Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Worksheet
If you're a student studying chemistry and need practice with Lewis structures and covalent bonding, this worksheet is designed to help you solidify your understanding. With a focus on these essential concepts, you'll have a valuable resource that allows you to practice and reinforce your knowledge in a structured and engaging way.
Table of Images 👆
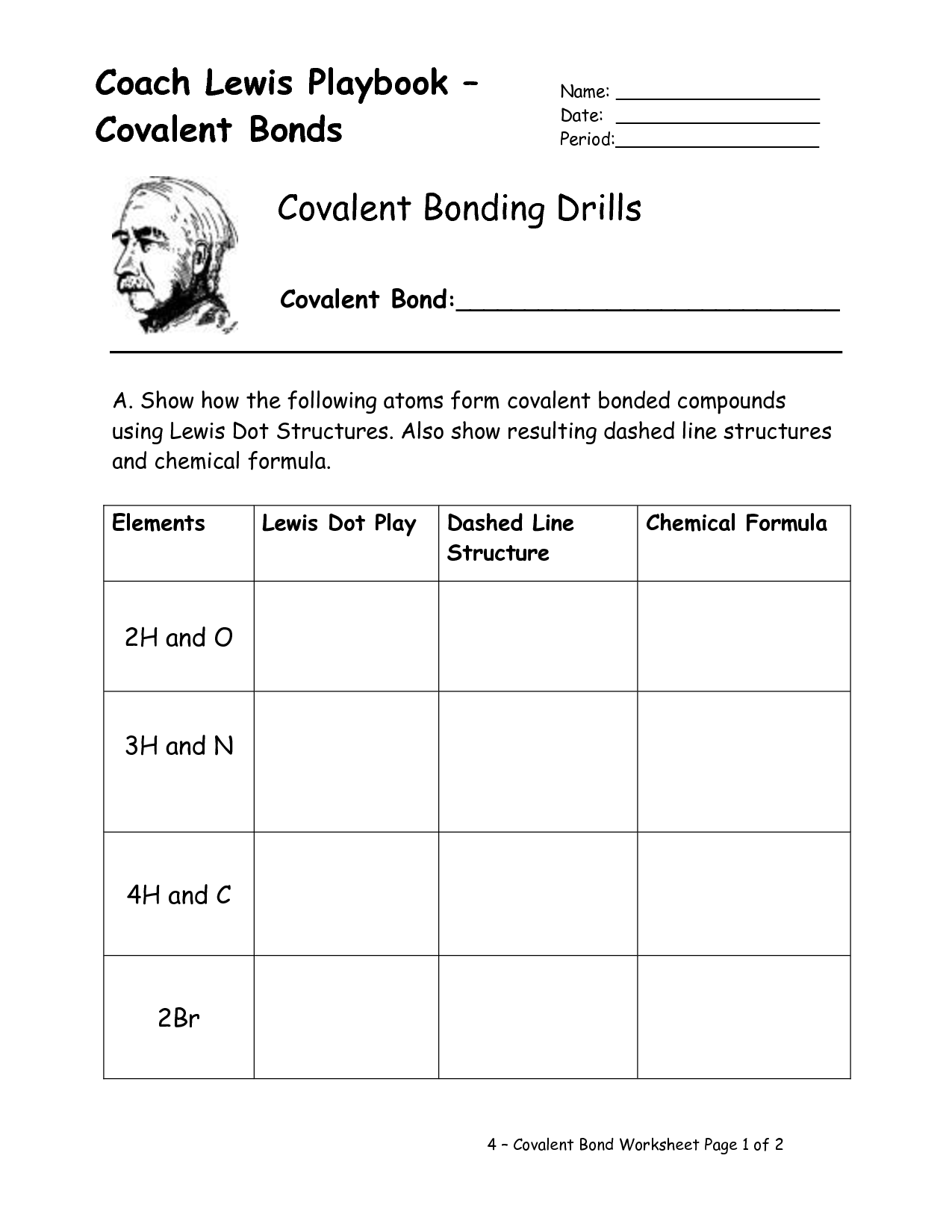
- Lewis Dot Covalent Bond Worksheet
- Lewis Structure Covalent Bond Worksheet
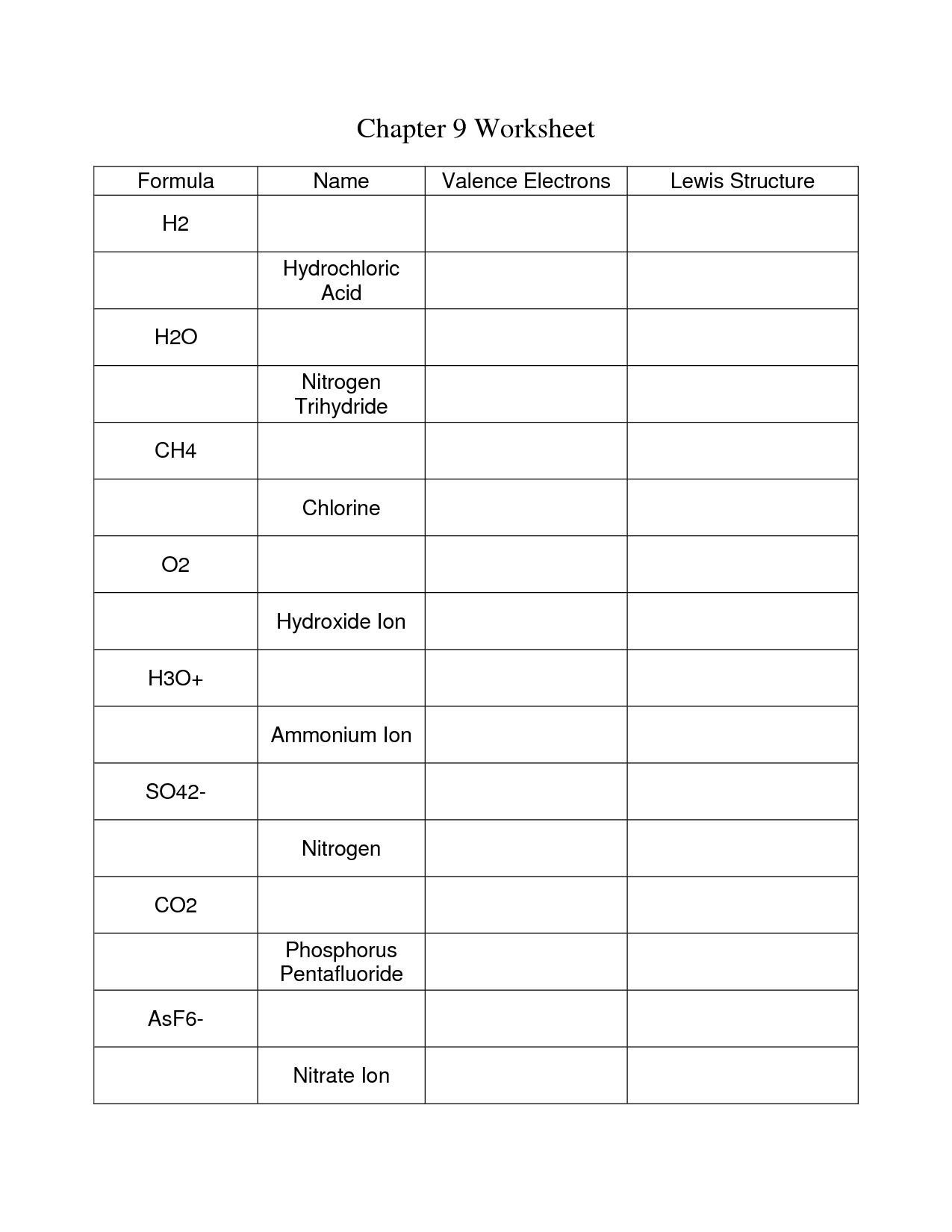
- Covalent Bonding Worksheet Answers
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bond Worksheet
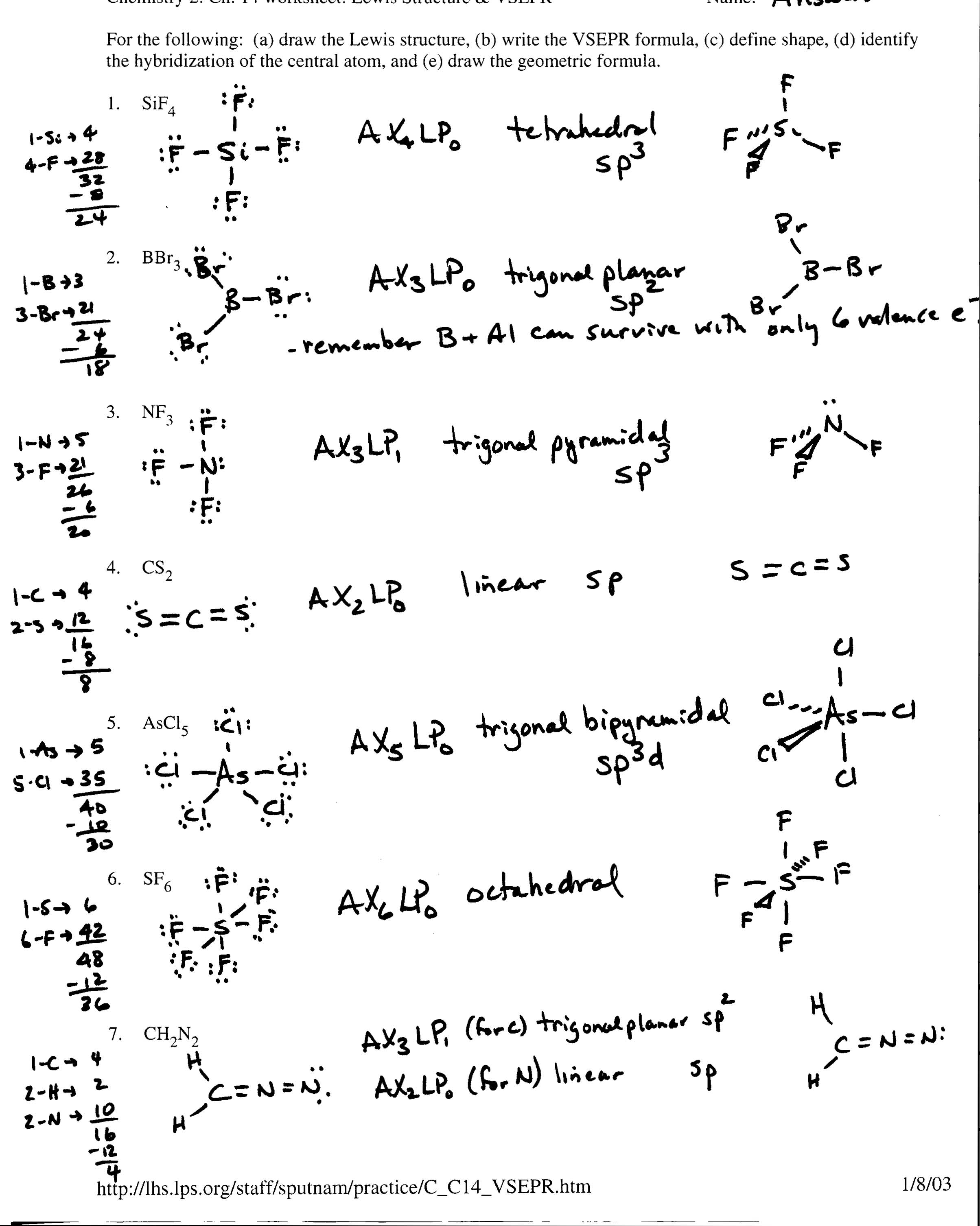
- Lewis Dot Structure Examples
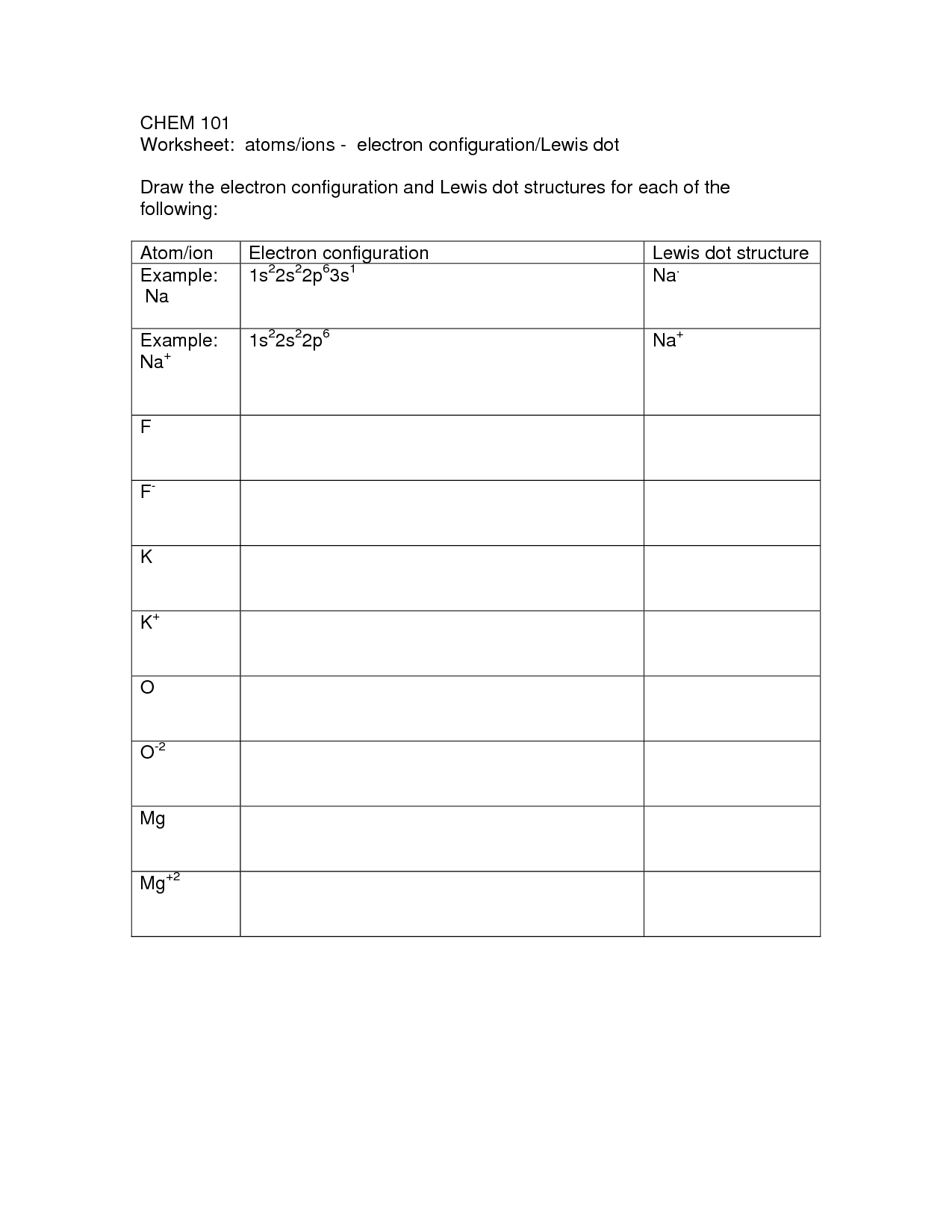
- Lewis Electron Dot Diagram Worksheet
- Lewis Dot Diagram Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Practice Ionic Covalent Compound Worksheet
- Lewis Dot Structure Ionic Compound Worksheet
- Lewis Dot Structure Practice Worksheet
- Lewis Structure Worksheet
- Ionic Covalent Bonding Worksheet
- Ionic Bonding Dot Diagram and Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of Lewis structures in covalent bonding?
The purpose of Lewis structures in covalent bonding is to visually represent the arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule, allowing us to predict the reactivity, polarity, and shape of the molecule. By showing the sharing of electrons between atoms through chemical bonds, Lewis structures provide a framework for understanding the stability and chemical behavior of covalent compounds.
Define covalent bonding and provide an example.
Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bonding where two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration. An example of covalent bonding is the bond between two hydrogen atoms in a molecule of hydrogen gas (H2), where each hydrogen atom shares its single electron with the other to form a covalent bond.
What are valence electrons, and how are they represented in Lewis structures?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in the electron cloud of an atom that are involved in chemical bonding. In Lewis structures, valence electrons are represented as dots around the symbol of the atom. Each dot represents one valence electron, and they are placed around the symbol to show the arrangement of electrons in the outer energy level of the atom. Lewis structures help in understanding how atoms bond with each other to form molecules by showing the sharing or transfer of valence electrons.
Explain how to calculate the total number of valence electrons in a molecule.
To calculate the total number of valence electrons in a molecule, first determine the number of valence electrons for each atom in the molecule based on its group number on the periodic table. Then, add up the total number of valence electrons for all the atoms in the molecule. For example, in a molecule like H2O, oxygen has 6 valence electrons, and each hydrogen has 1 valence electron, so the total number of valence electrons in H2O would be 6 (from oxygen) + 2 (from two hydrogens) = 8 valence electrons.
How is the octet rule applied in Lewis structures?
The octet rule is applied in Lewis structures by ensuring that atoms are surrounded by eight electrons (or two electrons for hydrogen and helium) in order to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to noble gases. This is typically achieved by sharing electrons between atoms to form covalent bonds or by transferring electrons to form ionic bonds, allowing each atom to achieve a full outer valence shell of electrons. The octet rule helps to predict the chemical behavior and stability of molecules based on the arrangement of electrons in their Lewis structures.
What is a single bond, and how is it represented in a Lewis structure?
A single bond is a chemical bond in which one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms. In a Lewis structure, a single bond is represented by a single line between the atoms, indicating the sharing of one pair of electrons.
Define double bond and provide an example.
A double bond is a type of covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. This results in the atoms being held together by two shared pairs of electrons, creating a stronger and more stable bond compared to a single bond. An example of a double bond is found in ethene (C2H4), in which two carbon atoms are bonded together by a double bond.
What is a lone pair, and how is it represented in a Lewis structure?
A lone pair is a pair of valence electrons that are not involved in bonding with other atoms. In a Lewis structure, a lone pair is represented as two dots placed next to the symbol of the atom to which the electrons belong. Lone pairs are important in determining the geometry and reactivity of molecules.
Explain the concept of formal charge and its significance in Lewis structures.
Formal charge is a calculation used in Lewis structures to determine the distribution of electrons in a molecule or ion. It helps to identify the most plausible structure by showing the charge separation within atoms. The significance of formal charge lies in predicting the stability of different resonance structures and determining the most appropriate arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule, which aids in understanding its chemical behavior and reactivity.
What are some limitations or exceptions to the octet rule in Lewis structures?
Some limitations or exceptions to the octet rule in Lewis structures include molecules with an odd number of valence electrons, such as free radicals; molecules with less than an octet of electrons, such as boron (which typically has six valence electrons); and molecules with expanded octets, like sulfur hexafluoride, where the central atom can have more than eight valence electrons due to the presence of d orbitals in the valence shell. These exceptions challenge the traditional concept of the octet rule but are commonly observed in chemical bonding.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments