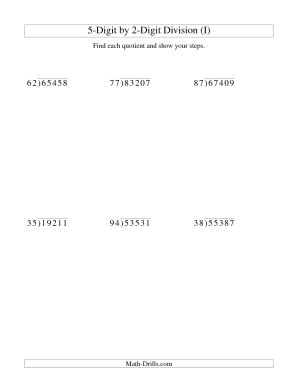
Long Division Steps Worksheet
Are you searching for an effective learning tool that helps elementary school students grasp the essentials of long division? Look no further! Our Long Division Steps Worksheet is designed to provide a clear and concise breakdown of the step-by-step process involved in solving long division problems.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of a long division steps worksheet?
The purpose of a long division steps worksheet is to help students practice and reinforce their understanding of long division process. By providing guided steps and exercises, the worksheet aims to improve students' proficiency in breaking down larger numbers into smaller parts, dividing them systematically, and deriving accurate quotients. This practice helps students develop their problem-solving skills, strengthen their mathematical abilities, and boost their confidence when dealing with division calculations.
How does long division differ from other division methods?
Long division differs from other division methods because it involves breaking down the dividend into multiple steps, with remainders carried over from one digit to the next. This method requires more steps and is typically used for dividing larger numbers that do not have easily calculable factors. Other division methods, such as short division or using a calculator, may be quicker for simpler divisions but may not be as precise or detailed as long division.
What are the main steps involved in long division?
The main steps involved in long division are: 1) Divide: Divide the leading digit of the dividend by the divisor. 2) Multiply: Multiply the divisor by the result obtained in the division step, and write the product below the dividend. 3) Subtract: Subtract the product from the dividend. 4) Bring down: Bring down the next digit of the dividend next to the remainder. 5) Repeat: Repeat steps 1-4 until there are no more digits in the dividend to bring down, and the final remainder is the result of the division.
How do you determine which numbers to divide?
To determine which numbers to divide, you first need to identify the dividend (the number being divided) and the divisor (the number you are dividing by). You typically choose which numbers to divide based on the problem or calculation you are trying to solve. For example, if you have a total amount that needs to be divided equally among a certain number of people, you would divide the total amount by the number of people. It is important to consider the context of the problem and the mathematical operation required to find the answer.
What do you do if the divisor can't divide into the first digit of the dividend?
If the divisor can't divide into the first digit of the dividend, you should consider including the next digit(s) of the dividend to form a larger number that the divisor can divide into. This involves considering a longer sequence of digits from the dividend to find a suitable number that the divisor can divide into evenly.
How do you calculate the quotient in long division?
To calculate the quotient in long division, you divide the dividend by the divisor, starting with the leftmost digits and working your way to the right. Each step involves dividing the current partial dividend by the divisor, recording the quotient above the line, multiplying the divisor by the quotient, subtracting this product from the current partial dividend to get a new partial dividend, then bringing down the next digit from the dividend to continue the process until you have no more digits to bring down. The final answer is the quotient obtained from these steps.
How do you determine the remainder in long division?
To determine the remainder in long division, you need to divide the dividend (the number being divided) by the divisor (the number you are dividing by) using the long division process. The remainder is the number left over after the division process is complete. It is the difference between the dividend and the product of the divisor and the quotient. The remainder represents what is left over that cannot be evenly divided by the divisor.
What should you do if the quotient has a decimal?
If the quotient has a decimal, you should consider whether you need to round the decimal to a certain place value or keep it as is for the required level of accuracy. Depending on the context of the problem, you may need to round up, down, or to the nearest decimal place, as specified in the instructions or requirements.
How can you check your work in long division?
To check your work in long division, you can do the reverse operation by multiplying the quotient you obtained with the divisor, and then adding the remainder. The result should be equal to the dividend you initially divided. This helps ensure that you made no errors during the division process.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using long division?
Some common mistakes to avoid when using long division include not carefully aligning the numbers in columns, forgetting to bring down the next digit from the dividend, incorrectly subtracting the product from the partial dividend, not keeping track of the place value and positioning within the division process, and rushing through the steps without double-checking your work. Remember to take your time, focus on each step, and stay organized to prevent errors in long division.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






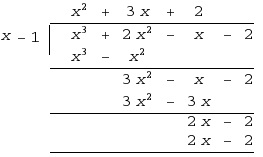
















Comments