Modern Biology Worksheet Answers
If you're a high school student studying biology and in need of additional practice or review material, you may have come across the term "worksheets." Worksheets are learning resources that provide a structured format for practicing and assessing your knowledge on various biology topics. Having access to modern biology worksheet answers can be immensely helpful in understanding and reinforcing key concepts.
Table of Images 👆
- Metric System Conversion Worksheet Answers
- Science Skills Worksheets Answer Keys
- Answer Key Chapter 7 Cell Structure Function
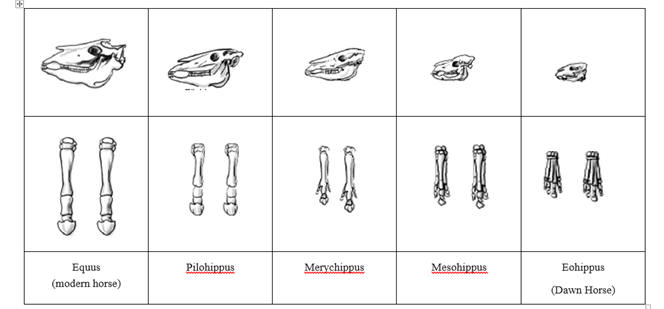
- Evidence of Evolution Worksheet Answers Horse
- Directed Reading Worksheet Answer Key Chapter 4
- Modern Chemistry Answers Chapter 8 Review
- Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Answers
- AP Biology Reading Guide Answers Chapter 14
- Grid References Worksheet
- Compound Microscope Parts Blank
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information within a biological system, stating that DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins. This foundational principle explains the fundamental processes through which genetic information is passed from DNA to RNA to proteins, driving the functioning and diversity of living organisms.
What is the function of DNA in living organisms?
The main function of DNA in living organisms is to store and transfer genetic information. DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, function, and reproduce. It serves as a blueprint for the synthesis of proteins and is crucial for the growth and maintenance of an organism. Through the processes of replication and gene expression, DNA plays a fundamental role in the inheritance and passing on of traits from one generation to the next.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that encloses their genetic material and various organelles that perform specific functions. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
How do cells replicate?
Cells replicate through a process called cell division, which involves several steps. First, the cell goes through a phase of growth and DNA replication in preparation for division. Next, the cell's nucleus divides in a process known as mitosis, where the duplicated DNA is evenly distributed into two daughter cells. Finally, the cell membrane pinches in at the center, separating the two new cells in a process called cytokinesis. This results in two identical daughter cells that carry the same genetic information as the original cell.
What is the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
Enzymes act as biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reactions to occur. They do so by binding to specific substrates and facilitating the conversion of these substrates into products. This enables the reactions to proceed at a much faster rate than they would without enzymes, thereby allowing essential biochemical processes in living organisms to occur efficiently.
What is the purpose of mitosis and meiosis in cell division?
The purpose of mitosis is to generate two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, ensuring growth, repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms. On the other hand, meiosis is specifically for sexual reproduction, producing gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell and promoting genetic diversity by creating genetically unique offspring through the process of fertilization.
How do genes determine the traits of an organism?
Genes determine the traits of an organism by encoding the instructions for specific proteins that play a role in various biological processes. These proteins then influence the development and functioning of different traits in the organism. Through processes like gene expression and interactions with other genes and environmental factors, genes ultimately determine an organism's physical characteristics and behaviors.
What is the process of protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells make proteins from amino acids based on instructions in DNA. It involves two main steps: transcription, where the DNA sequence is transcribed into mRNA, and translation, where mRNA is used as a template to assemble amino acids into a protein at ribosomes. The ribosomes read the mRNA codons and recruit transfer RNA molecules that carry specific amino acids, thereby linking the amino acids together in the correct order to form a functional protein molecule.
What are the different types of cellular respiration?
There are two main types of cellular respiration: aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen and produces more energy in the form of ATP, and anaerobic respiration, which does not require oxygen and produces less ATP. Aerobic respiration involves the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain, while anaerobic respiration can involve processes like fermentation.
How does natural selection contribute to evolution?
Natural selection is a key mechanism of evolution in which organisms that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring. Over time, this process leads to the accumulation of beneficial traits in a population, ultimately resulting in the evolution of new species that are better suited to their environment. Through natural selection, species continually adapt and change in response to their surroundings, driving the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments