Lipids Macromolecules Worksheet
Are you a high school or college student studying biology or chemistry? Have you been searching for a comprehensive and engaging resource to help you learn about lipids? Look no further! Introducing the Lipids Macromolecules Worksheet, a valuable tool designed to enhance your understanding of this essential topic.
Table of Images 👆
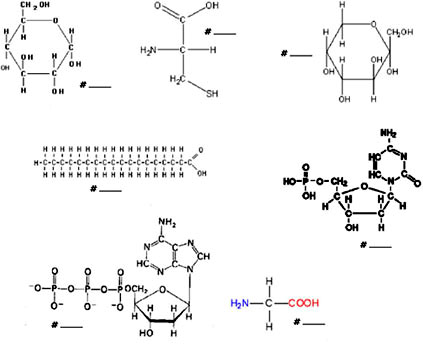
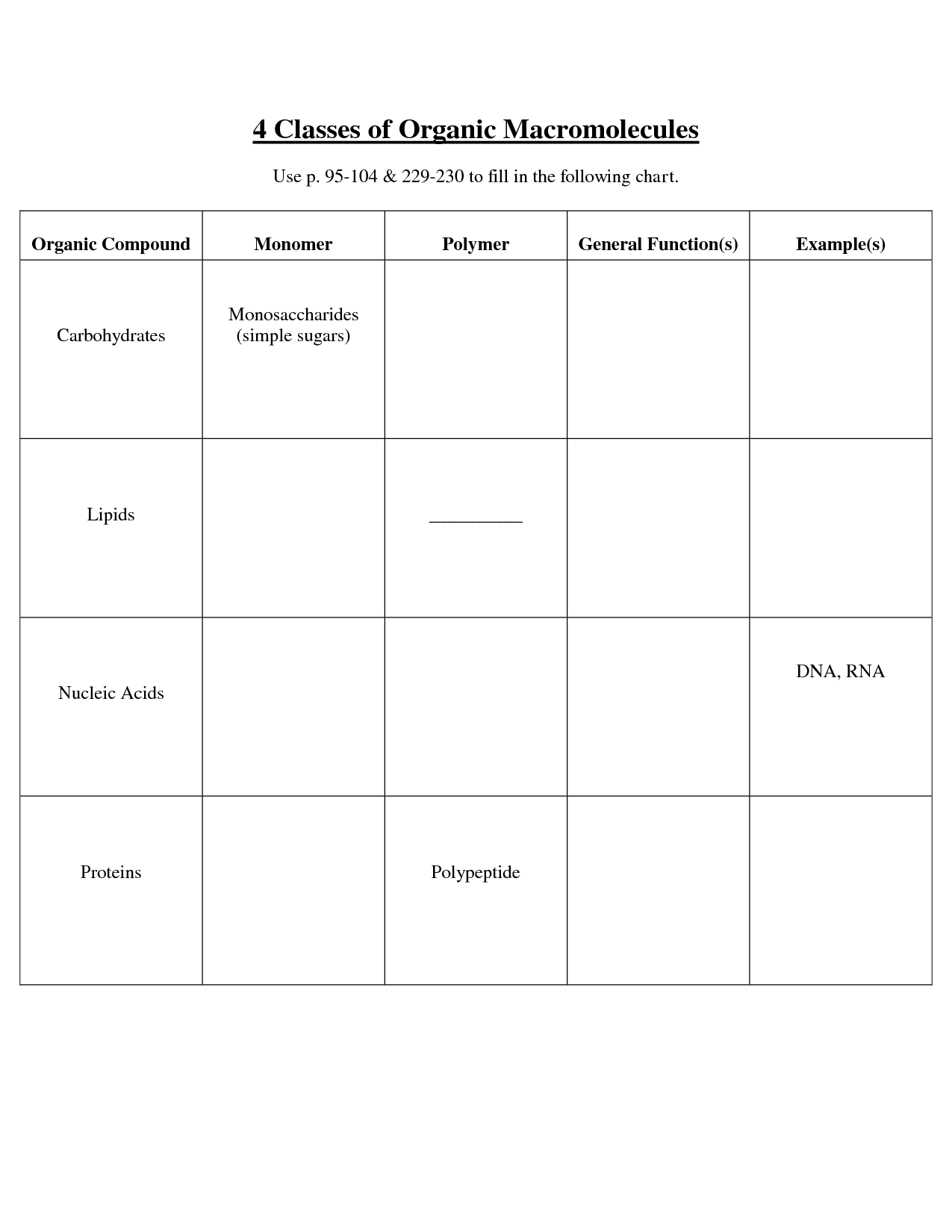
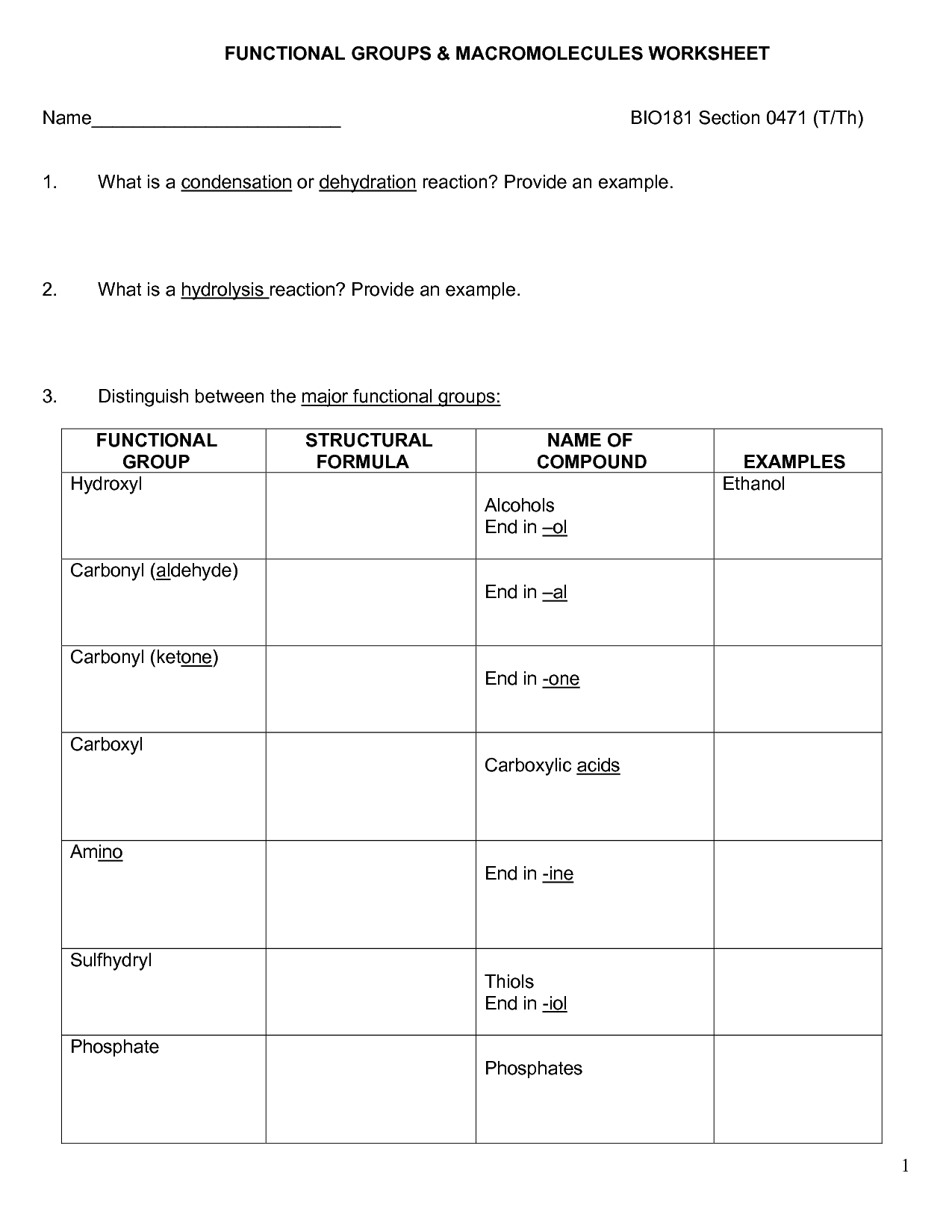
- Macromolecule Structure Worksheet
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
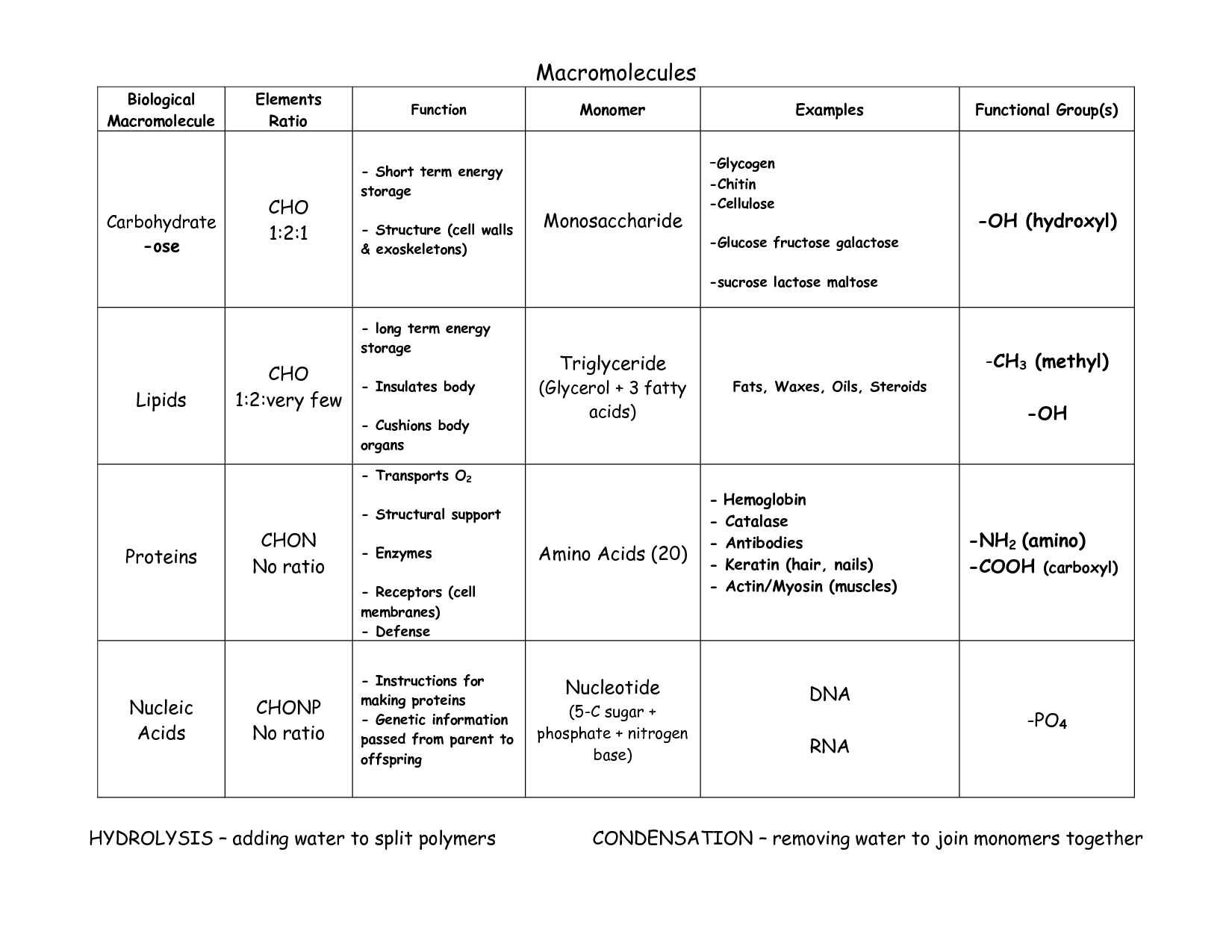
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet
- Macromolecules Chart
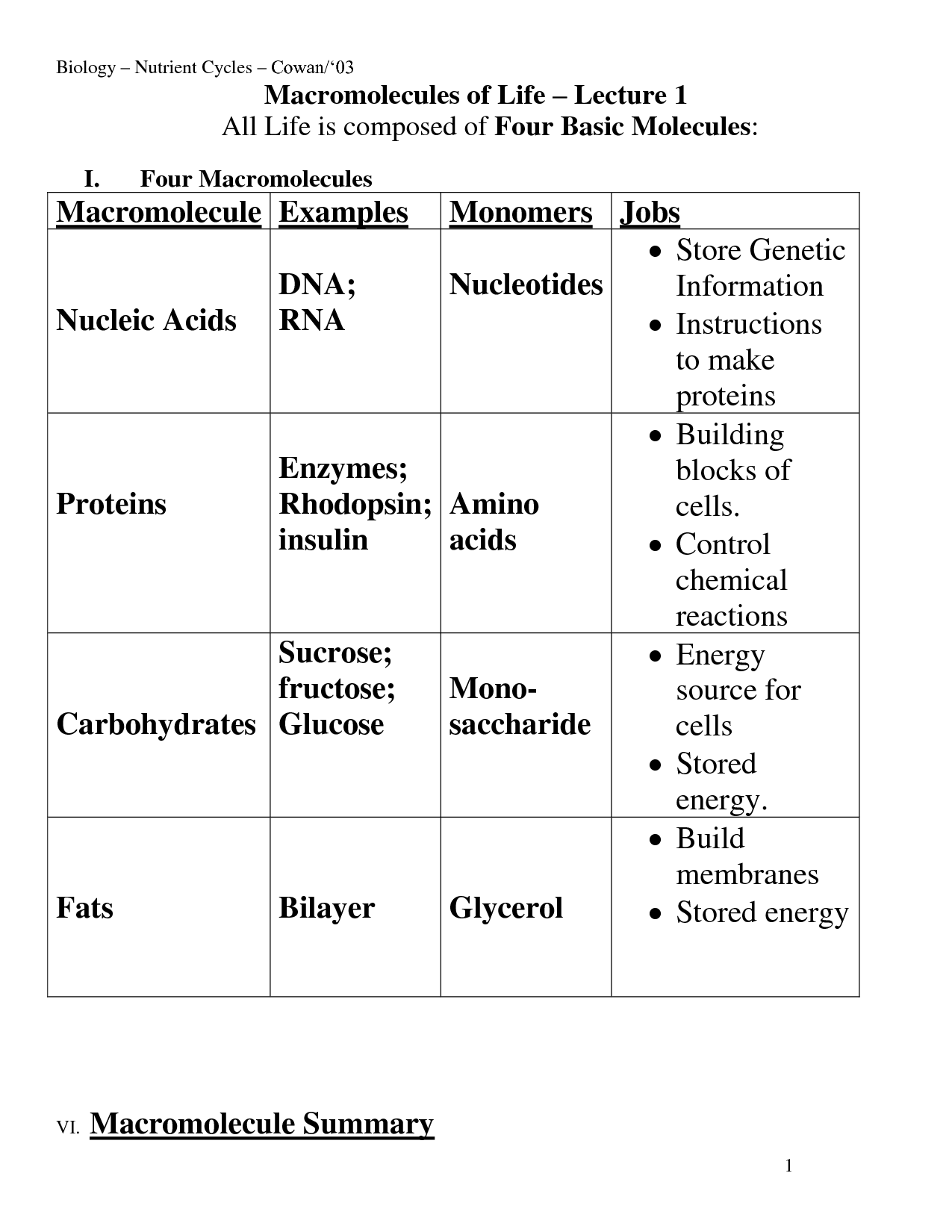
- 4 Types of Macromolecules and Their Functions
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Chart Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are lipids?
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids, and serve various functions in living organisms, such as energy storage, structural components of cell membranes, and cell signaling.
What is the main function of lipids in the body?
Lipids play a crucial role in the body by serving as a major source of energy, providing insulation to retain body heat, forming the structure of cell membranes, aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and serving as a protective layer for organs. Additionally, lipids are essential for hormone production and play a role in maintaining overall cellular function and health.
Name three examples of common lipids.
Three examples of common lipids are triglycerides (fats and oils), phospholipids (main components of cell membranes), and steroids (including cholesterol and hormones like testosterone and estrogen).
How are lipids different from other macromolecules?
Lipids are different from other macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids because they are hydrophobic and insoluble in water. They are essential for storing energy, forming cell membranes, and signaling pathways. Unlike proteins and carbohydrates, lipids do not have a defined monomeric structure and can be diverse in their composition, which includes fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids. Additionally, lipids contain a higher energy density compared to carbohydrates and proteins, making them an efficient form of energy storage in the body.
Describe the structure of a phospholipid.
A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule with a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails. The head consists of a phosphate group attached to a glycerol molecule, while the tails are made up of fatty acid chains. This unique structure allows phospholipids to form the basic building blocks of cell membranes, with the hydrophilic heads facing outward towards the watery environment and the hydrophobic tails pointing inward, creating a barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside.
How do lipids contribute to cell membrane structure and function?
Lipids play a crucial role in cell membrane structure and function by forming a lipid bilayer that serves as the main barrier between the cell's internal environment and the external environment. Phospholipids, a type of lipid, are amphipathic molecules with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads, allowing them to spontaneously assemble into a bilayer with the hydrophobic tails facing inward and the hydrophilic heads facing outward. This lipid bilayer provides flexibility, fluidity, and selective permeability to the cell membrane, allowing the cell to regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cell. Additionally, other lipid components such as cholesterol help maintain membrane fluidity and stability. Lipids also serve as anchor points for membrane proteins and facilitate cell signaling processes through the formation of lipid rafts.
Explain the role of lipids in energy storage.
Lipids play a crucial role in energy storage as they are a highly efficient way to store energy in the body. When consumed, lipids are broken down into fatty acids and stored in adipose tissue as triglycerides. These triglycerides can then be broken down through the process of lipolysis to release energy for the body to use when needed. Because lipids provide more than twice the amount of energy per gram compared to carbohydrates, they serve as a dense and long-term energy reserve for the body, helping to sustain metabolic processes during periods of fasting or energy deficit.
How do lipids help with insulation in the body?
Lipids help with insulation in the body by forming a layer of adipose tissue beneath the skin. This adipose tissue acts as an insulating layer, helping to regulate body temperature by reducing heat loss from the body. In addition, lipids serve as energy reserves that can be utilized when the body needs to generate heat in response to cold conditions, further supporting the insulation function of lipids in the body.
Describe the process of lipid digestion in the body.
When lipids are ingested, they enter the stomach where some initial breakdown occurs due to gastric lipase. However, the majority of lipid digestion takes place in the small intestine. Bile salts emulsify large lipid droplets into smaller droplets to increase the surface area for enzymes to work on. Pancreatic lipase enzymes then break down triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides, which can be absorbed by the intestinal cells. These products are then reassembled into triglycerides within the cells, packaged into chylomicrons, and transported via lymphatic vessels and blood to be utilized by cells throughout the body.
What are the health implications of an imbalance in lipid intake?
An imbalance in lipid intake can lead to serious health implications, including an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, obesity, and metabolic disorders such as diabetes. Consuming too much saturated and trans fats can raise cholesterol levels, leading to plaque buildup in arteries and an increased risk of heart disease. On the other hand, inadequate intake of essential fats like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids can disrupt cell function, impair brain health, and weaken the immune system. Therefore, it is important to maintain a balanced intake of different types of lipids to support overall health and well-being.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments