Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet Answers
This blog post provides the answers to the Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet, offering a helpful resource for individuals studying chemistry and seeking additional practice with gas laws. Whether you are a high school student preparing for an exam or a college student reviewing concepts, this worksheet will enhance your understanding of the subject.
Table of Images 👆
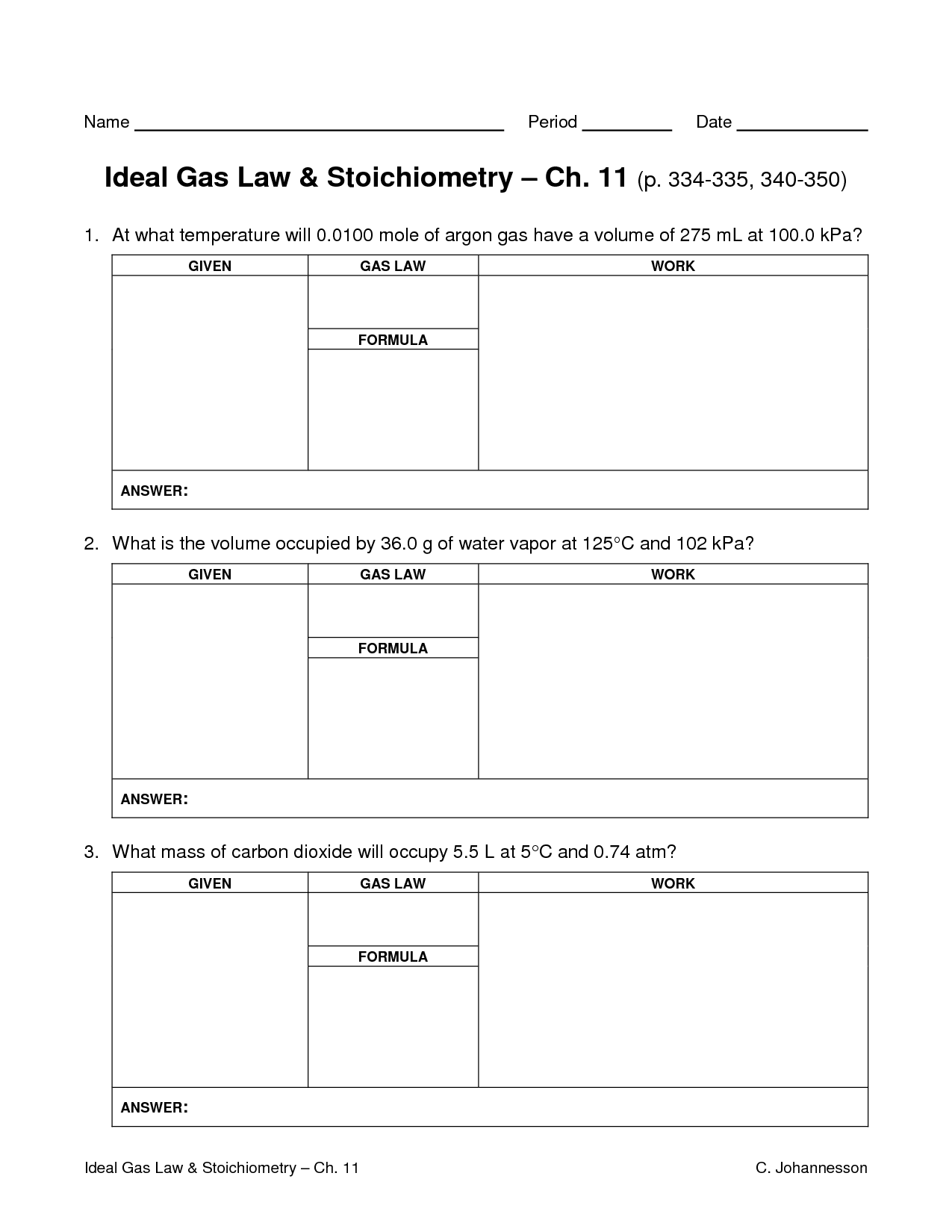
- Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet Answer Key
- Gas Laws Worksheet with Answers
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key
- Gas Laws Worksheet Answer Key
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers
- Gas Law Problems Worksheet with Answers
- Chemistry Gas Laws Worksheet
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet
- Gas Laws Worksheet
- Charles Law and Boyles Law Worksheet
- Combined Gas Law Worksheet
- Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are the mixed gas laws?
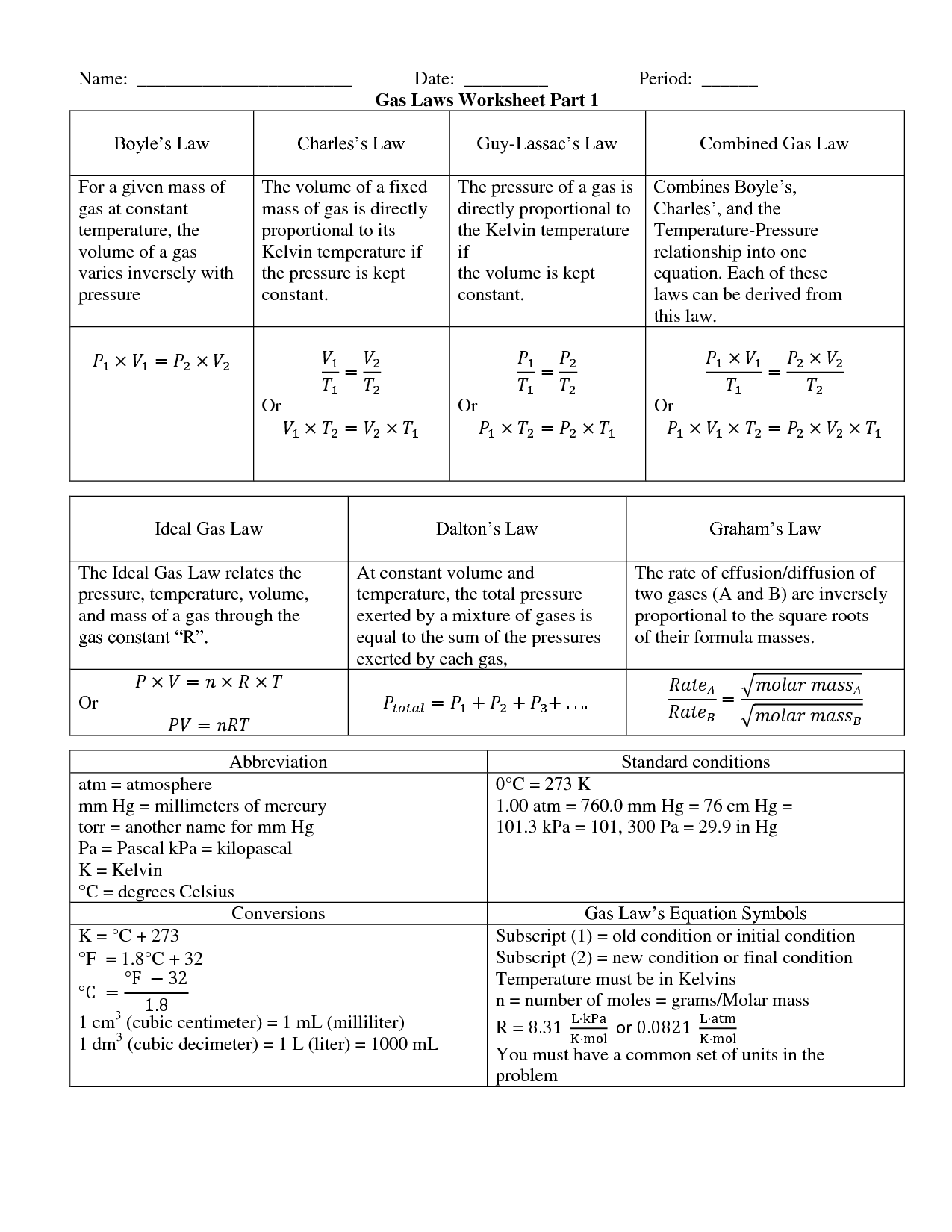
The mixed gas laws refer to the combination of Boyle's law, Charles's law, and Gay-Lussac's law into a single equation that describes the behavior of gases. This combined gas law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when temperature and amount of gas are held constant, directly proportional to its temperature when volume and amount of gas are constant, and directly proportional to the amount of gas when pressure, volume, and temperature are constant.
How are the mixed gas laws derived?
The mixed gas laws are derived from a combination of Dalton's law of partial pressures, which states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures that each gas would exert if it were alone in the same volume, and the ideal gas law, which relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. By combining these principles, we can derive equations that describe how the pressure, volume, and temperature of a mixture of gases are related when the number of moles of each gas is known.
What is the ideal gas law?
The ideal gas law is a fundamental equation in physics that describes the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and the amount of gas present (n). The equation is given as PV = nRT, where R is the gas constant. This law assumes that the gas behaves ideally, meaning that it is at low pressure and high temperature, and that the gas molecules have no volume and no interactions with each other.
How is Dalton's law of partial pressures applied in mixed gas laws?
In mixed gas laws, Dalton's law of partial pressures is applied by stating that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture. This means that in a system with multiple gases, each gas contributes to the total pressure based on its individual concentration and properties. By using Dalton's law, one can calculate the partial pressure of each gas in the mixture and analyze how they affect the overall pressure within the system.
What are the units used to measure pressure in mixed gas laws?
Pressure in mixed gas laws is typically measured in units such as atmospheres (atm), millimeters of mercury (mmHg), torr, or pascals (Pa). These units are commonly used in calculations involving the properties of gases in various gas laws.
How is the combined gas law formula utilized?
The combined gas law formula, which is stated as \( P_1 \cdot V_1 / T_1 = P_2 \cdot V_2 / T_2 \), is used to calculate the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas when one or more of these variables change. By rearranging the formula and plugging in the values for the initial and final states of the gas, you can determine the new pressure, volume, or temperature of the gas after the change has occurred. This formula is particularly useful in gas law problems where all three variables are involved.
Can the mixed gas laws be used to calculate the volume of a gas mixture?
Yes, the mixed gas laws, such as Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures and the ideal gas law, can be used to calculate the volume of a gas mixture. By knowing the individual pressures and volumes of the gases in the mixture, and applying the appropriate equations, it is possible to determine the total volume of the gas mixture.
What is the significance of the temperature in mixed gas laws?
In mixed gas laws, temperature plays a significant role in determining the behavior of gases. As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of gas molecules also increases, causing them to move faster and collide with each other more frequently. This results in an increase in pressure, volume, and density of the gas. Conversely, decreasing the temperature reduces the kinetic energy of gas molecules, leading to decreased pressure, volume, and density. Temperature is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of gas molecules in mixed gas laws, making it a crucial factor in understanding and predicting the behavior of gases under different conditions.
How does changing the amount of gas affect the calculations in mixed gas laws?
When changing the amount of gas in mixed gas laws, such as the ideal gas law or Dalton's law of partial pressures, the calculations are affected by adjusting the number of moles of gas involved. This alteration directly influences the overall pressure, volume, and temperature of the gas mixture, as the amount of gas can impact the total moles, which affects the overall behavior of the system according to the given gas laws.
Can the mixed gas laws be applied to all gases, regardless of their chemical properties?
Yes, the mixed gas laws such as Boyle's law, Charles's law, and Avogadro's law can be applied to all gases, regardless of their chemical properties. These laws describe the relationship between the pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas, and are based on the ideal gas behavior assumption that gas particles are point masses with no volume and no intermolecular forces. As long as the gas behaves like an ideal gas under the given conditions, the mixed gas laws can be applied to analyze and predict its behavior.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments