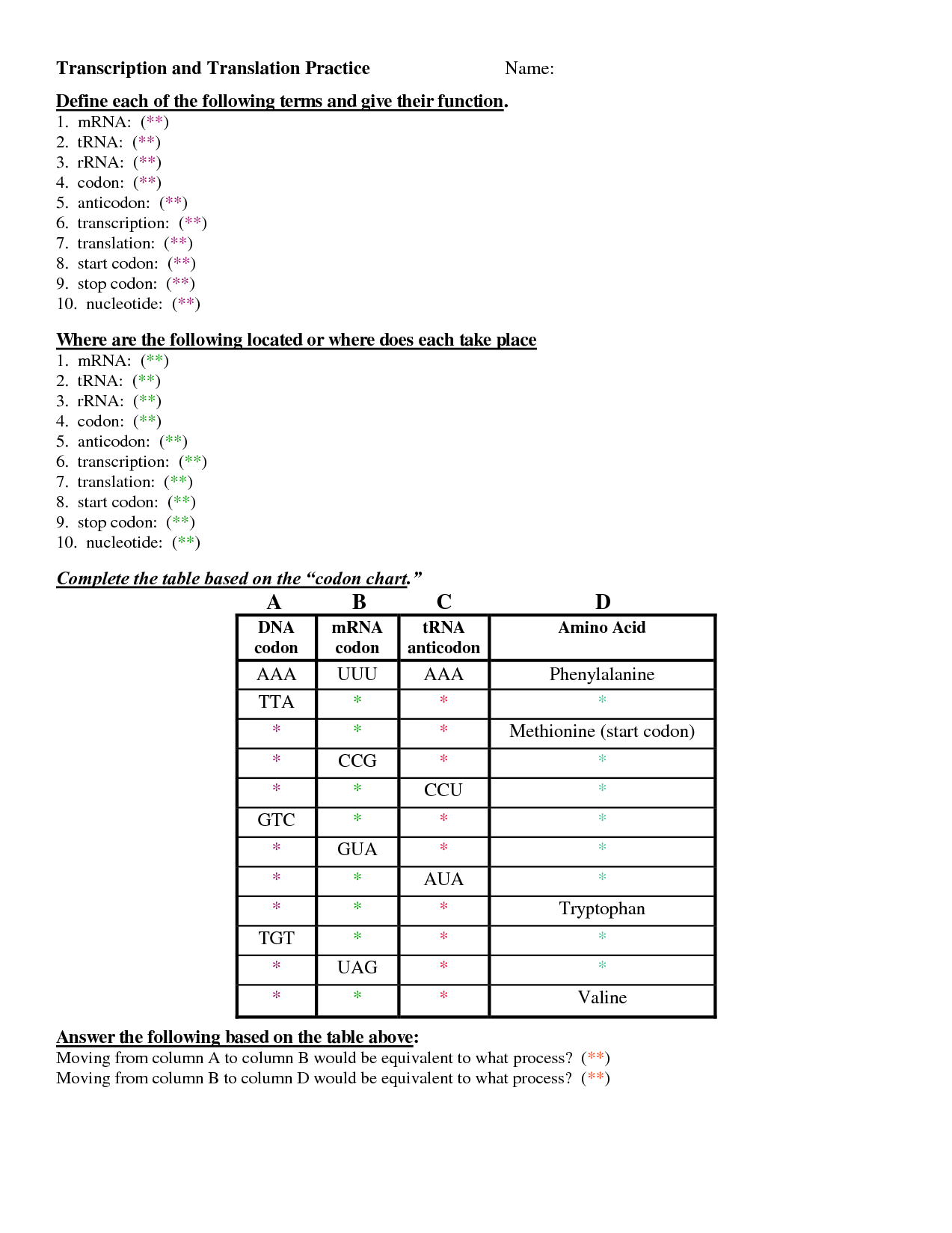
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
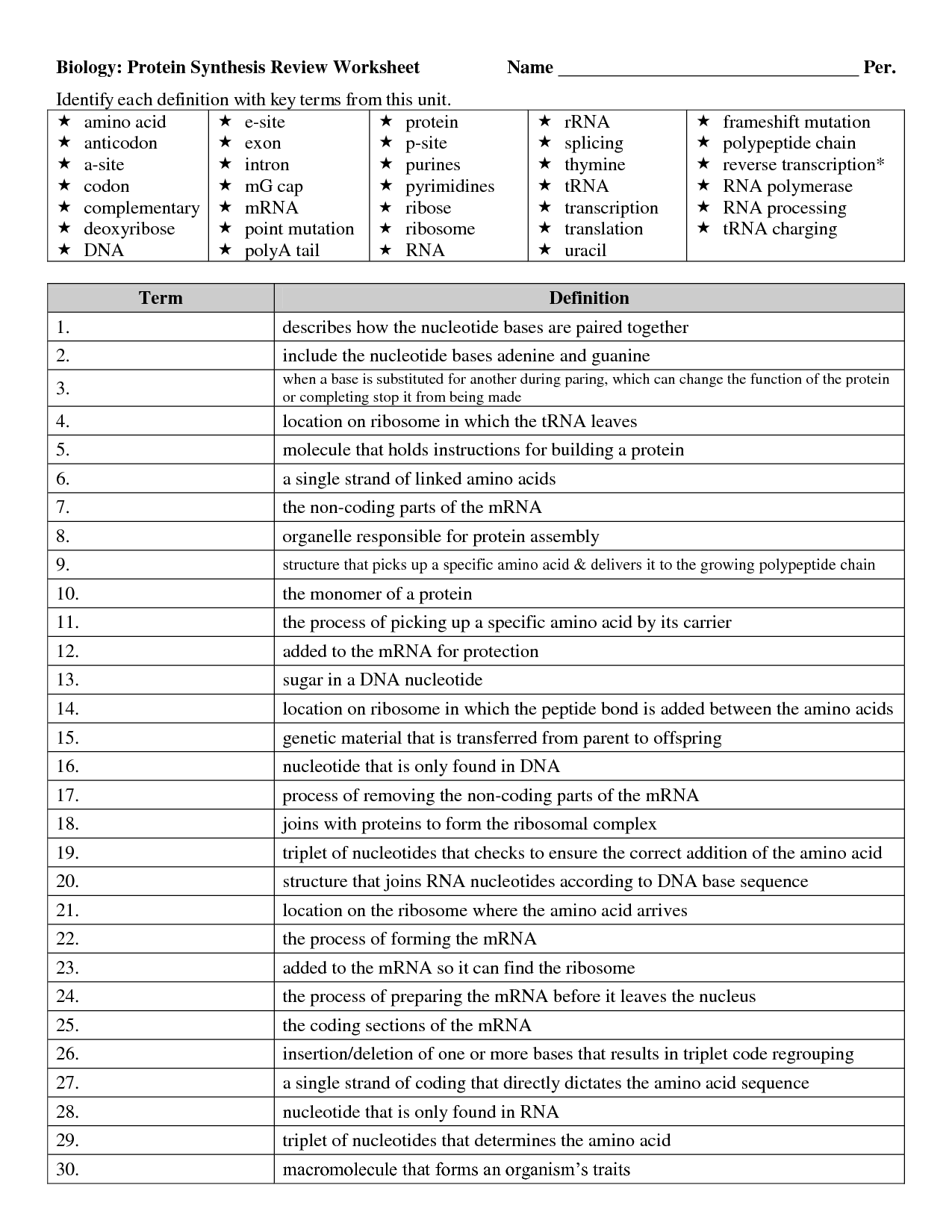
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Transcription Worksheet DNA mRNA Amino Acid
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the full form of mRNA?
The full form of mRNA is messenger ribonucleic acid.
What is the function of mRNA?
mRNA, or messenger RNA, plays a crucial role in the process of protein synthesis. It carries the genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. This information is then used by the ribosomes to assemble amino acids in the correct sequence to form proteins. Thus, mRNA acts as a messenger that helps translate the genetic code into functional proteins within the cell.
Where does transcription occur in a cell?
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of a cell.
What is the primary enzyme involved in transcription?
The primary enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase.
What is the role of promoter regions in transcription?
Promoter regions play a crucial role in transcription by serving as binding sites for RNA polymerase and transcription factors. They help initiate the transcription process by facilitating the binding of RNA polymerase to the specific DNA sequence, marking the starting point for transcription to begin. Additionally, promoter regions determine the level of transcription and regulate gene expression by interacting with various regulatory proteins that either enhance or inhibit transcription. Overall, promoter regions are essential for controlling the transcription of genes and regulating the overall gene expression in cells.
What is the difference between pre-mRNA and mRNA?
Pre-mRNA is the precursor to mRNA and contains introns that need to be removed while mRNA is the mature form that has had the introns removed and only contains exons. Once pre-mRNA undergoes splicing to remove introns, it becomes mRNA which carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
How is mRNA processed before it can be translated?
Before mRNA can be translated, it undergoes several processing steps in eukaryotic cells. This includes capping at the 5' end, addition of a poly-A tail at the 3' end, and removal of introns through a process called splicing. These modifications help stabilize the mRNA molecule, protect it from degradation, and ensure accurate translation by providing a template with a proper start and stop codon.Once these processing steps are complete, the mature mRNA is then ready for translation by ribosomes.
What is the significance of codons in mRNA?
Codons in mRNA are significant because they serve as the genetic code that specifies the amino acids that will be incorporated into a protein during translation. Each codon consists of a sequence of three nucleotides, and each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a signal to start or stop protein synthesis. This process is essential for translating the information stored in DNA into functional proteins necessary for various cellular processes and functions.
How does mRNA determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
mRNA determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein through a process known as translation. During translation, the mRNA molecule serves as a template for the assembly of amino acids into a specific sequence. This is achieved by the interaction of the mRNA with transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which carry specific amino acids and base pair with the mRNA at the ribosome. The ribosome then reads the mRNA codons in groups of three (codons) and matches them with the corresponding anticodons on the tRNA molecules, thereby linking the amino acids together in the correct order dictated by the mRNA sequence. This process continues until a stop codon is encountered, signaling the end of protein synthesis.
What happens to mRNA after translation is complete?
After translation is complete, mRNA can be degraded by cellular enzymes or recycled for further rounds of translation. Additionally, mRNA molecules that encode proteins destined for secretion or insertion into membranes are directed to the endoplasmic reticulum, where they are further processed, folded, and modified before being transported to their final destination within the cell or secreted outside of the cell.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments