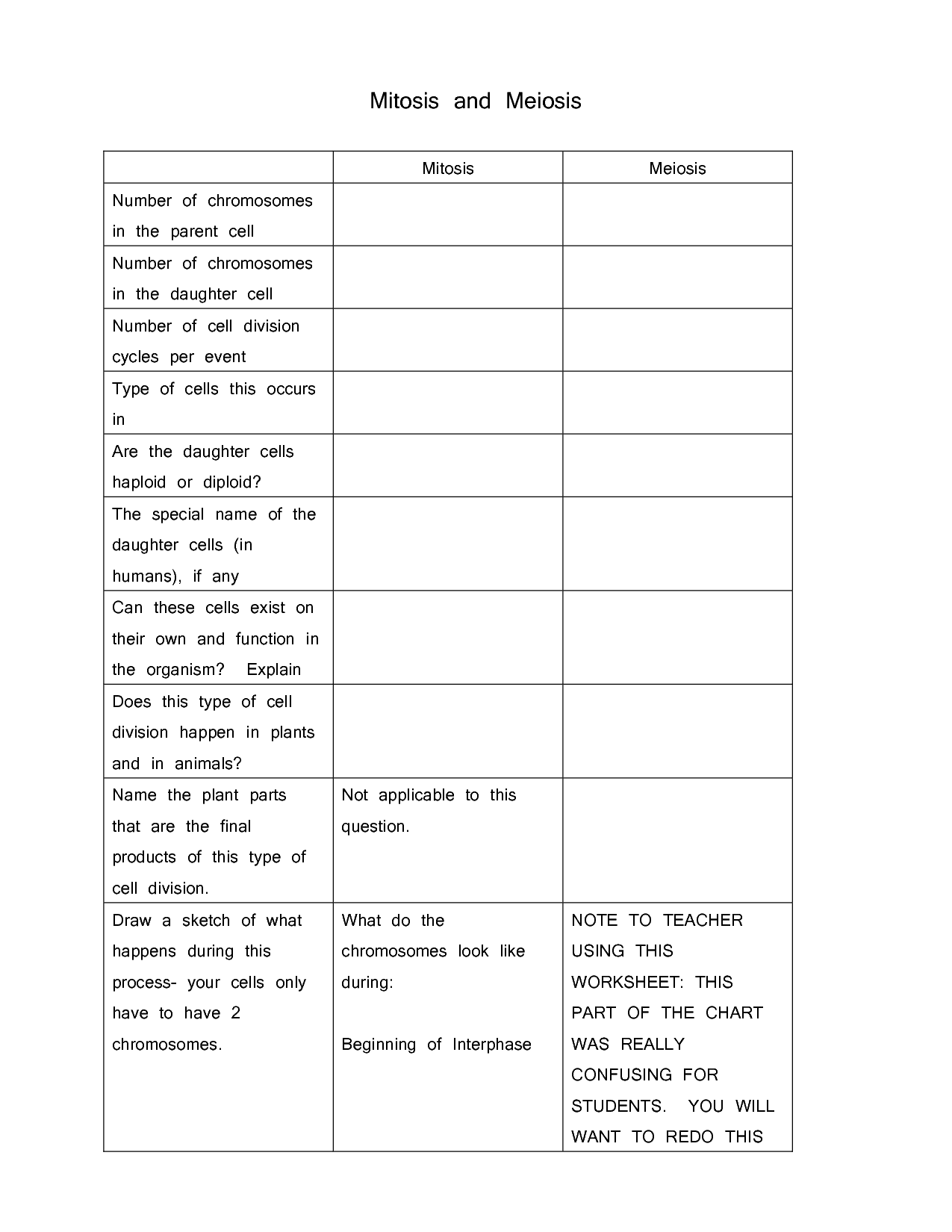
Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet High School
This high school level mitosis and meiosis worksheet is designed to enhance understanding of these key cellular processes. From labeling diagrams to answering critical thinking questions, this educational resource provides students with a comprehensive review of mitosis and meiosis. Whether you are a teacher looking for a supplemental activity or a student seeking to reinforce your understanding, this worksheet offers a valuable tool for mastering these concepts.
Table of Images 👆
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet
- Diagram Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis vs Mitosis Worksheet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Middle School
- Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Vocabulary
- Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is mitosis?
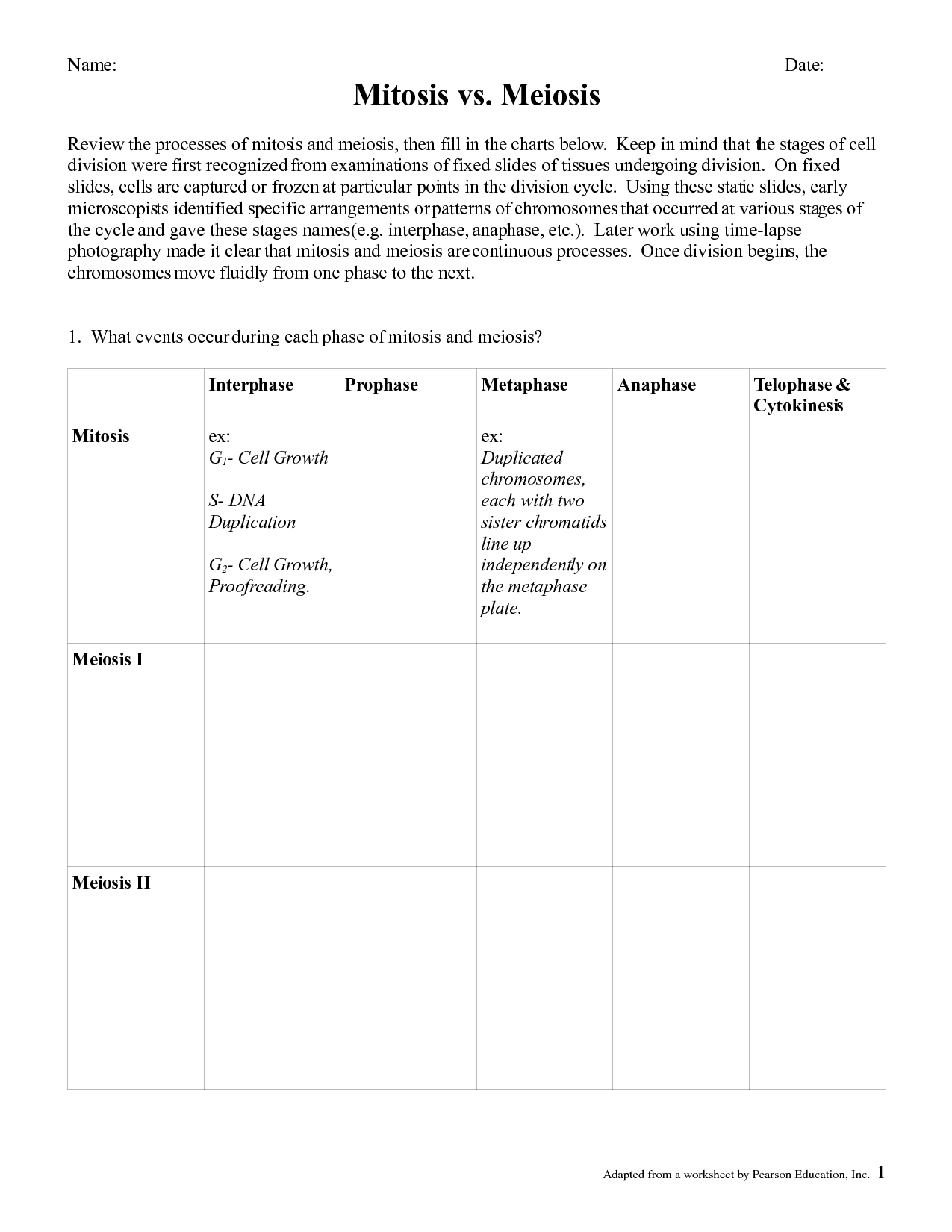
Mitosis is a process in which a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is a key part of the cell cycle and is essential for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms. During mitosis, the cell goes through several phases, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, ultimately resulting in the distribution of genetic material and organelles between the two daughter cells.
What are the main phases of mitosis?
The main phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase involves the condensation of chromatin into visible chromosomes, the dissolution of the nuclear envelope, and the formation of the mitotic spindle. Metaphase is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate in the center of the cell. Anaphase sees the separation of sister chromatids as they are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. Telophase involves the reformation of nuclear envelopes around the separated chromatids, leading to the formation of two daughter nuclei.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is to ensure accurate and equal distribution of genetic material (chromosomes) from a parent cell to two daughter cells during cell division, allowing for growth, development, and repair in multicellular organisms. This process is crucial for maintaining the genetic stability and integrity of cells by producing identical genetic copies during cellular reproduction.
How does mitosis contribute to growth and repair in multicellular organisms?
Mitosis is the process of cell division that allows for growth and repair in multicellular organisms by producing new cells. During growth, mitosis enables an organism to increase in size by creating more cells. Similarly, during repair, mitosis helps in replacing damaged or dying cells with healthy new cells. This continuous cycle of cell division and growth ensures that multicellular organisms can develop, regenerate, and maintain their tissues and organs for optimal function and survival.
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, resulting in the formation of gametes (sperm and egg) with half the normal number of chromosomes. It involves two rounds of division, producing four daughter cells that are genetically unique from each other and the parent cell. It plays a crucial role in genetic variability and ensures the offspring inherit a combination of traits from both parents.
What are the key differences between mitosis and meiosis?
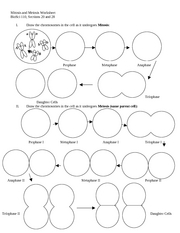
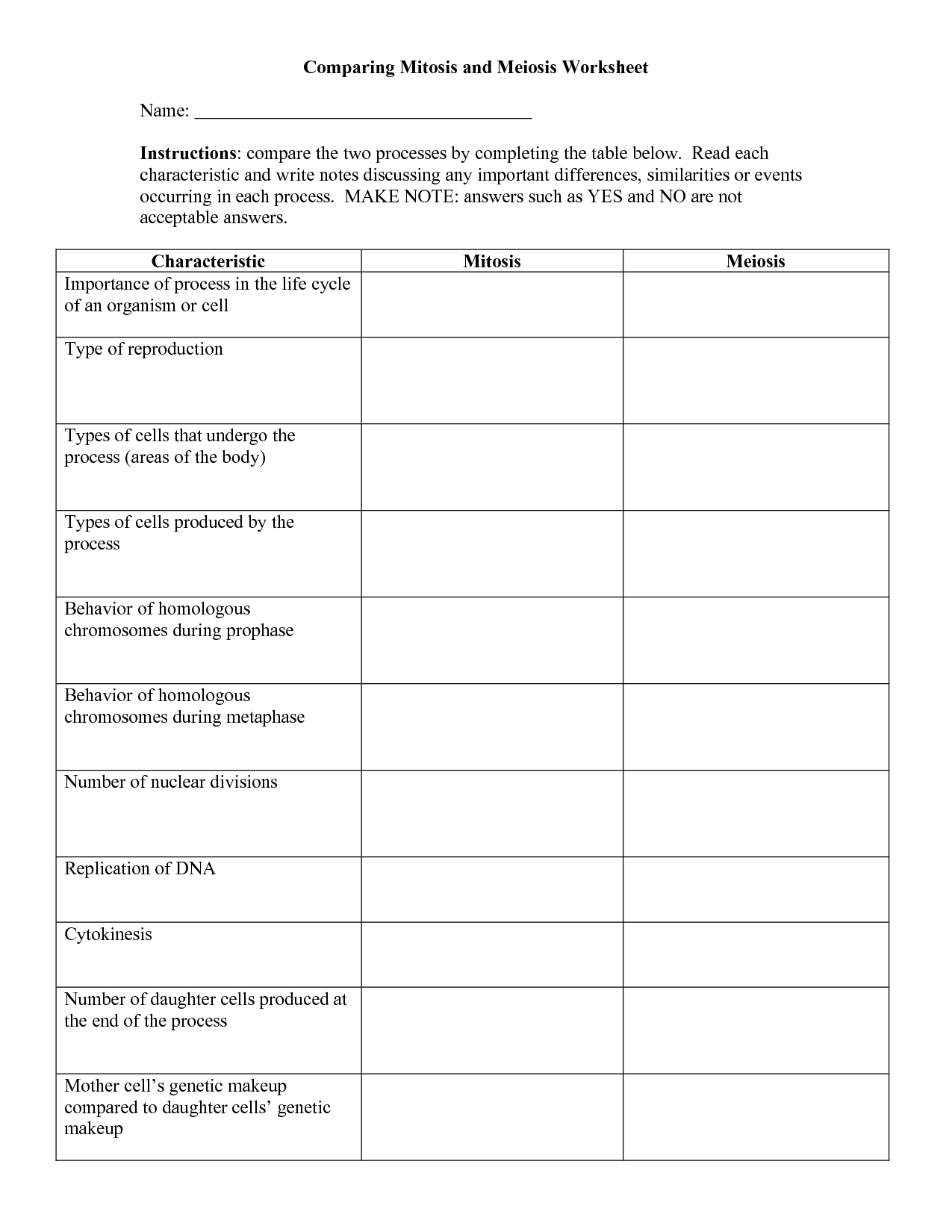
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four non-identical daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Mitosis is involved in growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction, while meiosis is involved in sexual reproduction to create genetic diversity. Additionally, mitosis involves one round of cell division, while meiosis involves two rounds of cell division.
What is the significance of sexual reproduction and meiosis?
Sexual reproduction and meiosis are significant because they promote genetic diversity in a population. During meiosis, genetic material is shuffled and recombined, leading to the creation of unique offspring with a combination of traits from both parents. This genetic variation is important for the adaptability and evolution of a species, as it allows for the selection and propagation of advantageous traits in changing environments. Additionally, sexual reproduction ensures the maintenance of a stable genome by repairing damaged DNA and reducing the accumulation of mutations over generations.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
Meiosis contributes to genetic diversity in sexual reproduction by creating new combinations of alleles through the processes of crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization. During crossing over, segments of homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, resulting in new genetic combinations. Independent assortment shuffles the assortment of different chromosomes, leading to varied combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes in gametes. Finally, random fertilization combines the genetic material from two different individuals, further increasing genetic diversity among offspring.
What are the main phases of meiosis?
The main phases of meiosis are similar to those of mitosis, but with distinct differences. In meiosis, after interphase, there are two rounds of cell division known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I consists of prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I, while meiosis II involves prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. These phases lead to the production of four genetically unique daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.
How does meiosis result in the formation of gametes?
Meiosis results in the formation of gametes through two rounds of cell division that produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over, leading to genetic diversity. Then, during meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome are separated, resulting in four haploid cells that become gametes (sperm or egg cells) with unique combinations of genetic information.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments