Light and Heat Worksheet
Are you a science teacher in search of a comprehensive worksheet to help your students understand the concepts of light and heat? Look no further! Our Light and Heat Worksheet is designed to engage students in hands-on activities and problem-solving tasks that reinforce their understanding of these essential topics.
Table of Images 👆
- Light and Heat Energy Worksheets
- Sound and Light Energy Worksheet
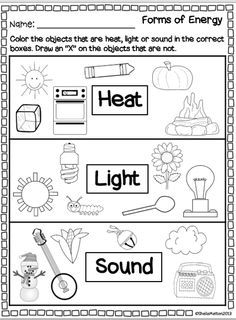
- Kindergarten Energy Worksheets
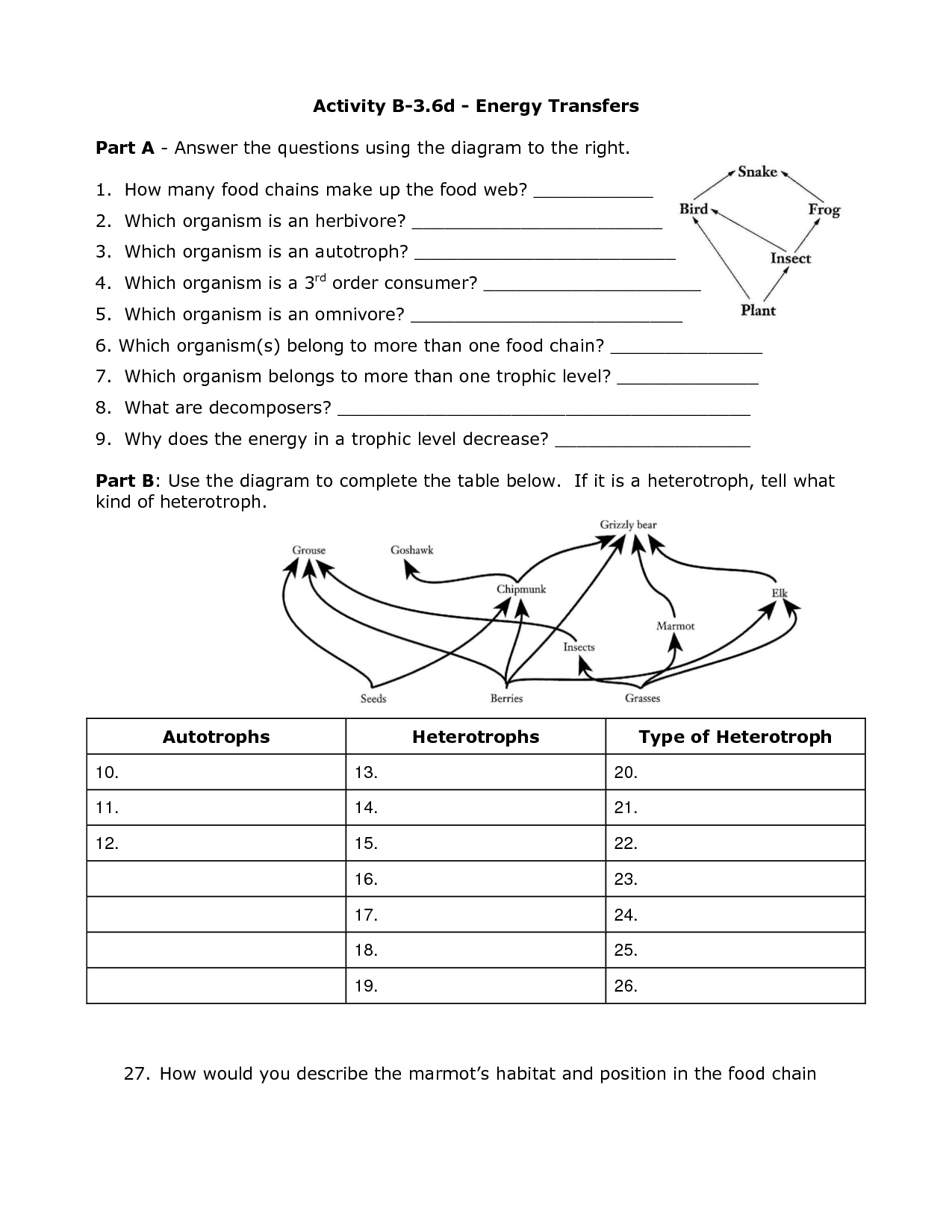
- Food Web Energy Transfer Worksheet
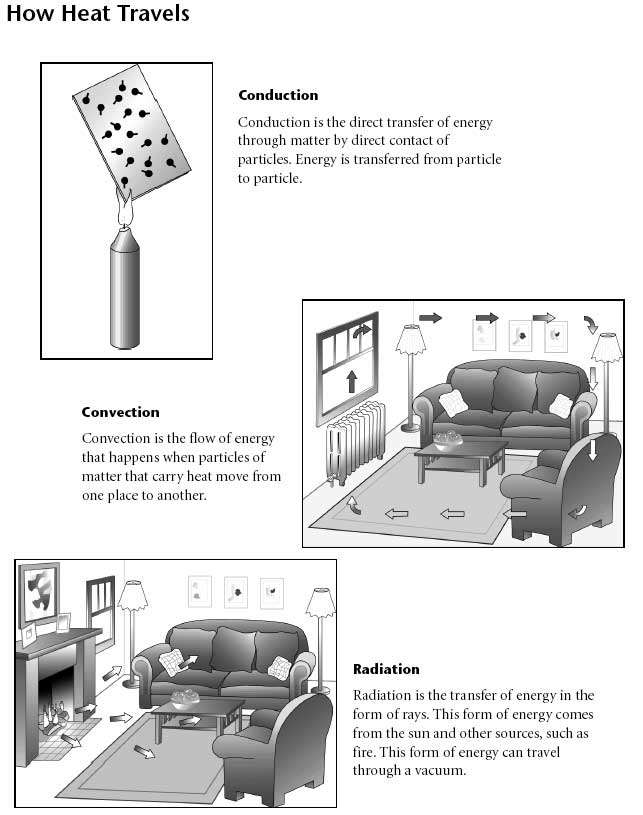
- Heat Energy Transfer Worksheet
- Three Types of Heat Transfer Worksheet
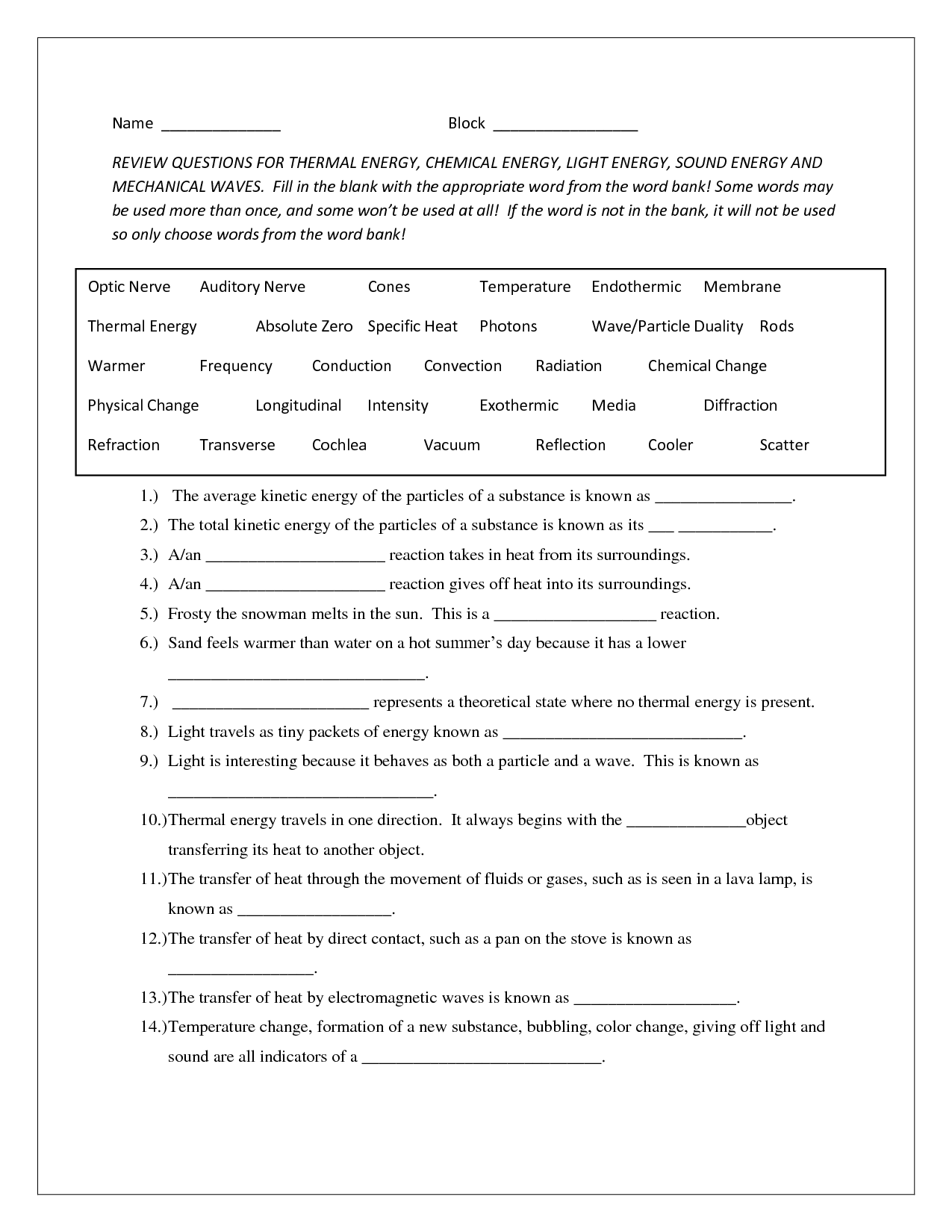
- Blank Fill in the Light and Sound Waves Worksheets
- Science Worksheets Light Energy and Heat
- Science Worksheets Heat Energy
- Light Sources Worksheets
- Heat Conductor and Insulator Worksheets 3rd Grade
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It consists of photons, which are particles that carry energy. Light travels in waves and can behave as both a particle and a wave. It is essential for vision, photosynthesis, and many other natural processes.
How does light travel?
Light travels in a straight line as a wave or a stream of particles called photons. It can travel through empty space, air, or transparent materials like water or glass due to its electromagnetic nature. When encountering a new substance, light can be absorbed, reflected, refracted, or scattered, which affects its speed and direction of travel.
How is light produced?
Light is produced through the movement of electrons within atoms. When electrons transition between energy levels, they emit photons, which are particles of light. This emission of photons creates electromagnetic waves that we perceive as light.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of radiation has different properties and wavelengths, with some being harmful (such as X-rays and gamma rays) and others being harmless (such as visible light and radio waves).
What are some sources of light?
Some sources of light include the sun, stars, fire, light bulbs, candles, fluorescent lamps, and LEDs.
What is heat?
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between objects or systems due to temperature differences. It flows from a higher temperature object to a lower temperature object, ultimately leading to a balancing of temperatures. Heat can be produced through various processes such as combustion, friction, or nuclear reactions, and is a key factor in many natural phenomena and human technologies.
How is heat transferred?
Heat can be transferred in three main ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when heat is transferred through a material without any movement of the material itself. Convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids like air or water. Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. These three methods work together to transfer heat from one object to another.
What are the three methods of heat transfer?
The three methods of heat transfer are conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material without any movement of the material itself. Convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves without the need for a medium.
How is heat measured?
Heat is typically measured using a unit called the Joule (J) in the International System of Units (SI) or the calorie (cal) in non-SI units. Other common units include British Thermal Units (BTU) and kilowatt-hours (kWh). Heat can be measured using devices such as calorimeters, thermocouples, thermistors, or infrared thermometers, depending on the specific application and the temperature range being measured.
What are some examples of heat sources?
Some examples of heat sources include the sun, fireplaces, stoves, furnaces, electric heaters, and geothermal energy.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments