Light Energy Worksheet Third Grade
In order to reinforce student learning and comprehension of light energy concepts, a specially designed worksheet can be an invaluable resource. Tailored to the specific needs of third-grade learners, this engaging and interactive tool provides an opportunity for students to explore the properties and behaviors of light in an organized and structured manner. By incorporating various activities and exercises, this worksheet aims to enhance students' understanding of this fundamental scientific concept.
Table of Images 👆
- First Grade Printable Science Worksheets
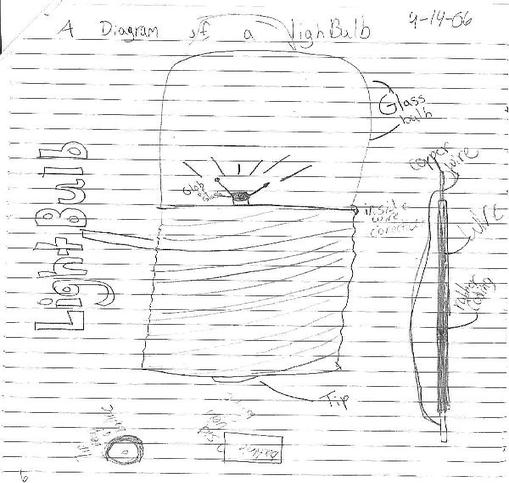
- 4th Grade Science Light Bulb Diagram
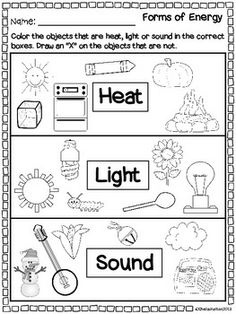
- Energy Worksheets 3rd Grade Forms
- Properties of Matter Worksheet Grade 2
- Forms of Energy Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Natural Resources Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Science States of Matter Worksheets
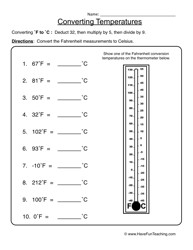
- Celsius Temperature Worksheets
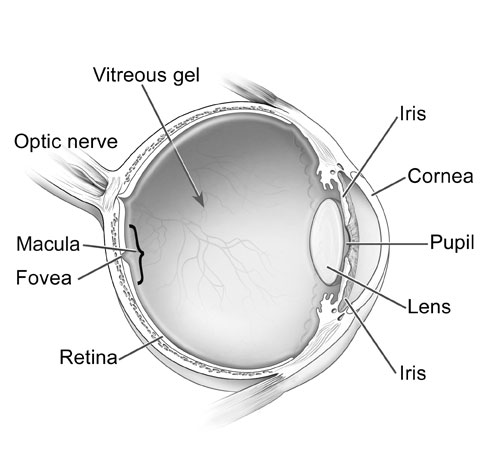
- Parts of the Human Eye Diagram
- Weather Instruments Worksheet
- Earth Layers Worksheet
- Farm Animal Worksheets
- State of Matter Gas Liquid and Solids Worksheets
More 3rd Grade Worksheets
Telling Time Worksheets 3rd GradeTime Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Multiplication Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Math Division Worksheets Printable
Short Reading Comprehension Worksheets 3rd Grade
Soil Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Cursive Writing Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Multiplication Properties Worksheet
First Day of School Worksheets 3rd Grade
What is light energy?
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It is a type of energy that enables us to see and perceive colors and shapes in our environment. Light energy is produced by the sun and other sources like light bulbs, and it plays a crucial role in various natural processes and technologies, such as photosynthesis, vision, and solar panels.
How is light energy produced?
Light energy is produced when atoms or molecules undergo a transition from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, emitting photons in the process. This can occur through various mechanisms such as thermal radiation, chemical reactions, electric discharge, or nuclear reactions. The emitted photons carry energy which manifests as visible light, ultraviolet light, or infrared radiation depending on the specific process involved.
What are the different sources of light energy?
Some sources of light energy include natural sources like the sun, stars, and fire, as well as artificial sources like light bulbs, LED lights, and neon lights. Light energy can also be produced through chemical reactions, such as with glow sticks, or through mechanical means, such as with laser beams. Additionally, bioluminescent organisms can emit light energy through biochemical processes.
How does light energy travel?
Light energy travels in waves as electromagnetic radiation. These waves do not require a medium to pass through and can travel through a vacuum. Light energy behaves both as a wave and a particle, known as a photon, and its motion is characterized by its frequency, wavelength, and speed. Light energy can travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 186,282 miles per second in a vacuum.
What materials can absorb light energy?
Materials that can absorb light energy include pigments, dyes, metals like gold and silver, semiconductors such as silicon, and carbon-based materials like graphene. These materials are able to absorb light energy due to their specific molecular structures and electronic configurations, allowing them to capture photons and convert them into other forms of energy like heat or electrical current.
How does light energy interact with objects?
Light energy interacts with objects through a process called absorption, reflection, or transmission. When light comes into contact with an object, it can be absorbed by the object where it is converted into heat or another form of energy. Alternatively, light can be reflected off the surface of an object, bouncing back into the environment. Lastly, light can also be transmitted through certain materials, allowing it to pass through without being absorbed or reflected. These interactions determine how objects appear to us visually and play a crucial role in various scientific fields such as optics and physics.
How can we use light energy in our daily lives?
We can use light energy in our daily lives by utilizing natural light for illumination inside buildings, using solar panels to generate electricity for powering devices and homes, and enjoying leisure activities such as photography or art that require light. Additionally, light energy is crucial for growing plants through photosynthesis, and we can also harness it for communication in technologies like fiber optic cables.
What are some examples of natural sources of light energy?
Some examples of natural sources of light energy include the sun, stars, lightning, bioluminescent organisms, and fireflies. These sources emit light through natural processes such as nuclear fusion, electrical discharge, chemical reactions within living organisms, and combustion.
How can we convert light energy into other forms of energy?
Light energy can be converted into other forms of energy through various methods such as photovoltaic cells in solar panels, which convert light energy into electrical energy, or through the use of solar thermal systems that utilize light energy to generate heat. Light energy can also be absorbed by plants during photosynthesis to convert it into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Additionally, light energy can be converted into mechanical energy through processes like photophosphorylation in cells or through optical devices such as solar concentrators that focus light to generate heat or drive turbines.
How does light energy affect the environment?
Light energy can impact the environment in various ways, including disrupting ecosystems by altering animals' behavior, migration patterns, and reproductive cycles. Light pollution can also have negative effects on wildlife, interfere with the natural circadian rhythms of plants and animals, and contribute to the disorientation and mortality of nocturnal species. Additionally, excessive artificial light can waste energy, contribute to carbon emissions, and disrupt stargazing and astronomical observations. Overall, managing and reducing light pollution is crucial to preserve natural habitats, conserve energy, and minimize the ecological impacts of excessive light exposure on the environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments