Long Division with Decimals Worksheets
If you're a math teacher or a parent helping your child with their math skills, you know how important it is to find resources that make learning engaging and effective. When it comes to practicing long division with decimals, finding the right worksheets can make all the difference.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
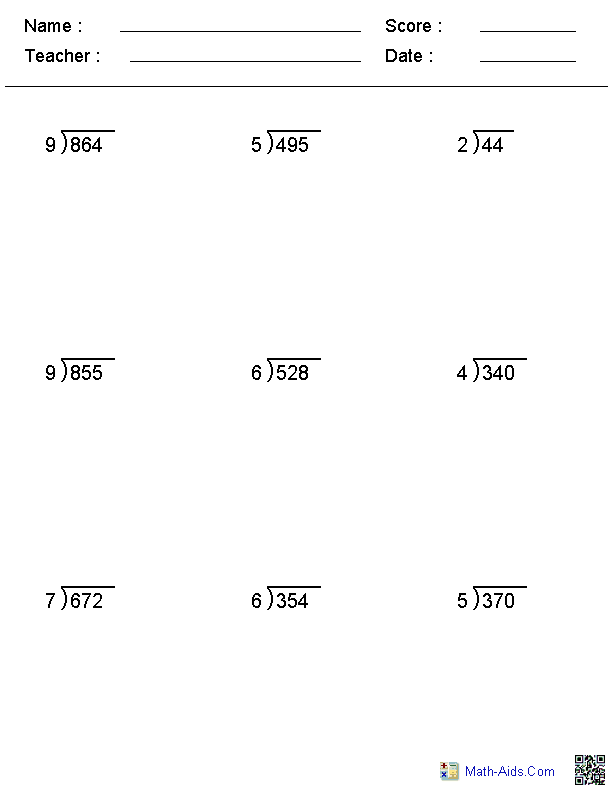
What is long division with decimals?
Long division with decimals is the process of dividing a decimal number by another decimal number using the same steps as traditional long division, but also considering the placement of the decimal point in the dividend and divisor. The key is to align the decimal points in the dividend and divisor, and then proceed with the division as usual, taking care to bring down additional decimal places as needed until the desired level of accuracy is achieved in the quotient.
How do you set up a long division problem with decimals?
To set up a long division problem with decimals, first write the dividend inside the division symbol and the divisor outside the division symbol. Then, proceed with the division as you normally would with whole numbers, making sure to align the decimal points in the dividend and quotient. If needed, you can add zeros to the right of the decimal point in the dividend to continue the division process. Finally, continue dividing until you reach the desired level of accuracy in your quotient.
What is the purpose of putting a decimal point in the quotient during long division with decimals?
The purpose of putting a decimal point in the quotient during long division with decimals is to show the correct placement of the decimal point when dividing by numbers that are not whole. By aligning the decimal places in the dividend and quotient, you ensure that the decimal point is positioned correctly in the final answer, maintaining the accuracy of the division with decimals.
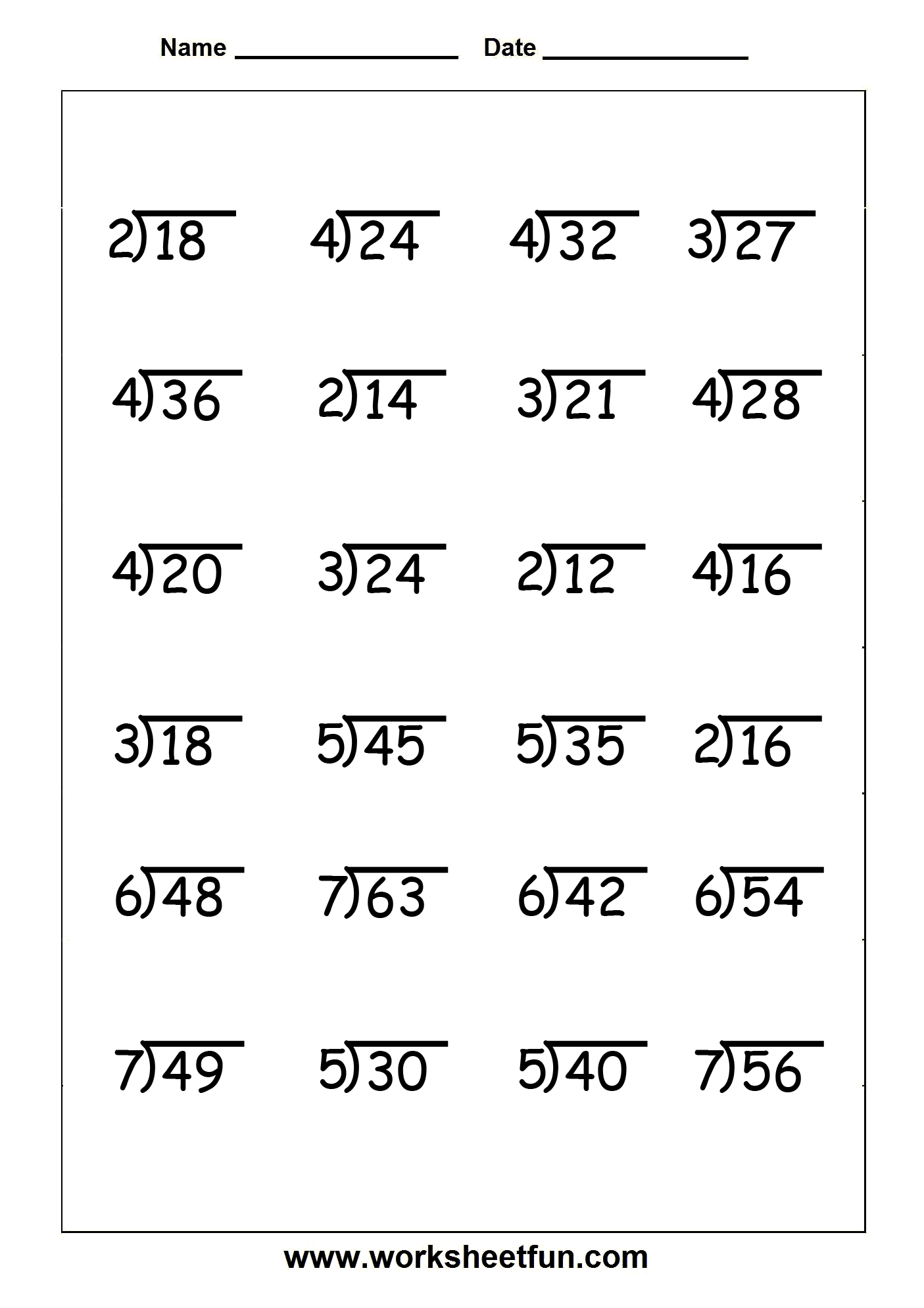
How do you determine the number of decimal places in the quotient during long division with decimals?
To determine the number of decimal places in the quotient during long division with decimals, count the total number of decimal places in both the dividend and the divisor. Then, place the decimal point in the quotient directly above the decimal point in the dividend and adjust as needed. The number of decimal places in the quotient should be equal to or less than the total number of decimal places in the dividend and divisor.
What do you do with any remaining decimal places during long division with decimals?
When performing long division with decimals, you can continue the division process and bring down additional zeros to the right of the decimal point in the dividend until you reach the desired level of accuracy or until the division terminates. If there are remaining decimal places in the quotient, you can either round the result to the desired number of decimal places or keep the result as an approximation depending on the context or instructions provided.
How do you handle repeating decimals during long division?
To handle repeating decimals during long division, you can first convert the decimal to a fraction. Identify the repeating pattern and use this to create an equation to solve for the decimal in terms of a fraction. Then, proceed with the long division process using the fraction form instead of the decimal form, making it easier to work with and obtain the final answer.
Can you divide a decimal by another decimal during long division?
Yes, it is possible to divide a decimal by another decimal using long division. Simply treat both decimals as whole numbers by moving the decimal point to the right to convert them into whole numbers. Then perform long division as you normally would with whole numbers. Finally, place the decimal point in the quotient directly above the decimal point in the dividend to find the correct decimal quotient.
How do you know if you need to add a zero to the dividend during long division with decimals?
When performing long division with decimals, you need to add a zero to the dividend when there are not enough decimal places in the dividend to perform the division. You continue adding zeros until you have enough decimal places to continue the division process.
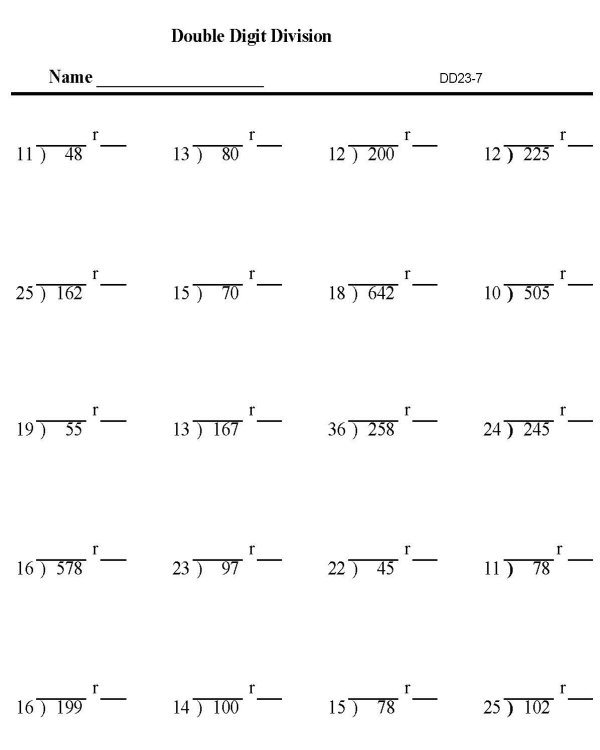
What happens if there is a remainder during long division with decimals?
If there is a remainder during long division with decimals, it means that the division did not result in a whole number quotient. The remainder represents the amount left over after dividing as much as possible by the divisor. It indicates that the division is not evenly divisible, and the remainder can be expressed as a decimal or fraction to show the exact amount left over.
How do you check your work after completing long division with decimals?
To check your work after completing long division with decimals, you can multiply the quotient by the divisor and add the remainder, if any. The result should be equal to the original dividend. This ensures that your division was done correctly and all the decimal places were accounted for. Additionally, you can use a calculator to double-check your work by dividing the original dividend by the divisor to see if you get the same quotient.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments