Mitosis Activity Worksheet
Are you a biology teacher searching for a practical and engaging way to teach your students about the intricate process of mitosis? Look no further! Our mitosis activity worksheet is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the stages and significance of cell division, making it an ideal resource for high school or college students studying biology.
Table of Images 👆
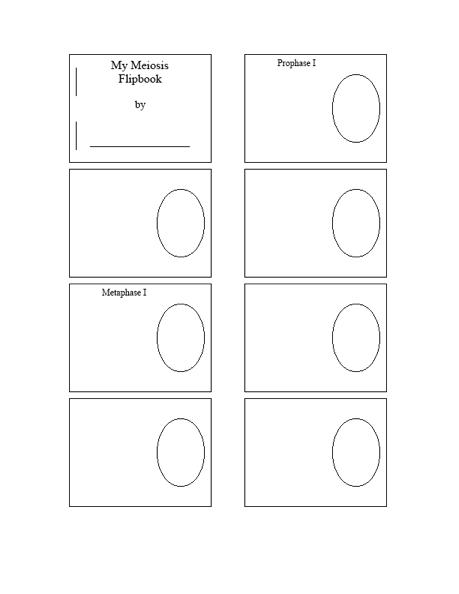
- Meiosis Flip Book Template
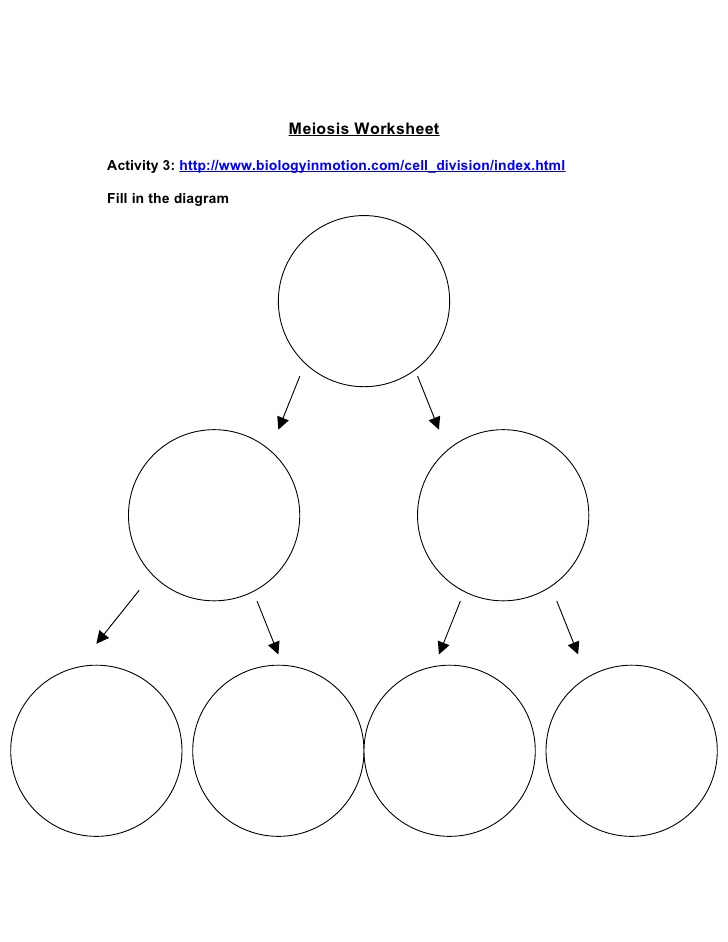
- Meiosis and Mitosis Diagram Blank
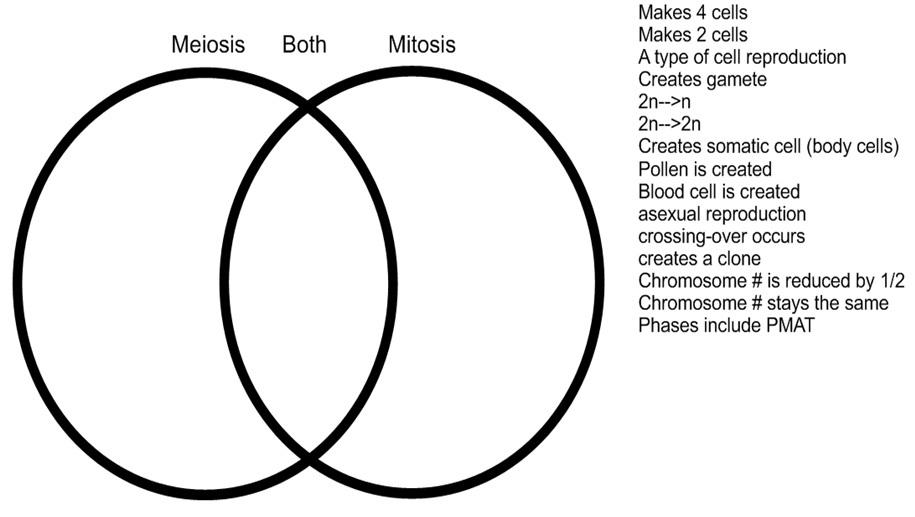
- Mitosis and Meiosis Venn Diagram
- Meiosis Lab Activity
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Axial Skeleton Review Sheet Answer
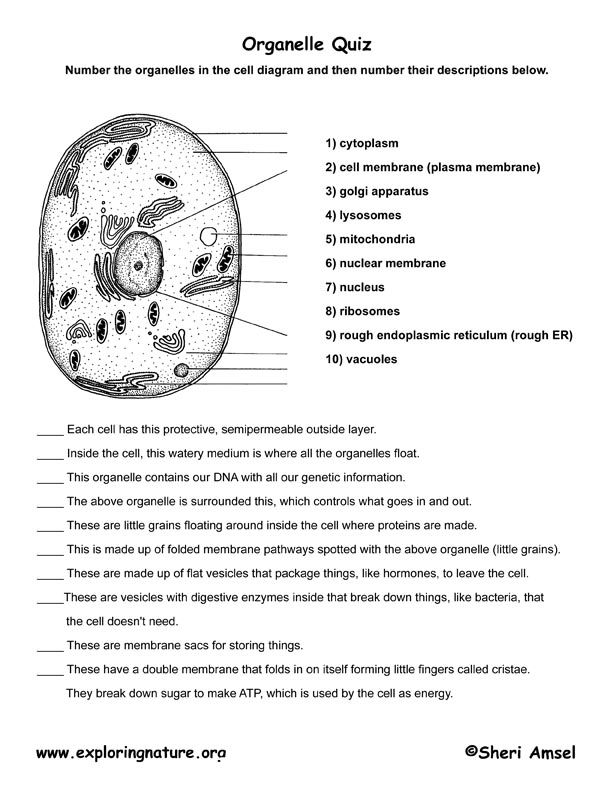
- Cell Organelle Quiz
- DNA Structure Coloring Worksheet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Worksheets Answer Key
- Cool Flower Coloring Pages
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of cell division in which a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. It is a crucial part of the cell cycle and is responsible for growth, development, and repair of multicellular organisms. During mitosis, the replicated chromosomes are separated and distributed equally into the two daughter cells to ensure genetic stability and proper functioning of tissues and organs.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is to enable the the growth, development, and maintenance of multicellular organisms by allowing cells to divide and create identical copies of themselves for tissue repair, growth, and asexual reproduction.
What are the main stages of mitosis?
The main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle fibers form. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate in the center of the cell. Anaphase is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids, which are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. Finally, in telophase, the chromosomes de-condense, the nuclear envelope re-forms around the separated chromosomes, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis to divide into two daughter cells.
Describe the prophase stage of mitosis.
The prophase stage of mitosis is the first stage where chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle fibers begin to form. The chromosomes become visible as pairs of sister chromatids held together by a centromere. This stage prepares the cell for division by ensuring that the genetic material is properly organized and ready to be separated into two daughter cells during later stages of mitosis.
Explain the metaphase stage of mitosis.
During the metaphase stage of mitosis, the duplicated chromosomes align along the center of the cell in a single plane known as the metaphase plate. The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each chromosome, positioning them in preparation for the subsequent separation of sister chromatids during anaphase. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes once division is complete, maintaining the genetic integrity of the new cells.
How does the anaphase stage of mitosis differ from the previous stages?
During the anaphase stage of mitosis, the sister chromatids are pulled apart by spindle fibers towards opposite ends of the cell. This differs from the previous stages because in metaphase, the sister chromatids are aligned along the equator of the cell but have not yet separated, and in prophase and prometaphase, the chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Anaphase marks the moment of chromosome separation, which is a critical step in ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes during cell division.
Describe the telophase stage of mitosis.
During telophase, the final stage of mitosis, the separated sister chromatids reach opposite poles of the cell, and nuclear envelopes reform around each set of chromosomes. The chromosomes begin to decondense back into chromatin, and the mitotic spindle apparatus disassembles. Additionally, cytokinesis also occurs during telophase, resulting in the physical splitting of the cell into two distinct daughter cells, each with a complete set of chromosomes.
What is cytokinesis, and when does it occur?
Cytokinesis is the process in cell division where the cytoplasm of a parent cell is divided to produce two daughter cells. It occurs after the nuclear division phases of mitosis (in eukaryotic cells) or after the separation of chromosomes in prokaryotic cell division.
How does mitosis differ from meiosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four non-identical daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Mitosis is involved in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, while meiosis is involved in sexual reproduction to produce gametes with genetic variation.
Why is mitosis essential for growth and repair in multicellular organisms?
Mitosis is essential for growth and repair in multicellular organisms because it is the process by which cells divide and replicate, allowing for the production of new cells that can replace damaged or dead cells. This enables the organism to grow in size and repair tissues that have been injured or worn out. Mitosis ensures that the organism can maintain its structure and function by continuously producing new cells to meet the organism's needs for growth and repair.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments