Middle School Physical Science Worksheets
Are you in search of engaging and informative worksheets to supplement your middle school physical science lessons? Look no further! Our collection of carefully crafted worksheets is specifically designed to help students grasp the essential concepts of physical science. From atoms and molecules to energy and forces, each worksheet focuses on a specific subject, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Table of Images 👆
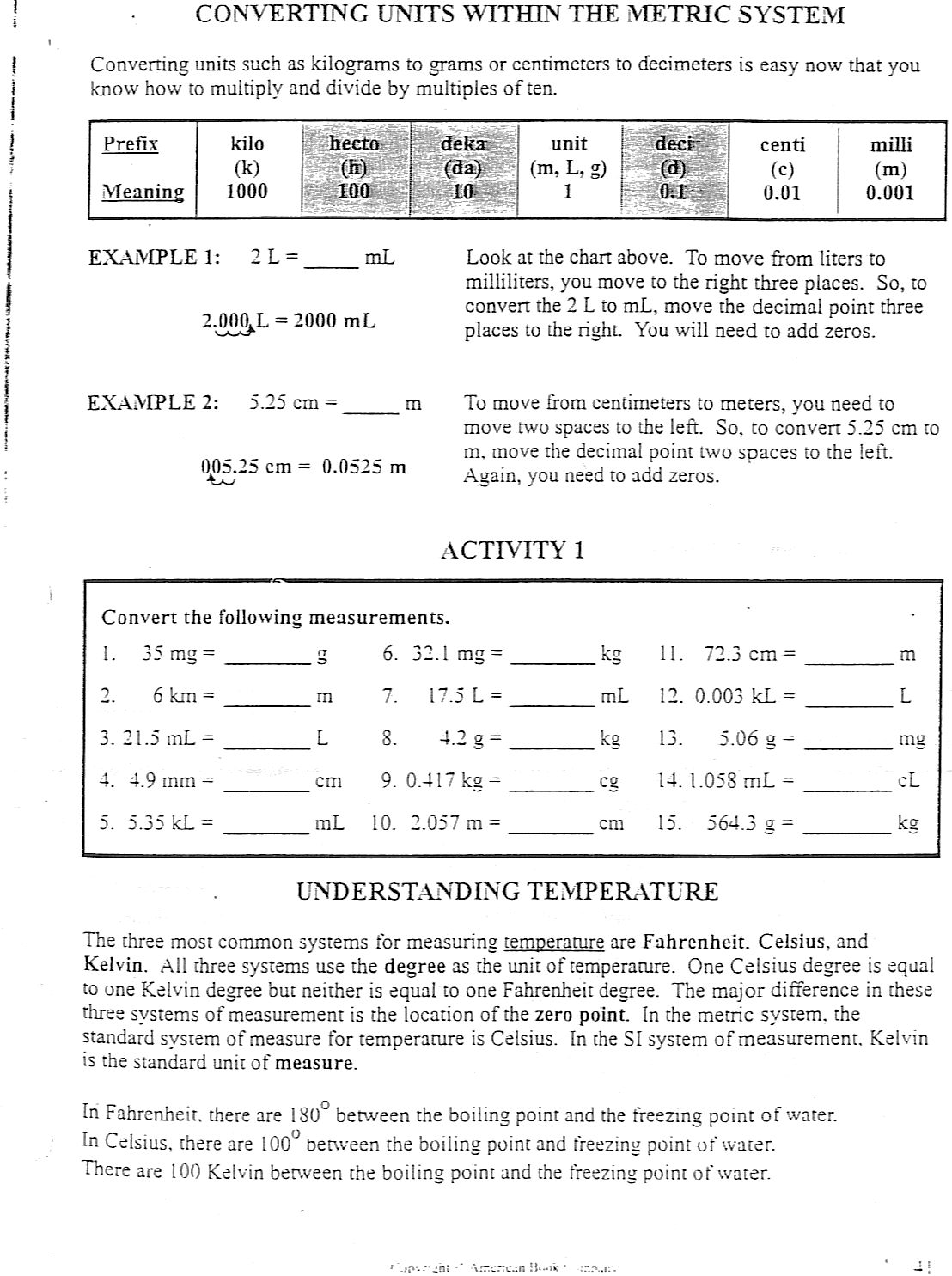
- Converting Metric Units Worksheet
- Body Systems Worksheets Middle School
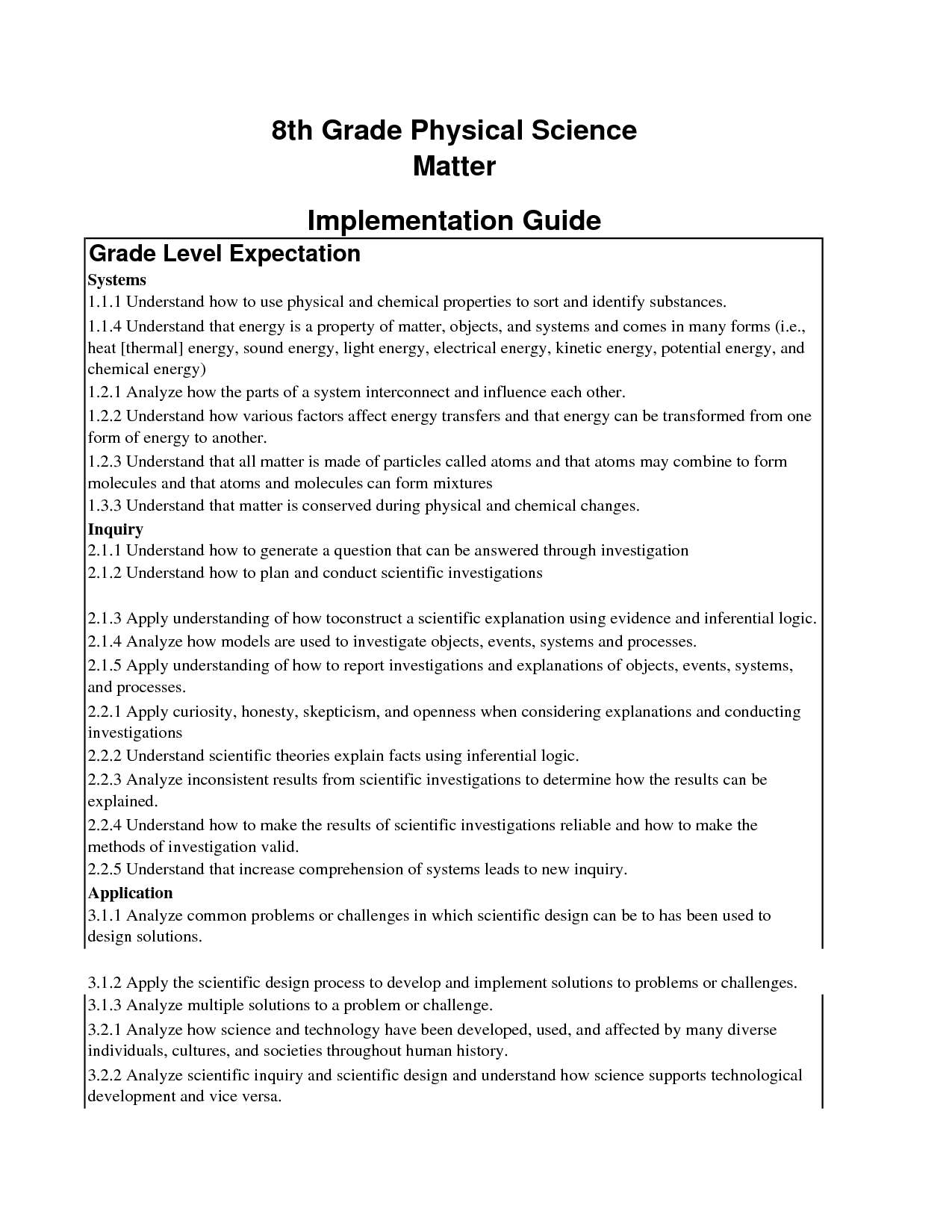
- 8th Grade Physical Science Worksheet Answers
- Middle School Science Worksheets
- Middle School Science Lab Safety Worksheet
- Physical Science Worksheets and Answers
- Middle School Science Word Search
- Forensic Science Worksheet Answers
- Earth Science Worksheets High School
- Free Printable Science Worksheets High School
- Weathering and Erosion Worksheets 3rd Grade
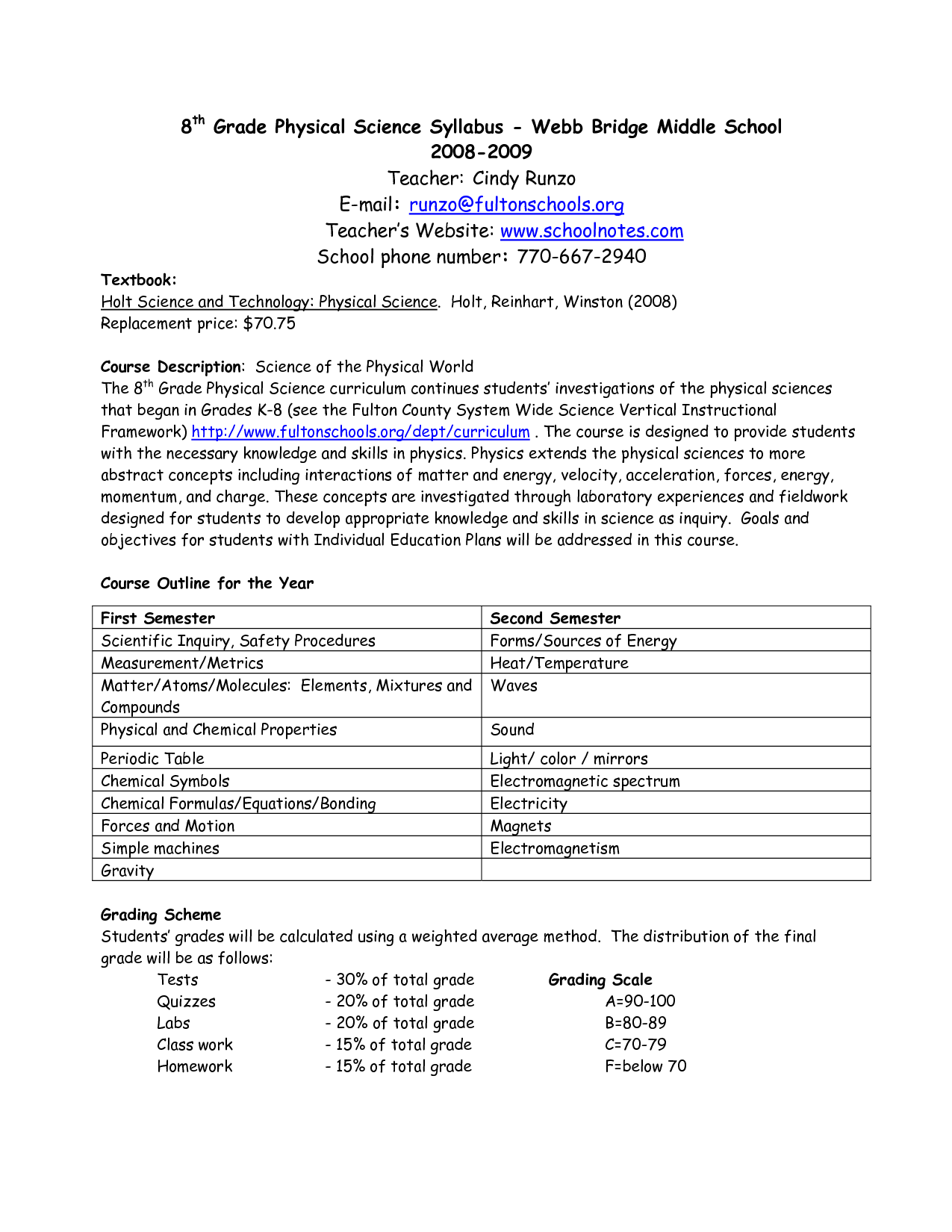
- Physical Science Syllabus Middle School
- Printable Science Worksheets Middle School
- Periodic Table Worksheets Middle School
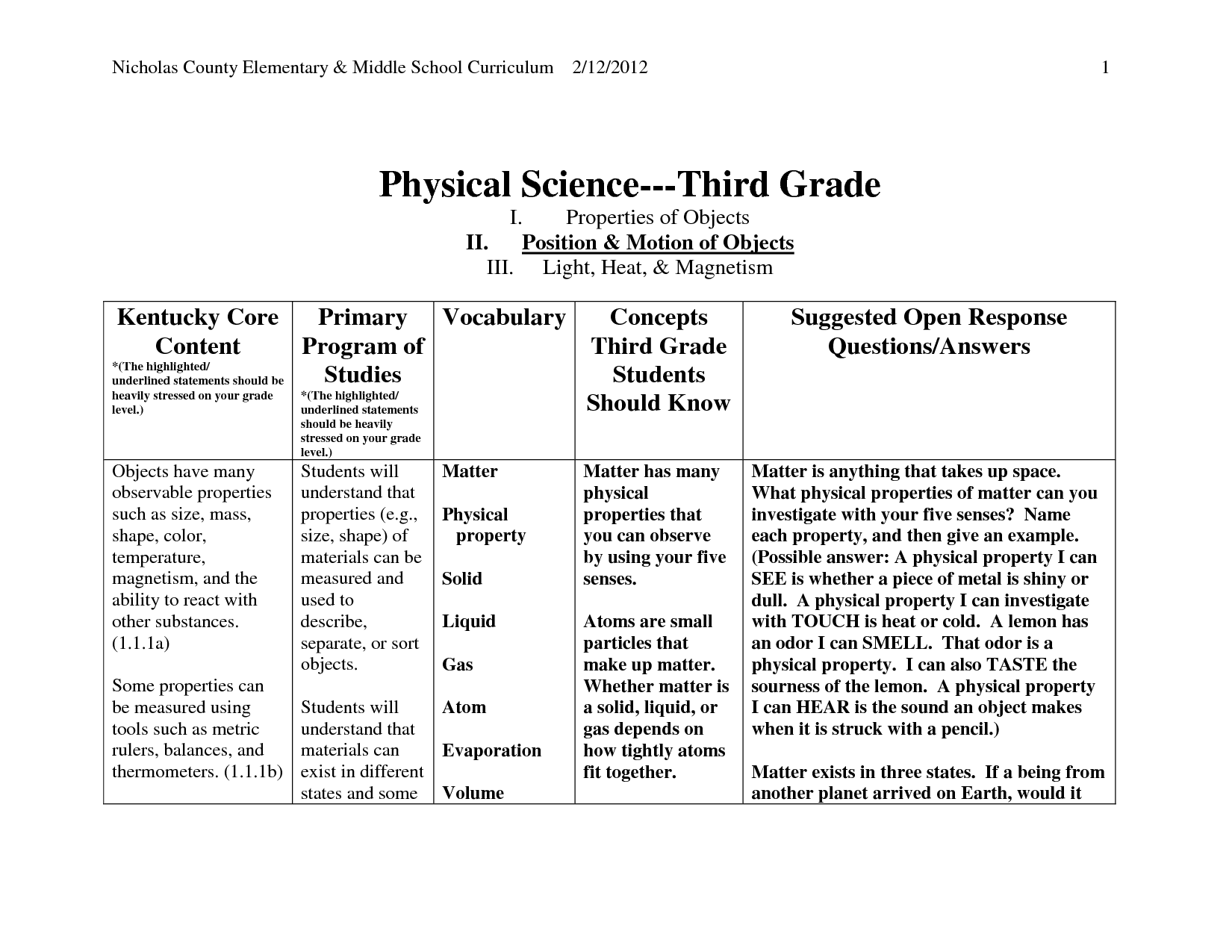
- Physical Science Worksheets 3rd Grade
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
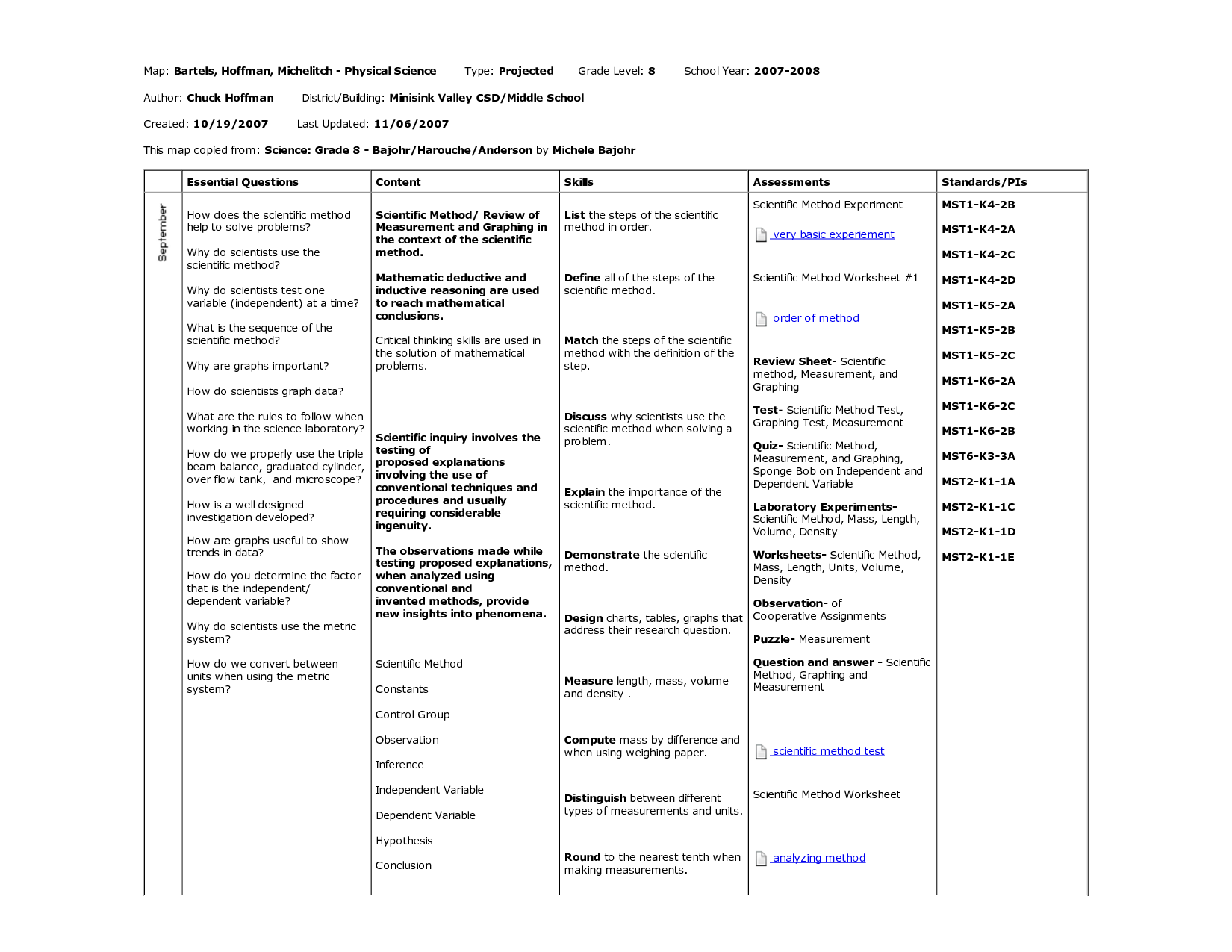
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the relationship between force and motion?
The relationship between force and motion is described by Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. In simpler terms, a force is required to make an object move, and the amount of force applied determines the object's acceleration or deceleration. This means that an object will remain in its current state of motion unless a force is applied to change it.
How does temperature affect the behavior of gases?
Temperature affects the behavior of gases by altering their kinetic energy. As temperature increases, gas particles move faster and collide more frequently, therefore increasing the pressure of the gas. Additionally, temperature affects the volume of gases by expanding or contracting them. This relationship is described by the ideal gas law, which shows that at constant pressure, the volume of a gas increases as temperature increases. Ultimately, temperature plays a significant role in determining the physical properties of gases.
What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is the stored energy possessed by an object due to its position or state, such as gravitational potential energy or chemical potential energy. On the other hand, kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object in motion. It is the energy that an object has due to its movement and is dependent on its mass and velocity. In simple terms, potential energy is energy at rest, while kinetic energy is energy in motion.
Describe the process of photosynthesis in plants.
Photosynthesis is a complex biochemical process in which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. It involves a series of interconnected reactions in chloroplasts, where chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and uses it to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen ions. The hydrogen ions and carbon dioxide from the air are then used to synthesize glucose, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. This process not only provides energy for the plant but also plays a vital role in producing oxygen and reducing carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, making it essential for life on Earth.
How does the structure of an atom determine its chemical properties?
The structure of an atom, including the arrangement of electrons in its orbitals, determines its chemical properties. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element and its identity, while the number of electrons and their distribution control how the atom interacts with other atoms. For example, the number of valence electrons influences an atom's tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons with other atoms to achieve a stable configuration, thus determining its reactivity and chemical behavior. Additionally, the arrangement of electrons in orbitals affects an atom's size, electronegativity, and ability to form chemical bonds.
Explain the concept of buoyancy and how it relates to objects floating or sinking in water.
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. This force is equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces. When an object is less dense than the fluid it is placed in, it will float because the buoyant force is greater than its weight, causing it to rise to the surface. Conversely, if an object is denser than the fluid, it will sink as the weight of the object exceeds the buoyant force. Therefore, buoyancy is what determines whether objects float or sink in water based on their density relative to the density of the water.
What causes the different colors we see in visible light?
The different colors we see in visible light are caused by the varying wavelengths of light waves. Each color corresponds to a different wavelength, with red having the longest wavelength and violet having the shortest. When white light passes through a prism or is dispersed through another medium, it separates into the different colors of the visible spectrum due to the bending of light waves of different wavelengths at different angles.
Describe the concept of electrical conductivity and what types of materials conduct electricity.
Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to allow the flow of electric current. Materials that conduct electricity typically have outer electrons that are loosely bound, allowing them to move freely in response to an applied electric field. Metals are excellent conductors of electricity due to their free-flowing electrons, while insulators, like rubber or glass, have tightly bound electrons and do not conduct electricity well. Semiconductors, such as silicon, have conductivity levels between that of metals and insulators and can be controlled to conduct electricity selectively.
How do magnets attract or repel each other?
Magnets attract or repel each other based on the alignment of their magnetic fields. When two magnets are brought close together, the magnetic fields interact either by attracting (opposite poles) or repelling (like poles) each other. This interaction is a result of the alignment of the magnetic domains within the materials of the magnets. The force of attraction or repulsion between the magnets is strongest when the poles are close together and decreases as the distance between them increases.
Explain the difference between a physical change and a chemical change.
A physical change involves a change in the physical properties of a substance, such as its shape, size, or state, without changing its chemical composition. Examples include melting, freezing, dissolving, or changing in state from solid to liquid. On the other hand, a chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties. This involves breaking and forming chemical bonds, resulting in a change in composition, such as burning a wood log to produce ash and smoke.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments