Integumentary System Worksheets
The integumentary system worksheets provide a comprehensive and structured way to learn and understand the various components and functions of the human skin. Designed for biology students and enthusiasts, these worksheets focus on the entity and subject of the integumentary system, offering a practical and engaging learning resource.
Table of Images 👆
- Matching Anatomy Integumentary System Answers
- Matching Anatomy Integumentary System Worksheet
- Integumentary System Skin Diagram Coloring Page of Of
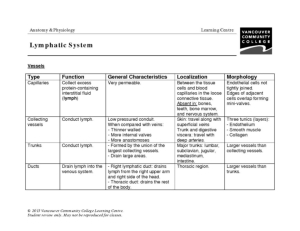
- Lymphatic System Worksheet
- Label Skin Diagram Worksheet
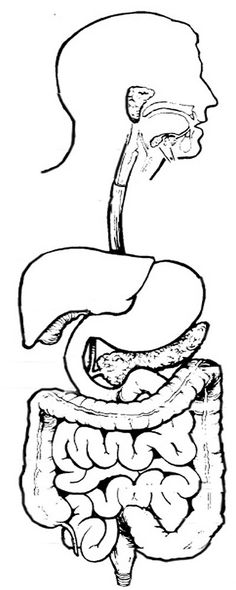
- Digestive System Worksheet
- Small Carousel Horse Cutouts
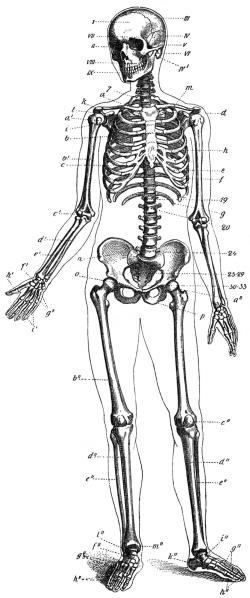
- Human Skeleton Drawing
- Brain Anatomy Diagram Unlabeled
- Female Uterus Anatomy Diagram
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are the main functions of the integumentary system?
The main functions of the integumentary system are protection from external threats, regulation of body temperature, sensation of touch, pressure, temperature, and pain, excretion of waste products through sweat, and synthesis of vitamin D through exposure to sunlight. It acts as a physical barrier to prevent entry of pathogens, regulates body temperature by adjusting blood flow and sweat production, enables the perception of various stimuli through sensory receptors, helps eliminate metabolic waste through sweat, and plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin and overall well-being.
What are the three layers of the skin?
The three layers of the skin are the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The epidermis is the outermost layer that provides protection against the environment, the dermis is located beneath the epidermis and contains hair follicles, sweat glands, and nerve endings, and the subcutaneous tissue (also known as the hypodermis) is the deepest layer that stores fat and provides insulation and padding.
What are the major components of the epidermis?
The major components of the epidermis are keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. Keratinocytes are the most abundant cells and produce the protein keratin, which provides structural strength to the skin. Melanocytes produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color and provides protection against UV radiation. Langerhans cells are part of the immune system and help defend against pathogens, while Merkel cells are involved in the sensation of touch.
How does the skin protect the body from pathogens?
The skin serves as a physical barrier that prevents pathogens from entering the body. It is composed of multiple layers of cells that are tightly packed together, making it difficult for pathogens to penetrate. Additionally, the skin produces antimicrobial substances that help to kill or inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The skin also plays a role in the immune response by activating immune cells when pathogens are detected. Overall, the skin's complex structure and defenses work together to protect the body from harmful invaders.
What is the role of sebaceous glands in the integumentary system?
Sebaceous glands in the integumentary system are responsible for producing sebum, an oily substance that helps to moisturize and protect the skin. Sebum is important for maintaining the skin's barrier function and preventing it from becoming dry and cracked. Additionally, sebum helps to lubricate the hair follicles and skin, as well as providing some protection against harmful bacteria and fungi.
What is the function of sweat glands?
Sweat glands are responsible for producing sweat, which helps regulate body temperature by cooling the skin through evaporation. They also play a role in excreting waste products, maintaining electrolyte balance, and helping to protect the skin by flushing out toxins and bacteria.
How does the skin help regulate body temperature?
The skin helps regulate body temperature through a process called thermoregulation. This involves the dilation or constriction of blood vessels in the skin, which allows for heat to be released or retained. Additionally, sweat glands in the skin produce sweat, which evaporates and helps to cool the body. The skin also contains sensory receptors that detect changes in temperature and signal the brain to initiate appropriate responses to maintain a stable internal temperature.
What are the four types of mechanoreceptors found in the skin?
The four types of mechanoreceptors found in the skin are Merkel discs, Meissner's corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, and Ruffini endings. Merkel discs detect pressure and texture, Meissner's corpuscles sense light touch and vibration, Pacinian corpuscles are sensitive to deep pressure and high-frequency vibrations, while Ruffini endings respond to skin stretch and continuous pressure. Together, these mechanoreceptors play a crucial role in transmitting sensory information related to touch, pressure, and vibration to the brain.
How does the integumentary system participate in vitamin D synthesis?
The integumentary system plays a crucial role in vitamin D synthesis through the production of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) in the skin. When the skin is exposed to UVB radiation from sunlight, a cholesterol derivative in the skin is converted into previtamin D3, which is then further transformed into vitamin D3. This vitamin D3 then travels to the liver and kidneys for further modifications to become the active form of vitamin D that is used by the body for various physiological functions, including regulating calcium and phosphate levels for bone health.
What are some common disorders or diseases that can affect the integumentary system?
Some common disorders or diseases that can affect the integumentary system include acne, eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, skin cancer, fungal infections, hives, and cold sores. Additionally, conditions such as alopecia (hair loss), vitiligo (loss of skin pigment), and keloids (raised scars) can also impact the health and appearance of the skin, hair, and nails.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments