Mitosis and Meiosis Coloring Worksheets
Are you looking for engaging and educational worksheets to help your students understand the processes of mitosis and meiosis? Look no further! Our mitosis and meiosis coloring worksheets are designed to captivate the attention of middle and high school students, making these complex concepts easier to comprehend.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
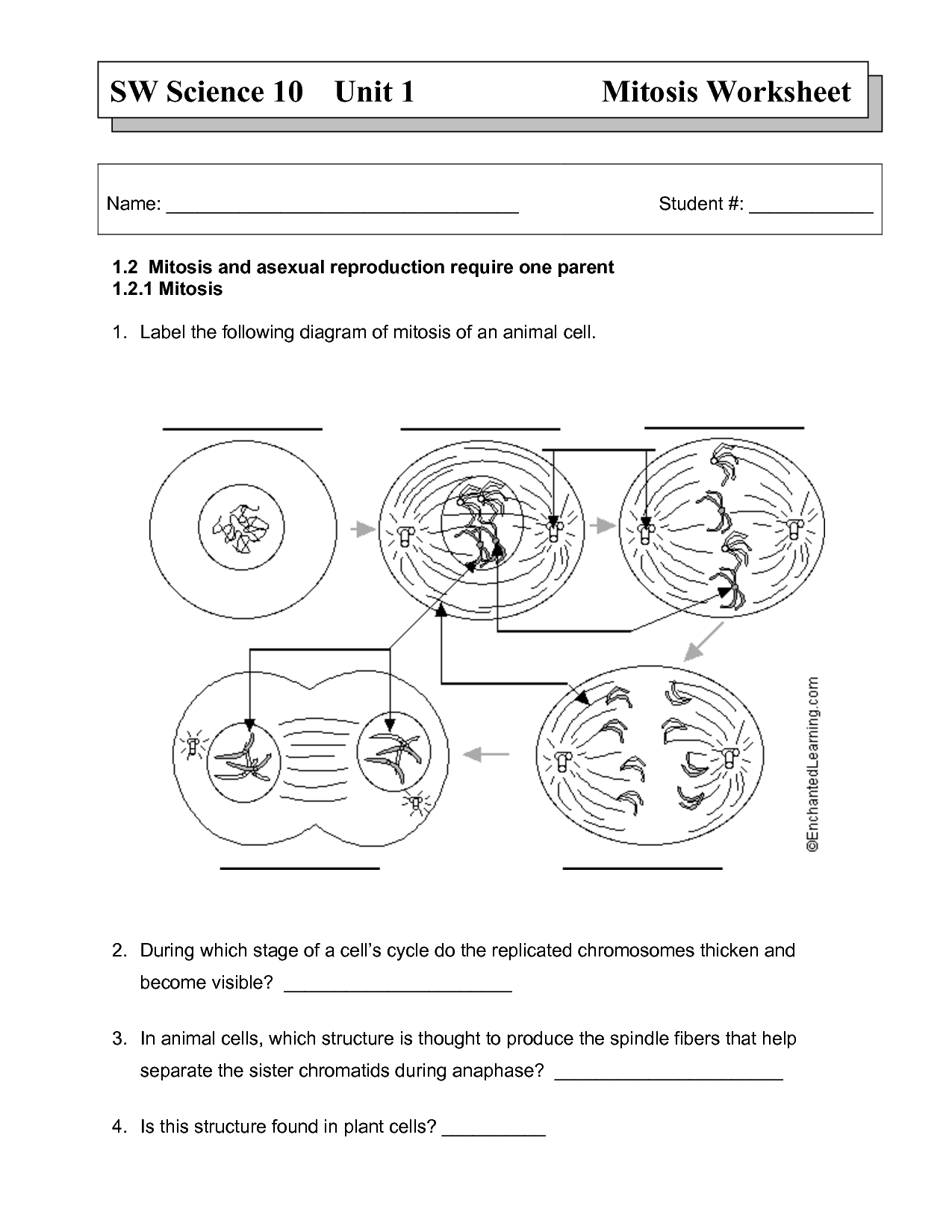
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is to enable cell division, leading to the growth, development, and repair of an organism. Mitosis ensures the equal distribution of genetic material (DNA) to two daughter cells, maintaining genetic continuity and functionality in the new cells. This process allows multicellular organisms to replace old or damaged cells, promote tissue growth, and support overall organismal development and maintenance.
How many cells are produced at the end of mitosis?
At the end of mitosis, two cells are produced, each with an identical set of chromosomes to the original cell.
Which phase of mitosis involves the separation of sister chromatids?
The phase of mitosis that involves the separation of sister chromatids is called anaphase. During anaphase, the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers towards opposite poles of the cell, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
What is the significance of cytokinesis in mitosis?
Cytokinesis is crucial in mitosis as it is the final stage where the cell physically divides into two daughter cells. During this process, the cytoplasm and organelles are divided equally between the new cells, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material necessary for carrying out cellular functions and maintaining normal physiological processes. Additionally, cytokinesis is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms, as it enables the distribution of genetic material to generate new cells for growth and repair.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
The main difference between mitosis and meiosis is that mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell, while meiosis is a type of cell division that produces four daughter cells that are genetically different from the parent cell and from each other. Additionally, mitosis is involved in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, while meiosis is specifically involved in sexual reproduction and produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
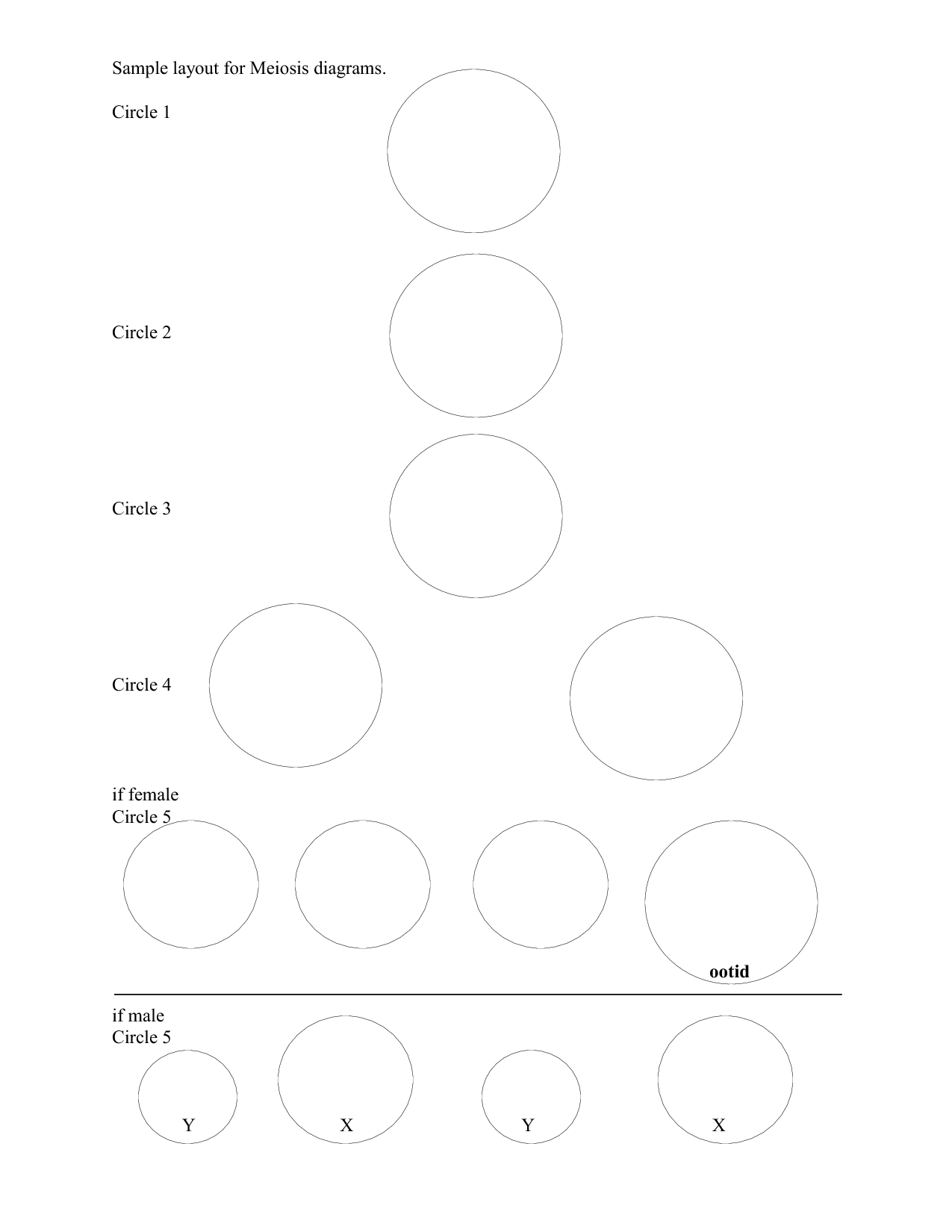
How many rounds of cell division occur during meiosis?
There are two rounds of cell division that occur during meiosis.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, allowing for sexual reproduction and genetic variation. This process creates genetic diversity by shuffling and recombining genetic material from the two parent organisms.
Which phase of meiosis involves crossing over?
Crossing over occurs during prophase I of meiosis. It is a process in which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, leading to genetic diversity among offspring.
What are the resulting cells at the end of meiosis?
At the end of meiosis, the resulting cells are four haploid daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. These daughter cells are genetically diverse due to crossing over and random assortment of chromosomes during meiosis I and meiosis II.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
Meiosis contributes to genetic diversity through several key mechanisms. It involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in the formation of haploid gametes with unique combinations of genetic material. Additionally, crossing over during prophase I allows for the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, further increasing genetic variation. Lastly, the random assortment of chromosomes during metaphase I creates different combinations of chromosomes in each gamete, resulting in a diverse range of genetic possibilities in offspring.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments