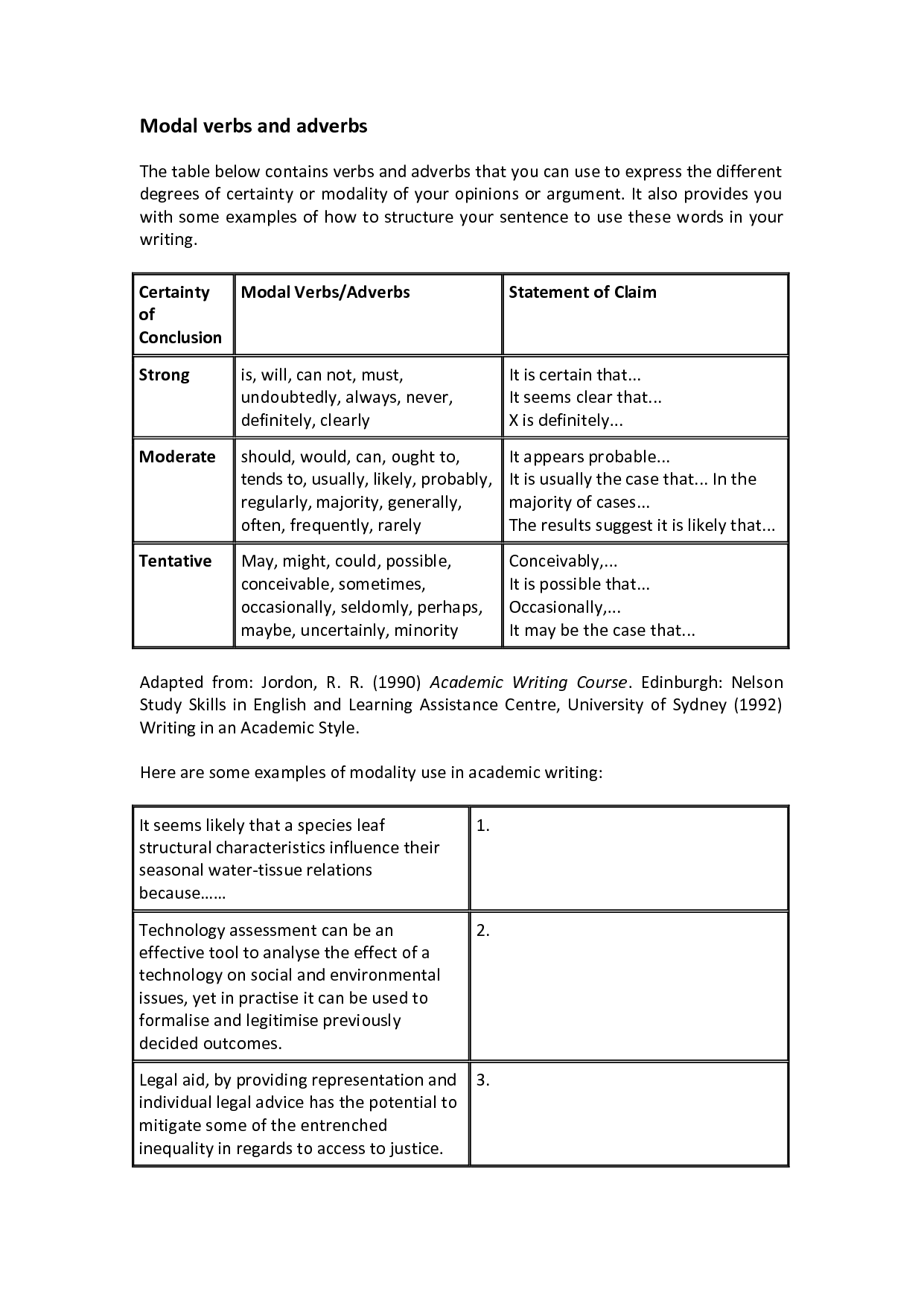
Modal Auxiliary Verbs Worksheets
Modal auxiliary verbs worksheets are a helpful resource for students who are learning English grammar. These worksheets provide exercises that focus on the proper use and formation of modal auxiliary verbs, making them suitable for students at various language proficiency levels. They offer a structured and engaging way for learners to practice using modal auxiliary verbs correctly in different contexts. Whether you are a teacher looking for supplemental materials or a student seeking extra practice, these worksheets are designed to enhance understanding and mastery of modal auxiliary verbs.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a modal auxiliary verb?
A modal auxiliary verb is a type of auxiliary verb that expresses necessity, possibility, permission, or ability in a sentence. Common modal auxiliary verbs include "can," "could," "may," "might," "will," "would," "shall," "should," "must," and "ought to." They usually accompany the base form of a main verb to provide additional meaning or indicate the speaker's attitude towards the action.
What are the main modal auxiliary verbs in English?
The main modal auxiliary verbs in English are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
How are modal auxiliary verbs used in sentences?
Modal auxiliary verbs are used to modify the meaning of other verbs in a sentence and indicate possibility, necessity, ability, or permission. They are typically followed by a base verb without "to." For example, in the sentence "She can swim," "can" is a modal auxiliary verb indicating ability, while "swim" is the base verb. Other common modal auxiliary verbs include "may," "might," "could," "shall," "should," "will," "would," "must," and "ought to.
What is the difference between a modal auxiliary verb and a main verb?
A modal auxiliary verb is used to express possibility, necessity, permission, or ability in a sentence, while a main verb is the primary verb in a sentence that carries the main meaning of the action. Modal auxiliary verbs are always followed by a main verb in a sentence and they help to convey the mood or attitude of the speaker, whereas main verbs are essential for providing the action or state of being in a sentence.
Can modal auxiliary verbs be used in all tenses?
Modal auxiliary verbs can be used in multiple tenses across English grammar such as present, past, future, and perfect tenses. However, modal auxiliary verbs do not have a specific tense of their own and instead rely on the main verb in the sentence to indicate the time frame of the action.
Can modal auxiliary verbs be used to express possibility and probability?
Yes, modal auxiliary verbs can be used to express possibility and probability. For example, modals like "might," "could," and "may" can indicate that something is possible, while modals like "must," "should," and "will" can suggest that something is probable or likely to happen based on the speaker's judgment or evidence.
What are some common examples of sentences using modal auxiliary verbs?
Common examples of sentences using modal auxiliary verbs include "I can swim," "She must study for the test," "He should apologize," "We will go to the party," and "They might be late." Modal auxiliary verbs express possibilities, permissions, obligations, or abilities in a sentence, helping to convey the attitude or tone of the speaker.
Can modal auxiliary verbs be used in negative and interrogative sentences?
Yes, modal auxiliary verbs can be used in negative and interrogative sentences. In negative sentences, the modal verb is typically followed by "not" to indicate the negation (e.g., cannot, should not). In interrogative sentences, the modal verb is often placed before the subject to form a question (e.g., Can you?, Should we?). These verbs help to convey nuances such as possibility, necessity, ability, and more in various sentence structures.
Are there any rules or restrictions when using modal auxiliary verbs?
Yes, there are rules and restrictions when using modal auxiliary verbs in English. Some common rules include using a base form of the main verb after the modal, using "not" to form negative sentences, and using the modal verb before the subject in questions. Additionally, modal verbs cannot be used with other auxiliary verbs, and they do not have past tense forms. It's important to follow these rules to ensure clear and accurate communication when using modal auxiliary verbs in sentences.
Can modal auxiliary verbs be used to express advice or suggestions?
Yes, modal auxiliary verbs can be used to express advice or suggestions. For example, "You should study more for the exam" or "You could try asking for help with that problem."Modal auxiliaries like "should," "could," "might," and "may" are commonly used to offer advice or make suggestions in English.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments