Macromolecules Worksheet 2
Does the world of macromolecules have you feeling overwhelmed and confused? Look no further, because we have the perfect solution! Introducing Macromolecules Worksheet 2, designed to provide a clear and concise understanding of entities and subjects within the world of macromolecules. This worksheet is tailored for students or individuals who are seeking a comprehensive comprehension of macromolecules and their basic components.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
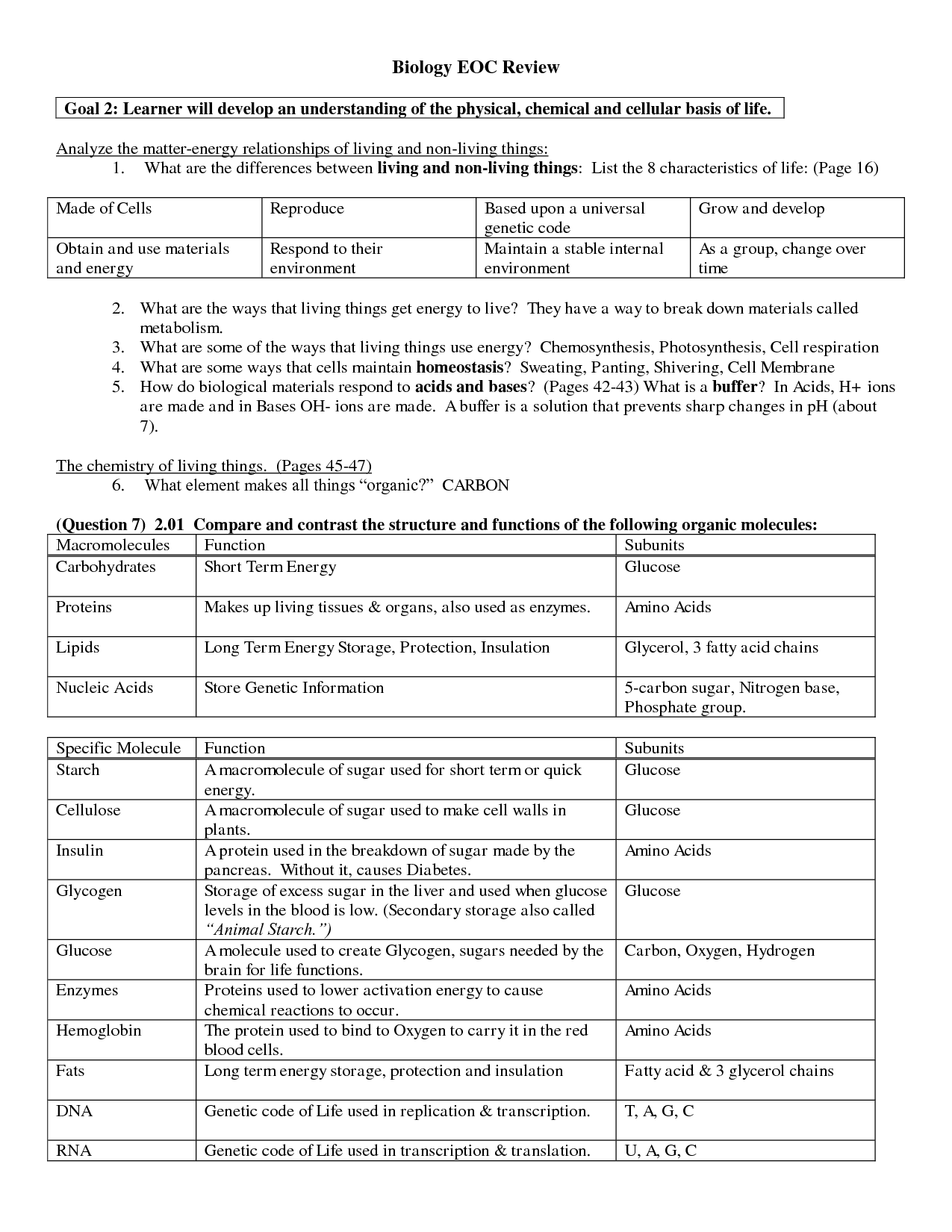
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large molecules composed of repeating subunits called monomers. Examples of macromolecules include proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), carbohydrates, and lipids. These molecules are essential for various biological processes and are the building blocks of life.
Provide examples of macromolecules.
Some examples of macromolecules include proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), carbohydrates (such as starch and cellulose), and lipids (such as fats and phospholipids). These molecules are large biological molecules made up of smaller subunits that are essential for various cellular functions and processes in living organisms.
Describe the structure of proteins.
Proteins are large complex molecules made up of long chains of amino acids folded into specific three-dimensional shapes. The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino acids, while its secondary structure refers to regular patterns like alpha helices and beta sheets. Tertiary structure is the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein, formed by interactions between amino acids, and quaternary structure involves the arrangement of multiple protein subunits. Proteins can have diverse functions based on their specific structures, enabling them to perform crucial roles in biological processes.
Explain what nucleic acids are and their role in living organisms.
Nucleic acids are biomolecules that play a critical role in living organisms as they carry genetic information. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA stores genetic information that determines an organism's traits and characteristics, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis and gene expression. Nucleic acids are essential for the functioning and growth of cells, as they act as the blueprint for building and maintaining living organisms.
How are carbohydrates classified and what are their functions?
Carbohydrates are classified into three main groups: monosaccharides (simple sugars), disaccharides (two monosaccharides linked together), and polysaccharides (long chains of monosaccharides). Their functions include providing energy for the body, serving as a quick source of fuel for physical activity, acting as a structural component in cell walls and tissues, aiding in digestion and supporting the growth and development of the body.
What is the structure and function of lipids?
Lipids are molecules comprised of hydrocarbons and play essential roles in living organisms. The structure of lipids typically includes a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end. Some common types of lipids include fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Lipids serve various functions such as storing energy, acting as structural components of cell membranes, serving as signaling molecules, and providing insulation and protection for organs. Overall, lipids are crucial for maintaining cellular health and function in organisms.
Discuss the importance of enzymes in biological reactions.
Enzymes are crucial in biological reactions as they act as catalysts, speeding up reactions that would otherwise occur too slowly to sustain life. By lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed, enzymes enable cellular processes to occur at a rate that is necessary for metabolism and growth. Enzymes are highly specific, binding to particular substrates and facilitating their conversion into products while remaining unchanged themselves, making them efficient and versatile tools in orchestrating the chemical reactions necessary for life. Additionally, enzymes play a role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating metabolic pathways within cells.
Describe the process of polymerization.
Polymerization is a chemical process in which small monomer molecules are joined together to form a large polymer molecule. This reaction is typically initiated by heat, light, or a catalyst, which allows the monomers to link together through covalent bonds. As the polymer chain grows, the resulting polymer can exhibit a range of properties depending on the structure of the monomers and the conditions of the polymerization reaction. These properties make polymers widely used in various industries, such as plastics, textiles, and coatings.
Explain how DNA and RNA differ in structure and function.
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that stores genetic information in the form of genes, while RNA is usually single-stranded and carries out various functions in the cell, such as protein synthesis. DNA contains the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, while RNA replaces thymine with uracil. Additionally, DNA is found in the cell nucleus, whereas RNA can be found both in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. These structural and functional differences reflect the unique roles that DNA and RNA play in the overall functioning of a cell.
Discuss the role of macromolecules in genetic information and heredity.
Macromolecules play a critical role in genetic information and heredity as they are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, the molecules that store and transmit genetic information. DNA, made up of nucleic acid macromolecules, carries the instructions for an organism's development, functioning, and characteristics, while RNA helps in the translation of these instructions into proteins. Proteins, composed of amino acid macromolecules, are essential for various biological processes and traits, ultimately determining an organism's traits and inheritance patterns. Thus, macromolecules are fundamental in the molecular mechanisms that govern genetic information and heredity.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments