Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet
Are you a biology student or science enthusiast seeking a comprehensive resource to enhance your understanding of macromolecules? Look no further! We have designed the perfect Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet specifically for you. This worksheet is tailored to help you grasp the concept of macromolecules and their distinct characteristics. With clear explanations and engaging exercises, this worksheet is ideal for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of this fundamental topic.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
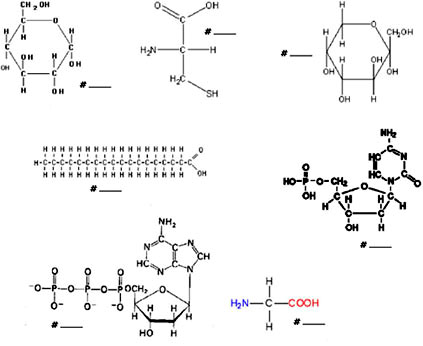
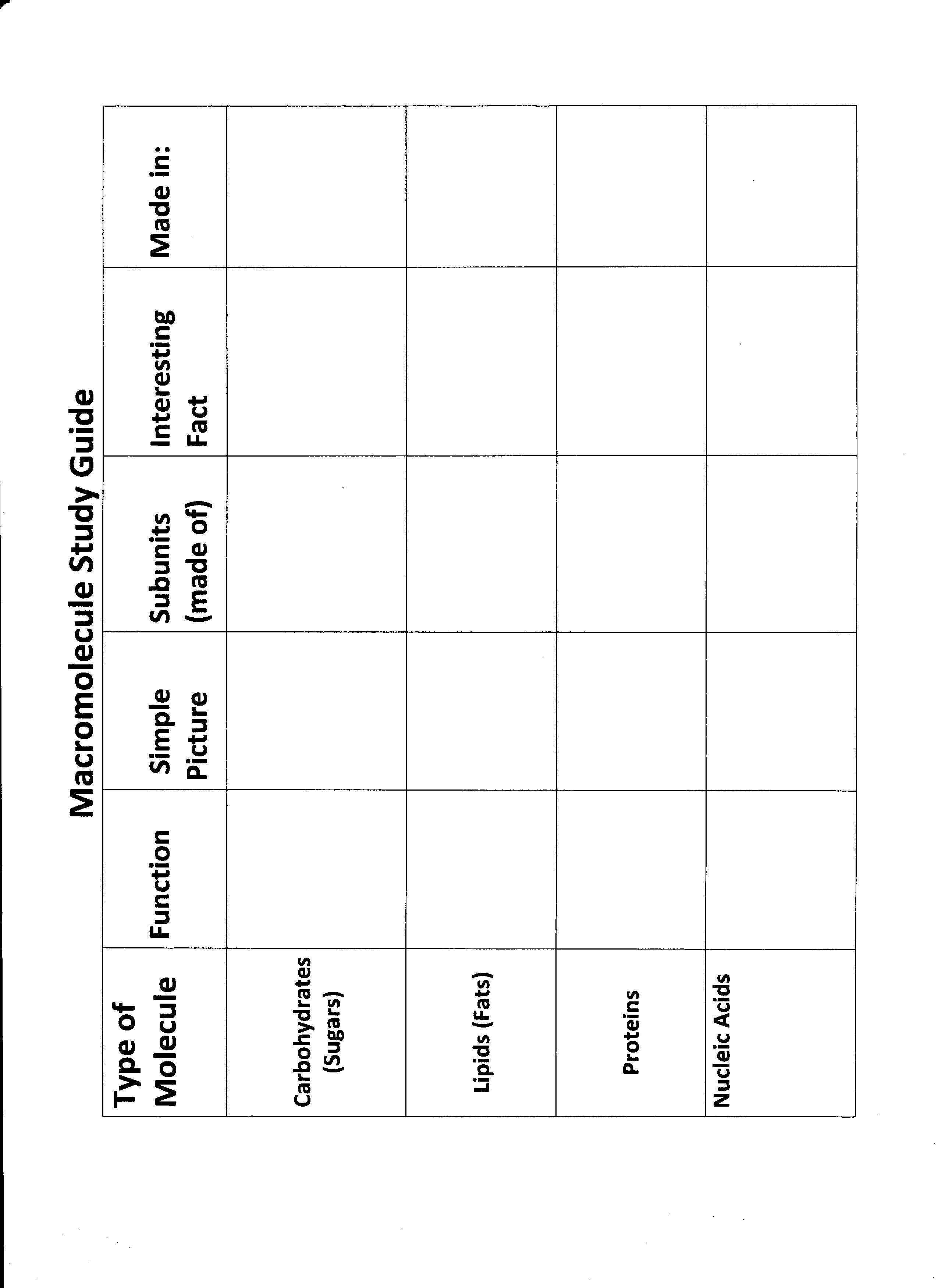
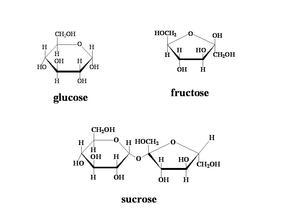
What is the main function of carbohydrates?
The main function of carbohydrates is to provide the body with a source of energy. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is used by cells as a primary source of fuel for various bodily functions, including muscle contraction, brain activity, and overall metabolism.
What is the structural unit of carbohydrates?
The structural unit of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide, which is a simple sugar molecule such as glucose, fructose, or galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates like polysaccharides and disaccharides.
Which molecule serves as the primary source of energy for living organisms?
The molecule that serves as the primary source of energy for living organisms is adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is produced during cellular respiration and is used by cells to carry out various biological processes, such as growth, repair, and movement.
What is the main function of proteins?
Proteins play a vital role in the body by serving as structural components of tissues, enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions, carriers of molecules such as oxygen, and as antibodies that help fight infections and diseases. Overall, the main function of proteins is to regulate, coordinate, and support essential processes in the body to maintain overall health and function.
What is the structural unit of proteins?
The structural unit of proteins is amino acids. Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids that are linked together by peptide bonds. There are 20 different amino acids that are commonly found in proteins, each with its own unique side chain that contributes to the structure and function of the protein.
How do proteins differ from carbohydrates and lipids?
Proteins differ from carbohydrates and lipids in terms of their structural composition and functions. Proteins are polymers made up of amino acids, which are essential for various biological functions including enzymes, hormones, and structural components in cells. Carbohydrates, on the other hand, are composed of sugars and are primarily used as a source of energy in the body. Lipids are characterized by their hydrophobic nature and include fats, oils, and cholesterol, serving important roles in energy storage, insulation, and cell membrane structure. Overall, while all three macromolecules are essential for the body, they have distinct structures and functions within biological systems.
What is the main function of lipids?
The main function of lipids is to store energy, insulate the body, cushion organs, and act as structural components of cell membranes.
What is the structural unit of lipids?
The structural unit of lipids is a molecule called a fatty acid, which consists of a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylic acid group at one end. Lipids are biologically important molecules that serve various functions in living organisms, including energy storage, cell membrane structure, and signaling pathways.
How are lipids different from carbohydrates and proteins?
Lipids are different from carbohydrates and proteins in their chemical structure and functions. Lipids are hydrophobic molecules made primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and include fats, oils, and cholesterol. They serve as a concentrated energy source, insulation, and are key components of cell membranes. In contrast, carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio, and are primarily used as a quick energy source and structural support. Proteins are made up of amino acids and play various roles in the body, including enzyme functions, structural support, and immune system function.
What is the main function of nucleic acids?
The main function of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, is to store and transmit genetic information within cells. DNA carries the genetic instructions necessary for growth, development, and functioning of all living organisms, while RNA plays a key role in protein synthesis by carrying out the instructions encoded in DNA.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments