Mitosis Worksheet Answer Sheet
Are you a biology student struggling to understand the intricate process of mitosis? Look no further! We have the perfect solution for you - a mitosis worksheet answer sheet that will guide you through each step of this fascinating cellular division. Whether you're studying for an upcoming exam or simply reviewing the subject, this worksheet will provide you with the detailed explanations and examples you need to fully grasp the concept of mitosis.
Table of Images 👆
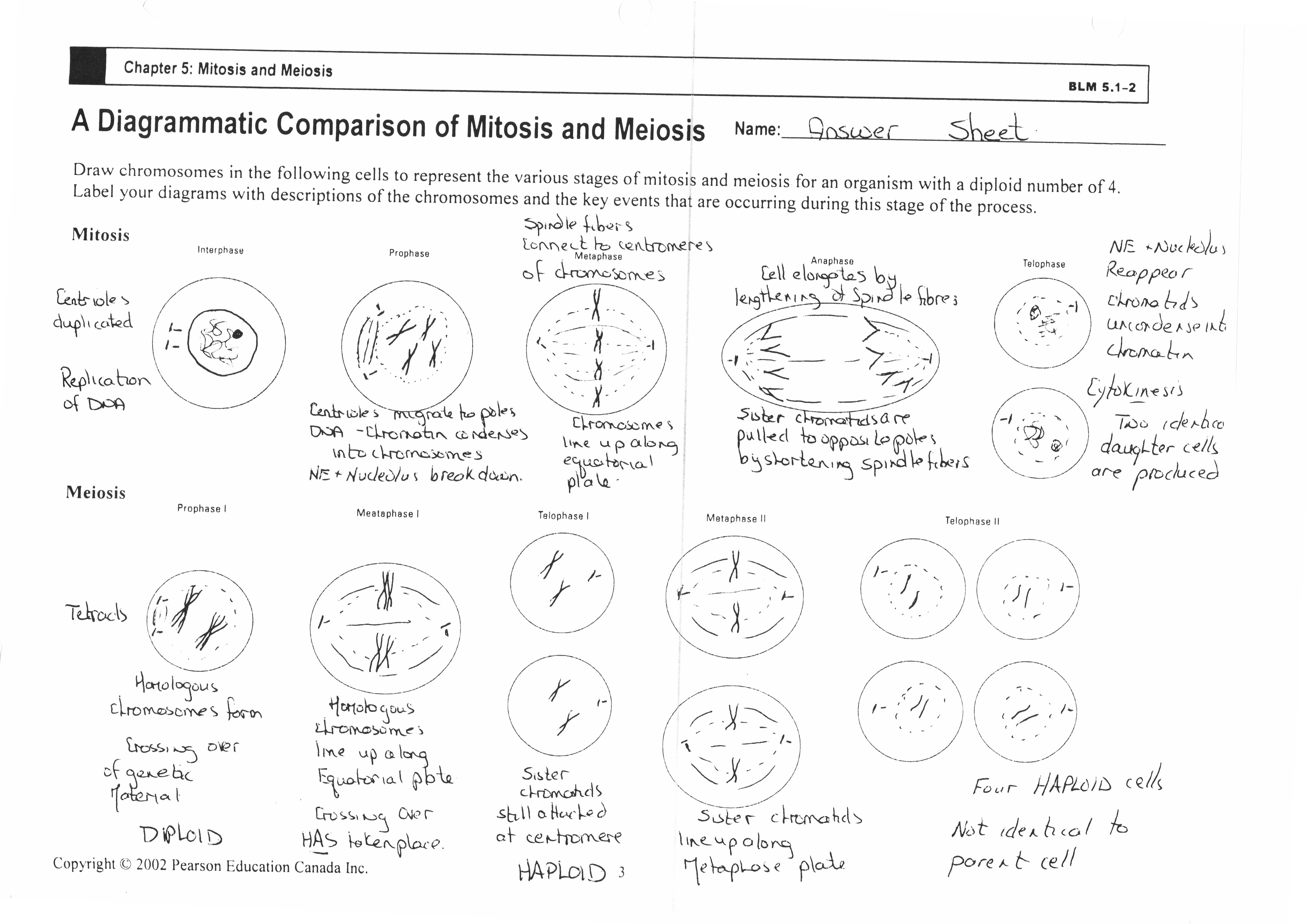
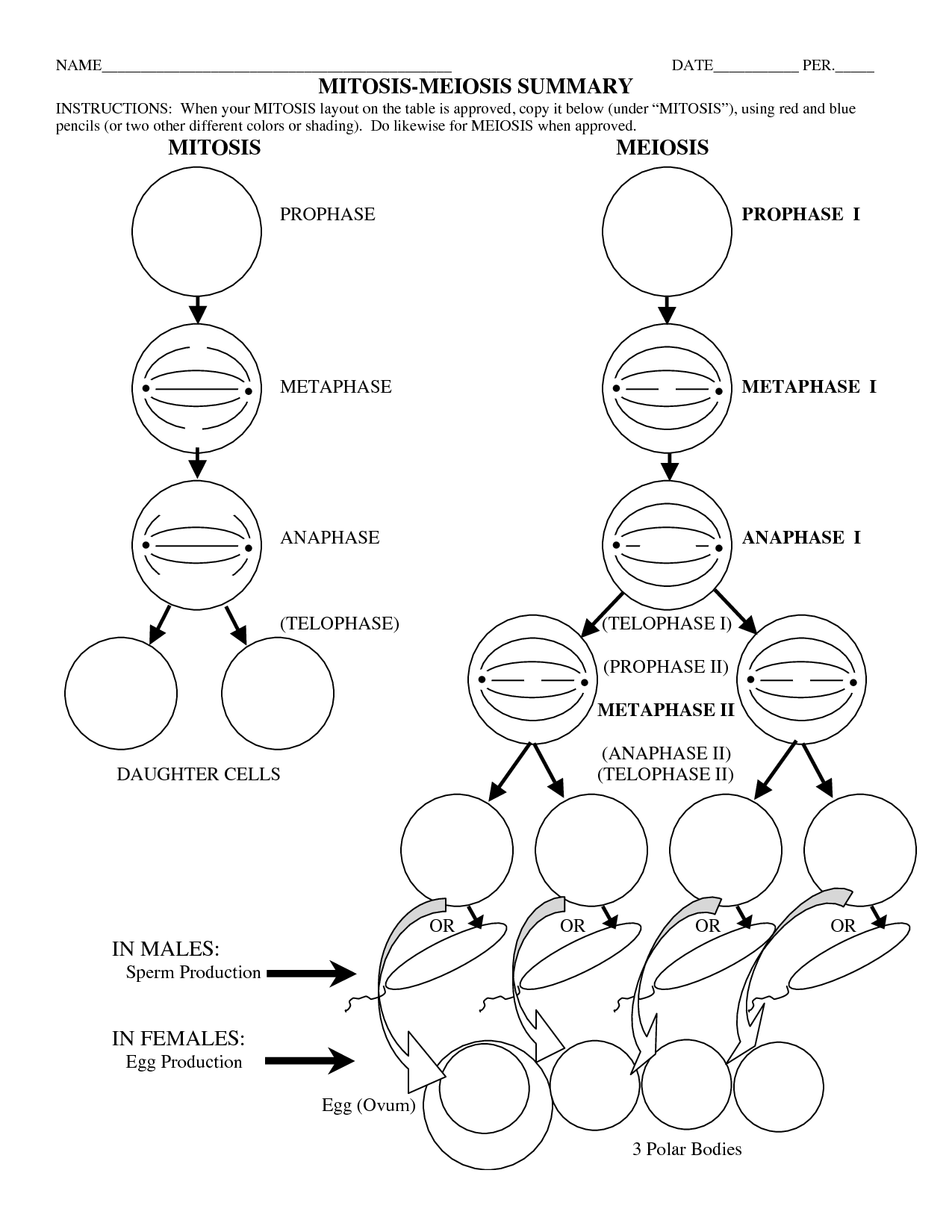
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
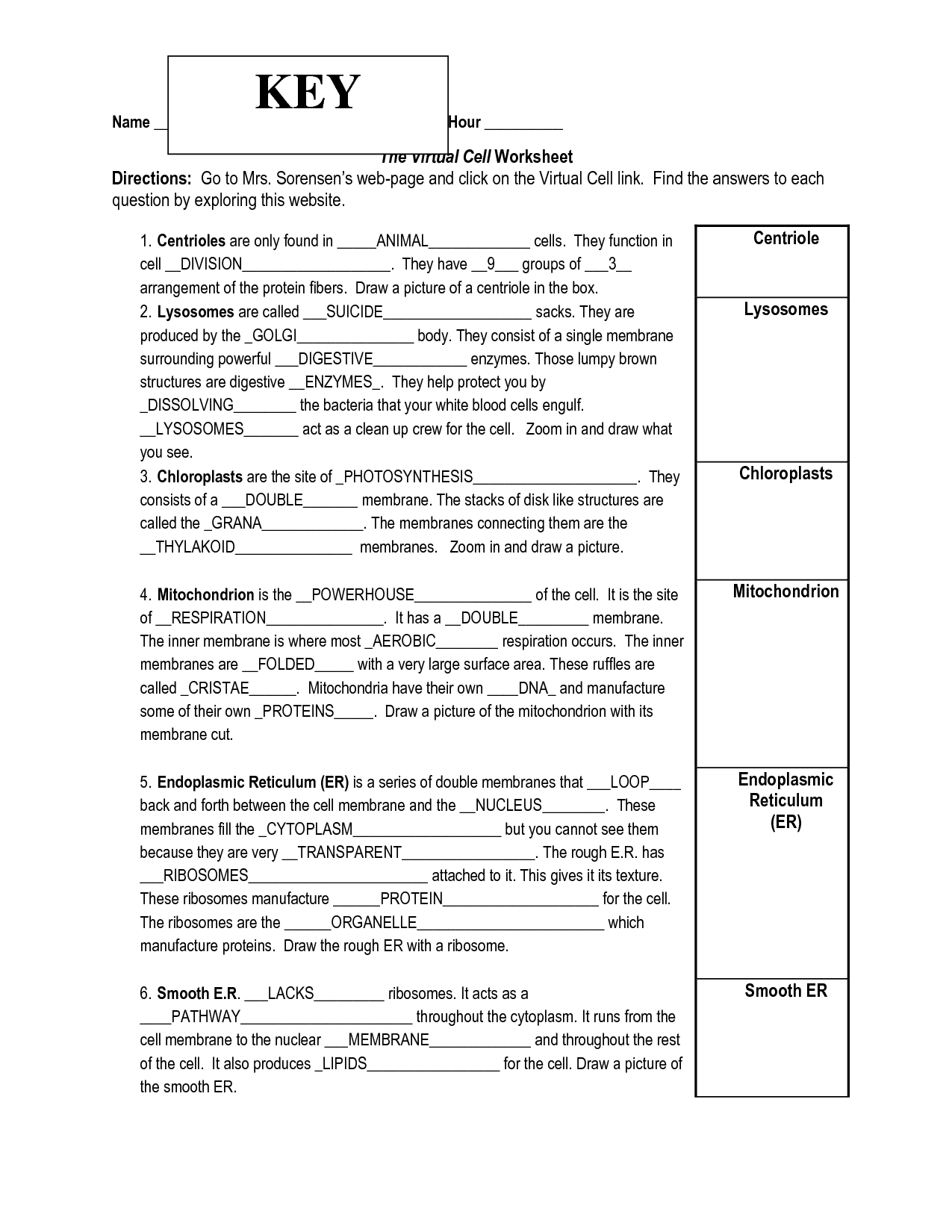
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Coloring Worksheets
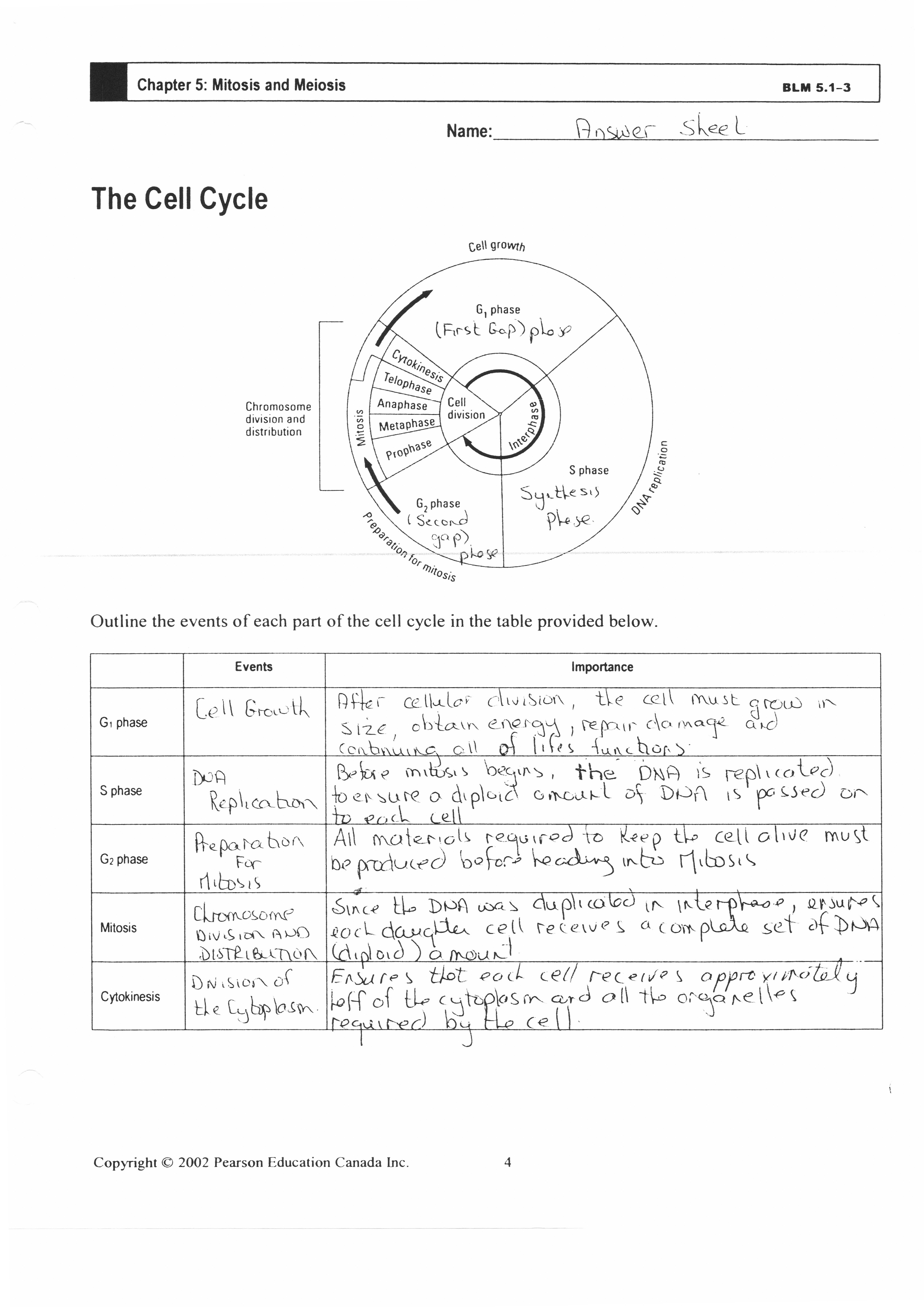
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Review Answer Key
- Science Fair Project Rubric
- DNA Replication Coloring Sheet
- Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle POGIL Biology Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of cell division in which a parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. This is a crucial part of the cell cycle and is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of multicellular organisms. During mitosis, the cell's genetic material is duplicated and then evenly distributed between the two daughter cells to ensure they have the same genetic information as the parent cell.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is to ensure growth, repair, and maintenance of the body's cells. It is a process of cell division in which a cell duplicates its chromosomes and divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis plays a crucial role in the development and regeneration of tissues in multicellular organisms.
What are the stages of mitosis?
The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase is when the chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Metaphase is when the chromosomes align along the cell's equator. Anaphase is when the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles. Telophase is when two new nuclei form around the separated chromatids, and the cell begins to divide.
What happens during prophase?
During prophase, the first stage of mitosis, the chromatin condenses to form visible chromosomes, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form. The chromosomes become visible under a microscope and consist of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. Additionally, the centrioles migrate to opposite poles of the cell, and spindle fibers extend from the centrioles towards the chromosomes. Overall, prophase is characterized by the preparation of the cell for division and the organization of key structures needed for proper chromosome segregation.
What happens during metaphase?
During metaphase, the replicated chromosomes line up along the center of the cell, forming a single line known as the metaphase plate. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell will receive the correct number of chromosomes during cell division. Additionally, spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes, helping to move them into their proper position for separation during anaphase.
What happens during anaphase?
During anaphase, the sister chromatids, which are copies of the same chromosome, are pulled apart by the spindle fibers attached to the centromeres. As the spindle fibers contract, the sister chromatids move towards opposite ends of the cell, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. This is a crucial stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis.
What happens during telophase?
During telophase, the final stage of mitosis, the sister chromatids reach the opposite poles of the cell and begin to decondense into chromatin. The nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes, creating two separate nuclei. Meanwhile, the spindle fibers disassemble, and the nucleolus reappears within each new nucleus. Ultimately, the division of the genetic material is completed, setting the stage for cytokinesis, the final step in the cell division process.
How is cytokinesis different from mitosis?
Cytokinesis is the process of cell division following mitosis, where the cytoplasm of the cell is divided into two daughter cells. Mitosis, on the other hand, is the division of the cell's nucleus into two identical sets of chromosomes. While mitosis involves the separation of genetic material, cytokinesis involves the physical separation of the two daughter cells. Essentially, mitosis is the division of the nucleus, while cytokinesis is the division of the cell itself.
Why is mitosis important for growth and development?
Mitosis is important for growth and development because it is the process by which cells divide to produce new identical cells, enabling an organism to grow in size and repair damaged tissues. During development, mitosis allows for the formation of new tissues, organs, and structures essential for the organism to mature and develop properly. Without mitosis, growth, development, and maintenance of the body's various systems would not be possible.
Are all cells capable of undergoing mitosis?
No, not all cells are capable of undergoing mitosis. Mitosis is a form of cell division that occurs in somatic cells to produce two identical daughter cells with the same genetic information as the parent cell. However, some cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, are terminally differentiated and no longer undergo mitosis. Additionally, cells like red blood cells undergo a different form of cell division known as erythropoiesis.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments