Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet
Are you a physics student or enthusiast looking to practice and refine your skills in ray diagram analysis? If so, you've come to the right place! In this blog post, we will introduce you to a comprehensive and engaging Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet that will help you gain a thorough understanding of the topic.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a lens?
A lens is a piece of transparent material, usually glass or plastic, that is curved or shaped in a way that light passing through it is refracted or bent. Lenses are commonly used in optical devices such as cameras, eyeglasses, and microscopes to focus light and form images.
How does a convex lens differ from a concave lens?
A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges, bending light rays towards a central focal point to converge them, which is used in magnifying glasses and cameras. On the other hand, a concave lens is thicker at the edges and thinner at the center, causing light rays passing through it to diverge, spreading them out, which is used in correcting myopia.
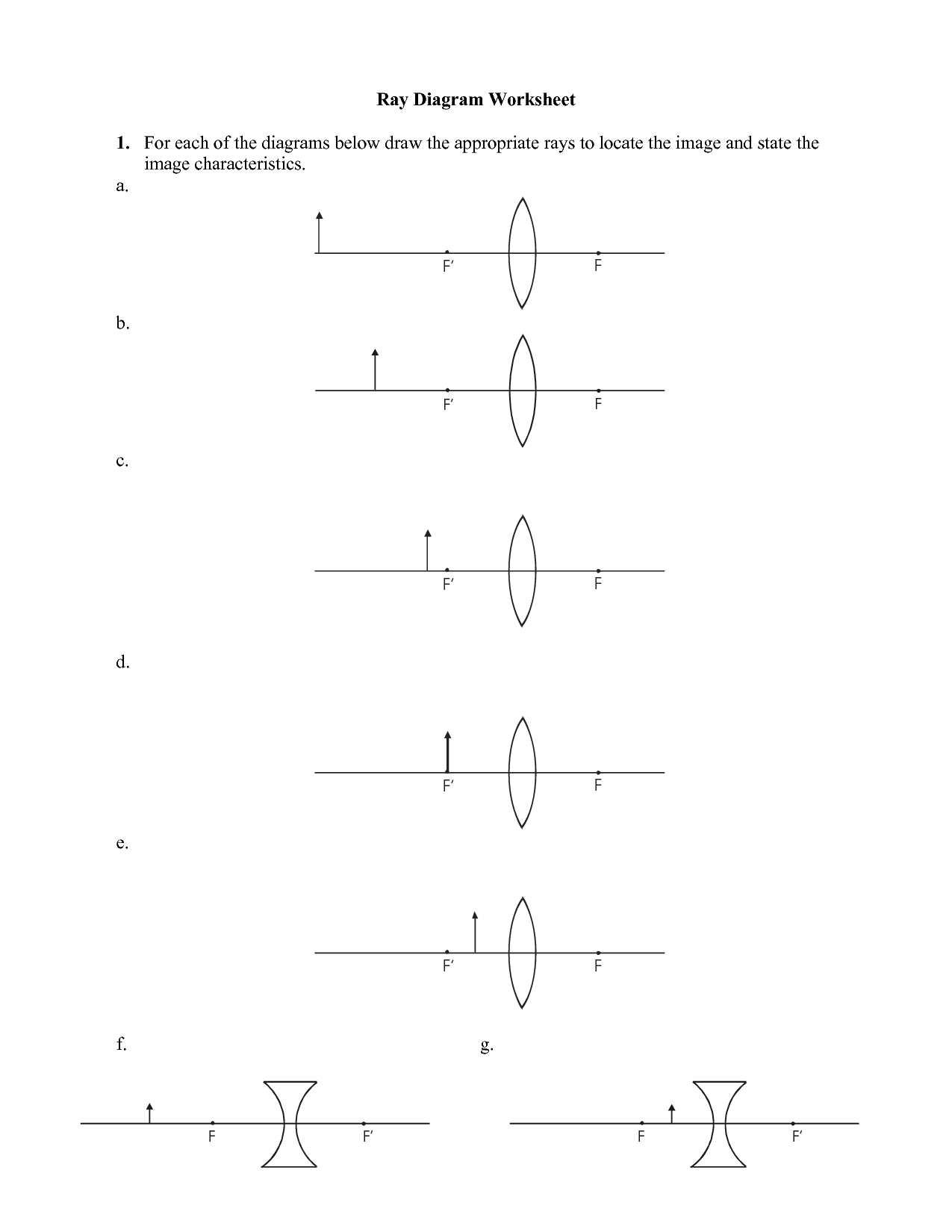
Describe the process of drawing a ray diagram for a convex lens.
To draw a ray diagram for a convex lens, start by drawing a horizontal line to represent the principal axis of the lens. Then, place the lens in the middle of the line, with the convex side facing outward. Draw a vertical line through the center of the lens to represent the optical axis. To locate the focal point on the principal axis, use the lens formula (1/f = 1/v + 1/u), where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance. Draw parallel rays from the top and bottom of the object to the lens; these rays will either refract through the focal point after passing through the lens or appear to converge at the focal point before reaching the lens. Finally, draw a third ray through the center of the lens, which will continue straight without bending. The intersection of these rays will show the position and size of the image formed by the convex lens.
What happens when a ray of light passes through the center of a convex lens?
When a ray of light passes through the center of a convex lens, it continues in a straight line without any deviation. This is because the center of a convex lens is the thinnest part, causing the light to pass through without any bending or refraction.
Explain what happens to a ray of light when it passes through the focal point of a convex lens.
When a ray of light passes through the focal point of a convex lens, it will continue to travel in a straight line and diverge. This is because the focal point is where the parallel rays of light converge after passing through the lens. Therefore, once a ray of light passes through the focal point, it will no longer be focused by the lens and will diverge away from the lens.
How is the image formed when an object is placed beyond the focal point of a convex lens?
When an object is placed beyond the focal point of a convex lens, an inverted and magnified image is formed on the opposite side of the lens. This type of image is known as a real image, as it can be projected onto a screen. The image is also located further away from the lens than the object, in the same direction as the incident light, due to the way the light rays converge after passing through the lens.
Describe how a ray diagram for a concave lens is different from that of a convex lens.
In a ray diagram for a concave lens, the incoming parallel rays diverge after passing through the lens, causing them to appear to originate from the lens's focal point on the same side as the object. This results in virtual, upright, and diminished images being formed. Conversely, in a ray diagram for a convex lens, the incoming parallel rays converge after passing through the lens, meeting at the lens's focal point on the opposite side from the object. This leads to real, inverted, and magnified images being produced.
What happens to a ray of light when it passes through a concave lens?
When a ray of light passes through a concave lens, the light rays are diverged, or spread out. This is because a concave lens is thinner at the center than at the edges, causing the light rays to refract away from each other. As a result, the image formed by a concave lens is virtual, upright, and smaller in size compared to the original object.
Explain how the image is formed when an object is placed in front of a concave lens.
When an object is placed in front of a concave lens, the light rays coming from the object diverge. The concave lens then causes these light rays to spread out even more, resulting in the formation of a virtual and erect image on the same side as the object. The image appears smaller than the object, and it cannot be projected onto a screen as it does not actually exist, but is an optical illusion caused by the refraction of light through the concave lens.
What are the similarities between the ray diagrams for a convex and concave lens?
Both convex and concave lenses have similar ray diagrams, where parallel rays of light will converge at a focal point on the other side of the lens. In addition, rays passing through the center of the lens will continue in a straight line with no deviation. Both lens types also have a focal point on each side of the lens, with the focal length representing the distance between the lens and the focal point.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments