Ionic Bonding Worksheet
If you're searching for a comprehensive and practical resource to solidify your understanding of ionic bonding, look no further than this Ionic Bonding Worksheet. This worksheet is specially designed for students who are studying chemistry and are aiming to strengthen their knowledge and skills in the subject of ionic bonding. With clear explanations and thoughtfully crafted exercises, this worksheet will serve as an excellent tool to reinforce the concepts surrounding ionic bonds.
Table of Images 👆
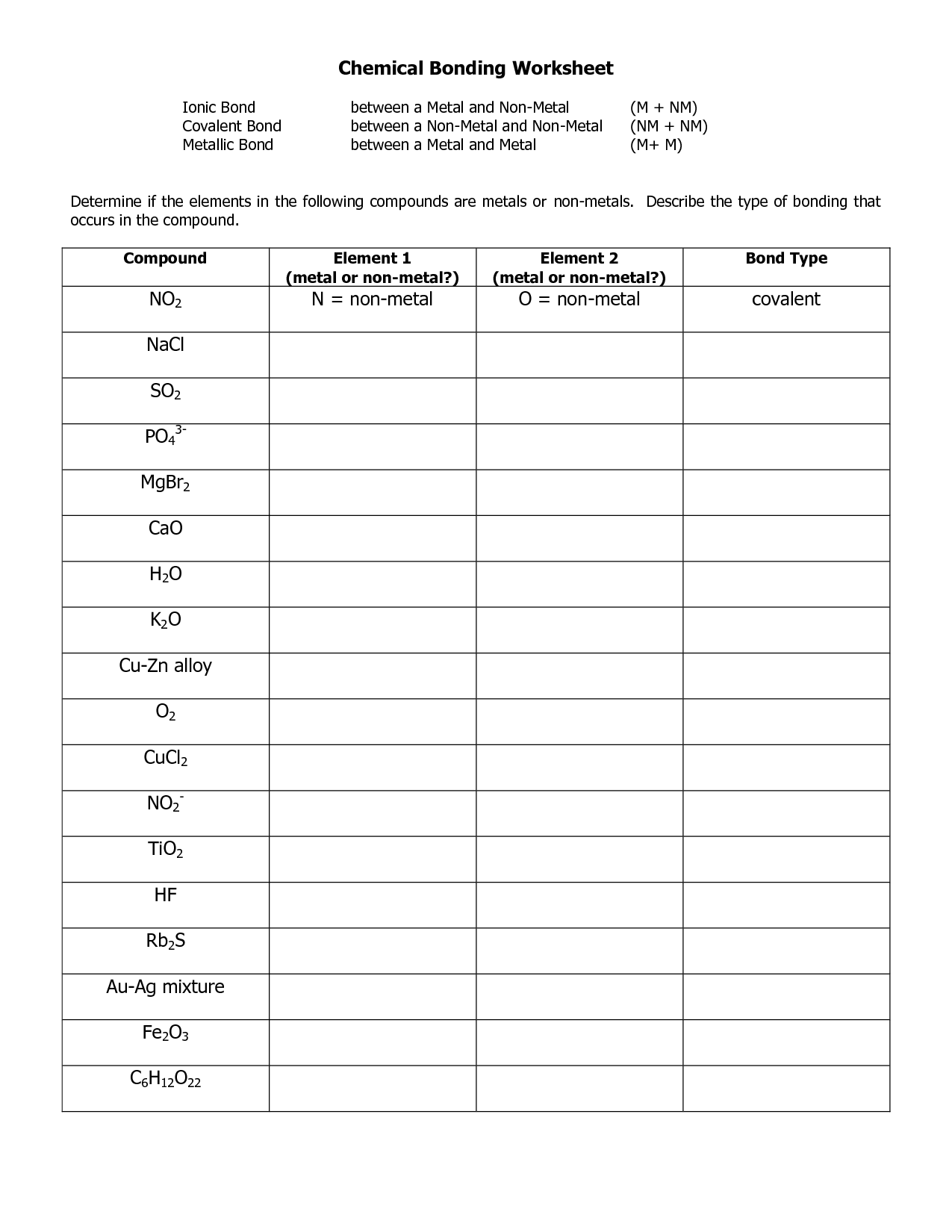
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Worksheet
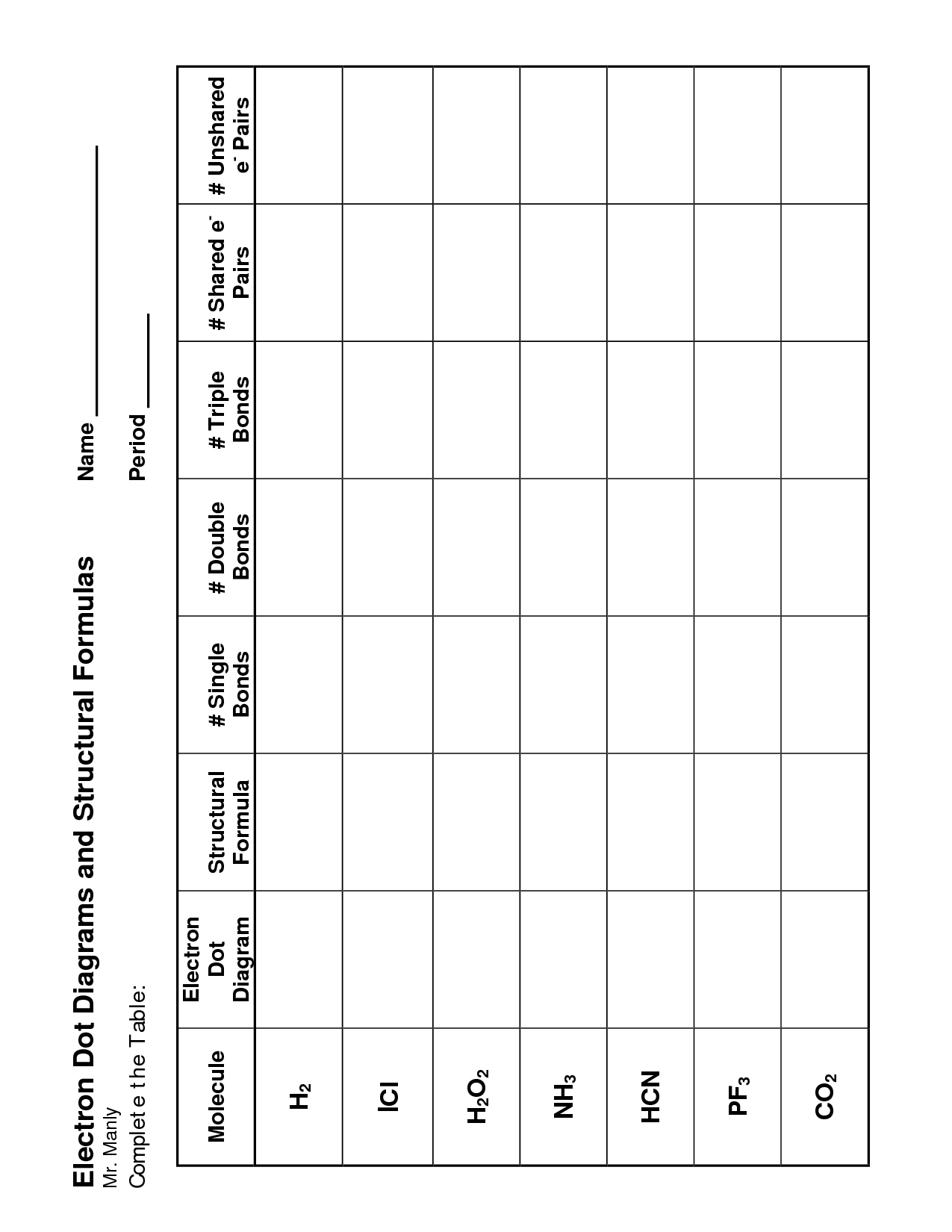
- Ionic Bond Electron Dot Diagram Worksheet
- Formulas with Polyatomic Ions Worksheet Answers
- Ionic Bond Practice Worksheet
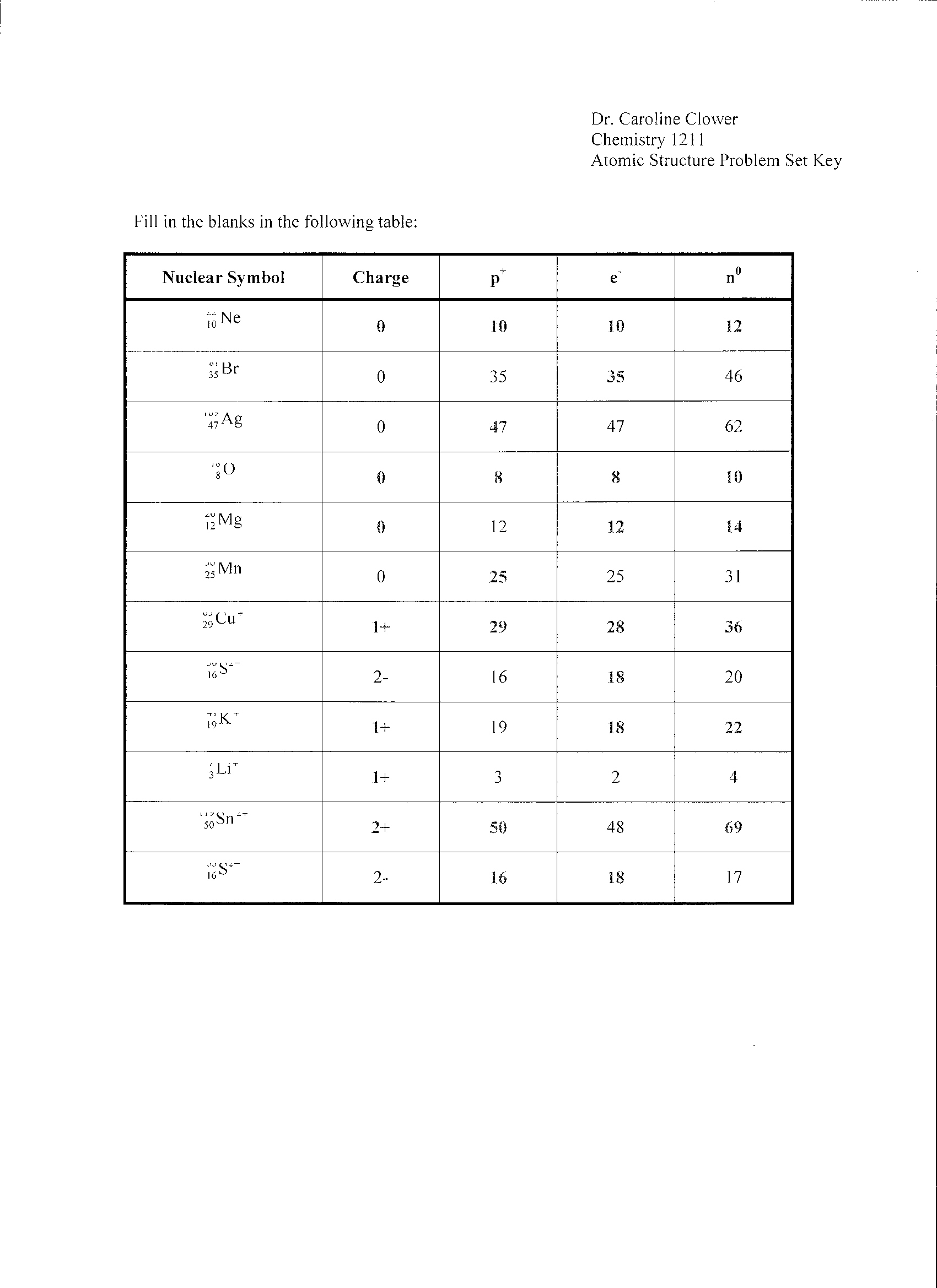
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
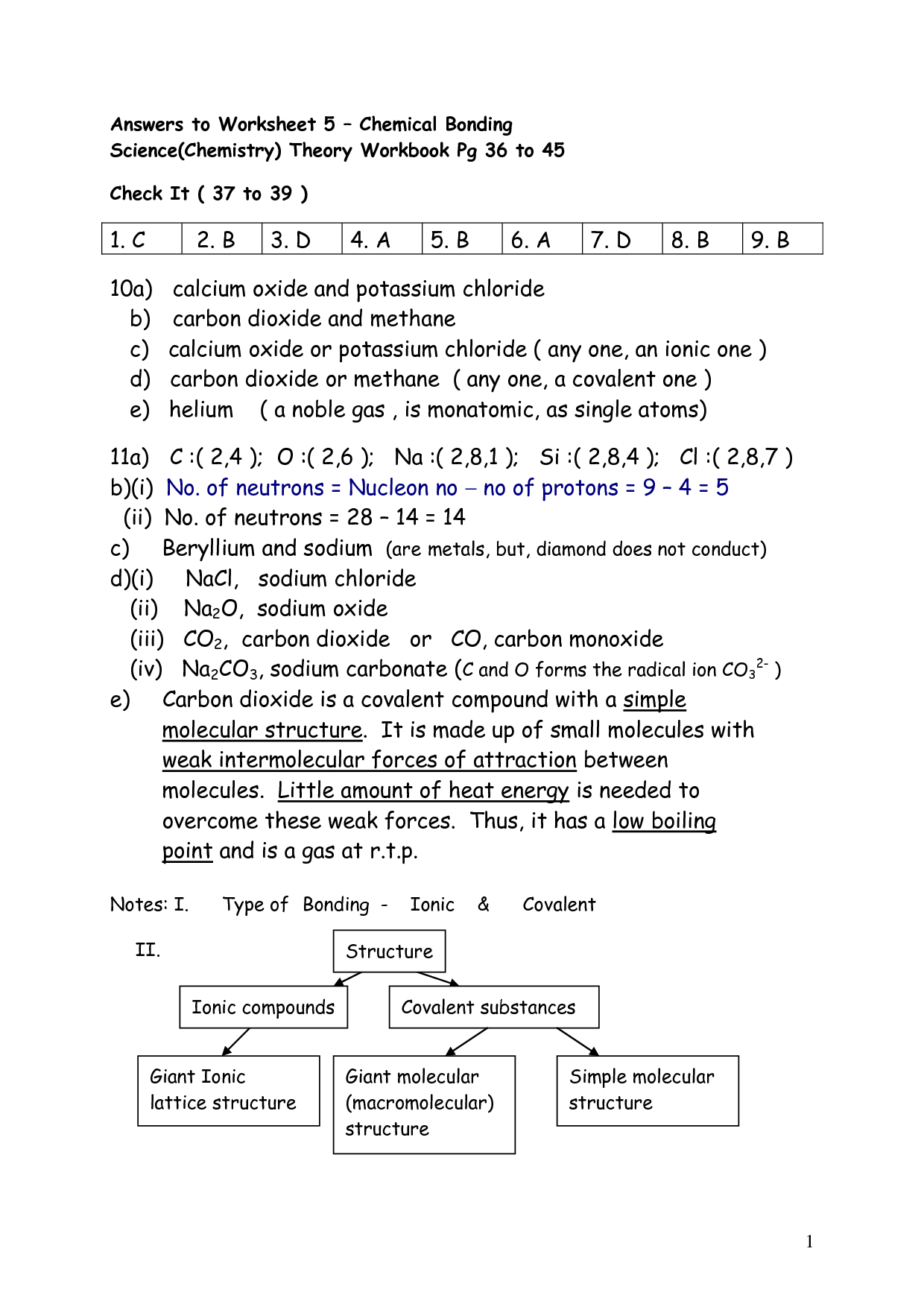
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Ionic Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Bonding Basics Worksheet Answers
- Drawing Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Polar Bonds and Molecules Worksheet Review Answers Section
- Chemistry Molarity and Stoichiometry Worksheet
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Worksheet
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an ionic bond?
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between ions of opposite charges. It occurs when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions that are attracted to each other due to their opposite charges. This attraction holds the two ions together in a stable bond.
How are electrons transferred in an ionic bond?
In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from one atom to another. One atom loses one or more electrons to become positively charged (cation), while the other atom gains those electrons to become negatively charged (anion). The resulting electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions forms the ionic bond, holding the two atoms together in a stable compound.
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Positive ions, known as cations, have lost electrons and negative ions, known as anions, have gained electrons. Ions are important in chemical reactions, biological processes, and electricity conductivity.
How is an ion formed?
An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons, resulting in a positive or negative charge. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion, while if it loses electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. This process can occur through various chemical reactions or interactions with other atoms.
What types of elements typically form ionic bonds?
Ionic bonds are typically formed between elements with significantly different electronegativities, such as metals and nonmetals. Metals tend to lose electrons to form positively charged ions (cations), while nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form negatively charged ions (anions). The strong attraction between these oppositely charged ions leads to the formation of ionic bonds.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
A cation is a positively charged ion, formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. An anion is a negatively charged ion, formed when an atom gains one or more electrons. In summary, cations are positively charged ions and anions are negatively charged ions, with the charge resulting from the gain or loss of electrons by an atom.
How does the size of ions compare to the size of atoms?
Ions are typically larger than atoms due to the addition or removal of electrons, which can alter the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus, resulting in a larger effective size of the ion compared to the neutral atom. This is especially true for ions with multiple charges, where the repulsion between electrons can lead to the ion being significantly larger than the original atom.
Why do ions attract each other?
Ions attract each other because of electrostatic forces. Positively charged ions are attracted to negatively charged ions, creating an overall force of attraction between them. This attraction is a result of the imbalance of charge on the ions, causing them to be attracted to each other in order to achieve a neutral state and lower their potential energy.
How does the strength of an ionic bond compare to other types of bonds?
Ionic bonds are generally stronger than other types of bonds such as covalent and metallic bonds. This is because ionic bonds involve the attraction between oppositely charged ions, which are held together by strong electrostatic forces, leading to a strong bond. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, which may not be as strong as the attraction between ions in an ionic bond, whereas metallic bonds involve delocalized electrons which can be less strong than ionic bonds as well.
How is the formula of an ionic compound determined?
The formula of an ionic compound is determined by balancing the charges of the cations and anions in the compound. Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions. The subscripts in the formula are used to ensure that the total positive charge from the cations balances the total negative charge from the anions. This is done by combining the cations and anions in ratios that cancel out the charges to achieve an electrically neutral compound. The simplest ratio that maintains this charge balance is used to determine the chemical formula of the ionic compound.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments