Light Problems Worksheet
Are you struggling to solve light-related problems? Look no further! This blog post will provide you with a carefully curated selection of worksheets designed to help you understand and apply the concepts of light. Whether you are a student studying physics or a self-learner interested in unraveling the mysteries of optics, these worksheets will provide you with a solid foundation in this fascinating subject. So, let's dive in and explore the world of light together!
Table of Images 👆
- Bohr Atomic Models Worksheet Answers
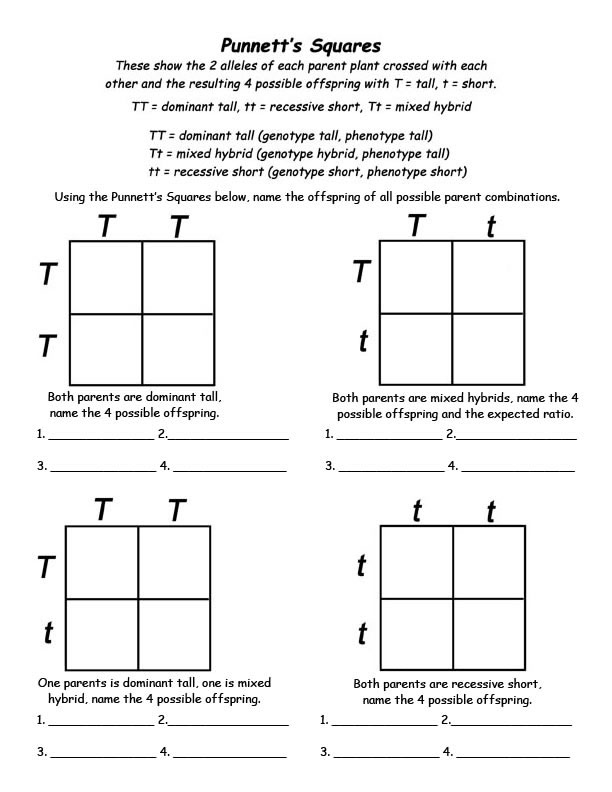
- Punnett Square Worksheets
- Light and Atoms Worksheet 2 Answers
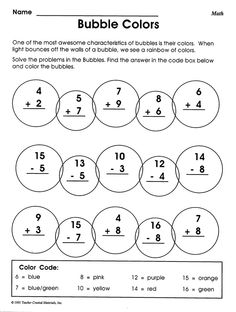
- Bubble Math Worksheets
- Note Taking Worksheet Answers
- Mole Calculation Worksheet Answer Key
- Solubility Curve Practice Worksheet 1 Answer Key
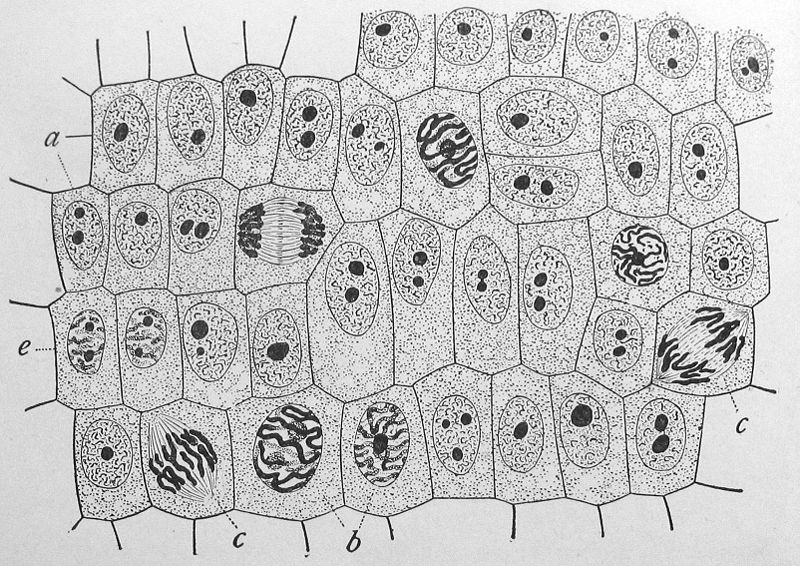
- Onion Cell Mitosis Drawing
- Mad Minute Math Worksheets Printable
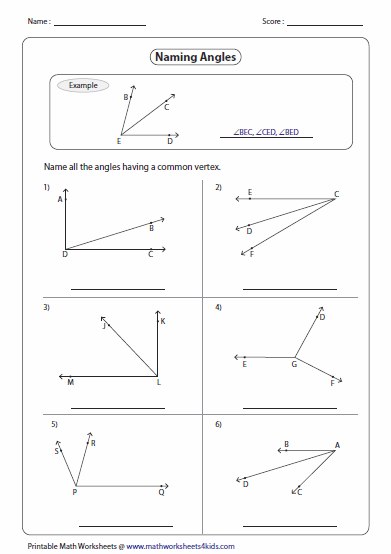
- Naming Angles Worksheets
- Schwa Sound Worksheets
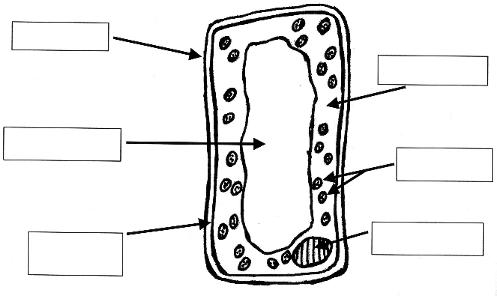
- Plant Cell Diagram without Labels
- Sin and Cosine Formulas
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye and travels in waves at a speed of about 186,282 miles per second. It consists of particles called photons and carries energy and information through space.
How does light travel?
Light travels in a straight line as a form of electromagnetic radiation at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second in a vacuum. It can also propagate through different mediums such as air, water, and glass, but its speed may vary depending on the medium's density and refractive index. Light behaves like a wave and a particle, following the principle of wave-particle duality, where it exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties simultaneously.
What are the primary sources of light?
The primary sources of light are natural sources such as the sun, stars, lightning, and bioluminescence, as well as artificial sources like light bulbs, lamps, and fluorescent tubes. Each of these sources emits light either through a natural process, such as nuclear fusion in the sun, or by converting electrical energy into light through various mechanisms.
What are the main properties of light?
Light is an electromagnetic wave that travels in a straight line, has a constant speed in a vacuum, can be reflected, refracted, diffracted, and absorbed, and exhibits both wave-like and particle-like behavior known as wave-particle duality. It has a spectrum of colors determined by its frequency and wavelength, can be polarized, and obeys the laws of reflection and refraction. Additionally, light can be described in terms of intensity, brightness, and color temperature, and it can interact with matter to produce effects like fluorescence and phosphorescence.
How does light interact with different materials?
Light can interact with different materials in a variety of ways. When light passes through transparent materials such as glass or water, it may refract or bend. In opaque materials like wood or metal, light is typically absorbed or reflected. Some materials, like mirrors or metallic surfaces, can reflect light with very little absorption. Other materials, such as fluorescent or phosphorescent substances, can absorb light and re-emit it at different wavelengths. Additionally, some materials can scatter light, causing it to change direction as it passes through. Overall, the interaction of light with different materials depends on their properties such as transparency, reflectivity, and scattering ability.
What is the role of reflection in the formation of an image?
Reflection plays a crucial role in the formation of an image as it is the process by which light waves strike a surface and bounce back towards the viewer's eyes, allowing us to see objects. Without reflection, light waves would simply pass through objects, making them invisible to the human eye. Reflection is what enables us to perceive the world around us by creating the visual representation of objects that we see.
What is refraction and how does it affect the path of light?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, such as from air to water. This bending occurs because light changes speed when it moves from one medium to another with a different optical density. The degree of bending is determined by the angle at which the light enters the new medium. As a result of refraction, the path of light can be altered, causing it to change direction and potentially focus or disperse.
What are the different types of lenses and their characteristics?
There are several types of lenses used in optics, including convex lenses that converge light rays and are thicker at the center than the edges, concave lenses that diverge light rays and are thicker at the edges than the center, and plano-convex and plano-concave lenses that have one flat and one curved surface. Each type of lens has unique characteristics that affect the way they refract light. Convex lenses can produce real or virtual images, while concave lenses only produce virtual images. Additionally, the focal length, power, and magnification of a lens are determined by its shape and curvature.
How does the human eye perceive light and form an image?
The human eye perceives light through the cornea and lens, which focus the light onto the retina at the back of the eye. The retina contains light-sensitive cells called photoreceptors (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve, where they are processed and interpreted as images. The brain processes these signals to create a cohesive image based on the differences in light intensity and color detected by the photoreceptors.
How does light behave in different atmospheric conditions, such as rainbows or mirages?
Light behaves differently in various atmospheric conditions, creating phenomena such as rainbows and mirages. Rainbows occur when sunlight is refracted, reflected, and dispersed by water droplets, producing a spectrum of colors. Mirages, on the other hand, are caused by the bending of light as it passes through air layers of different temperatures, creating optical illusions of water or objects that are not actually there. These atmospheric conditions demonstrate how light can be refracted, reflected, and dispersed in unique ways, resulting in the beautiful and fascinating phenomena we observe in nature.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.










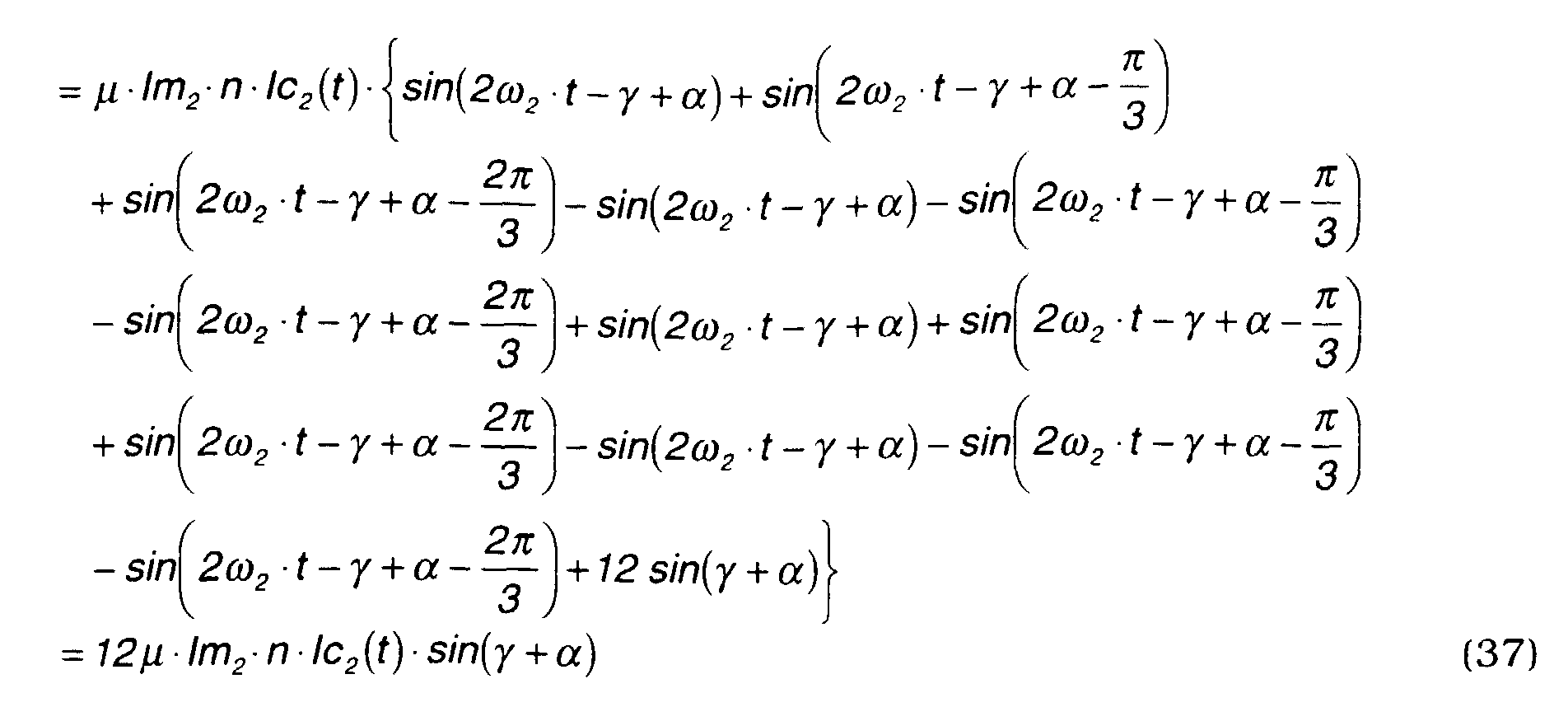
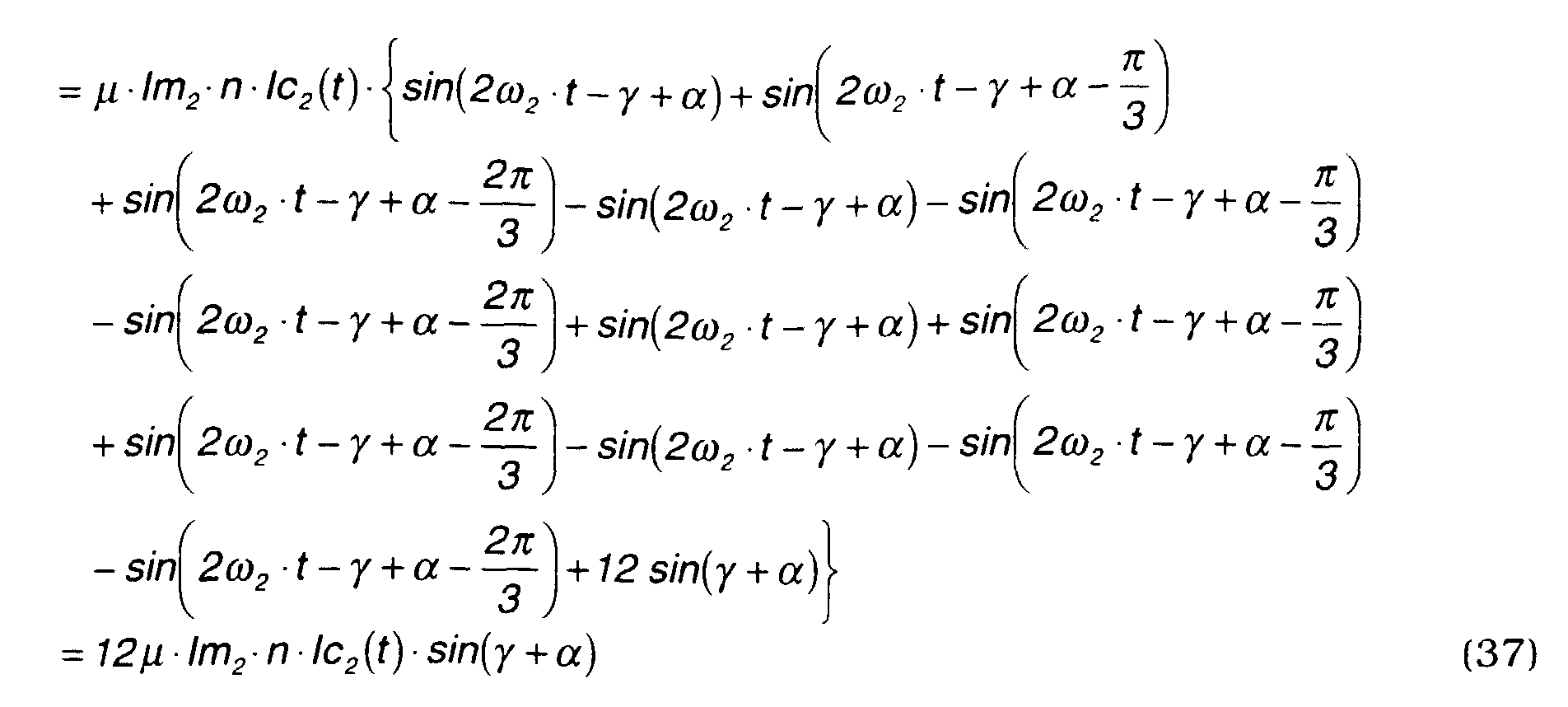














Comments