Holt Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
Are you searching for a reliable answer key for the Holt Chemical Bonding worksheet? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with a detailed answer key that covers all the important concepts and questions included in the worksheet. Whether you are a student studying chemistry or a teacher looking for a valuable resource to assess your students' understanding, this answer key will be a helpful tool to guide you through the learning process.
Table of Images 👆
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Matter Worksheet Answer Key
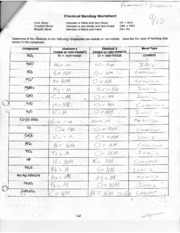
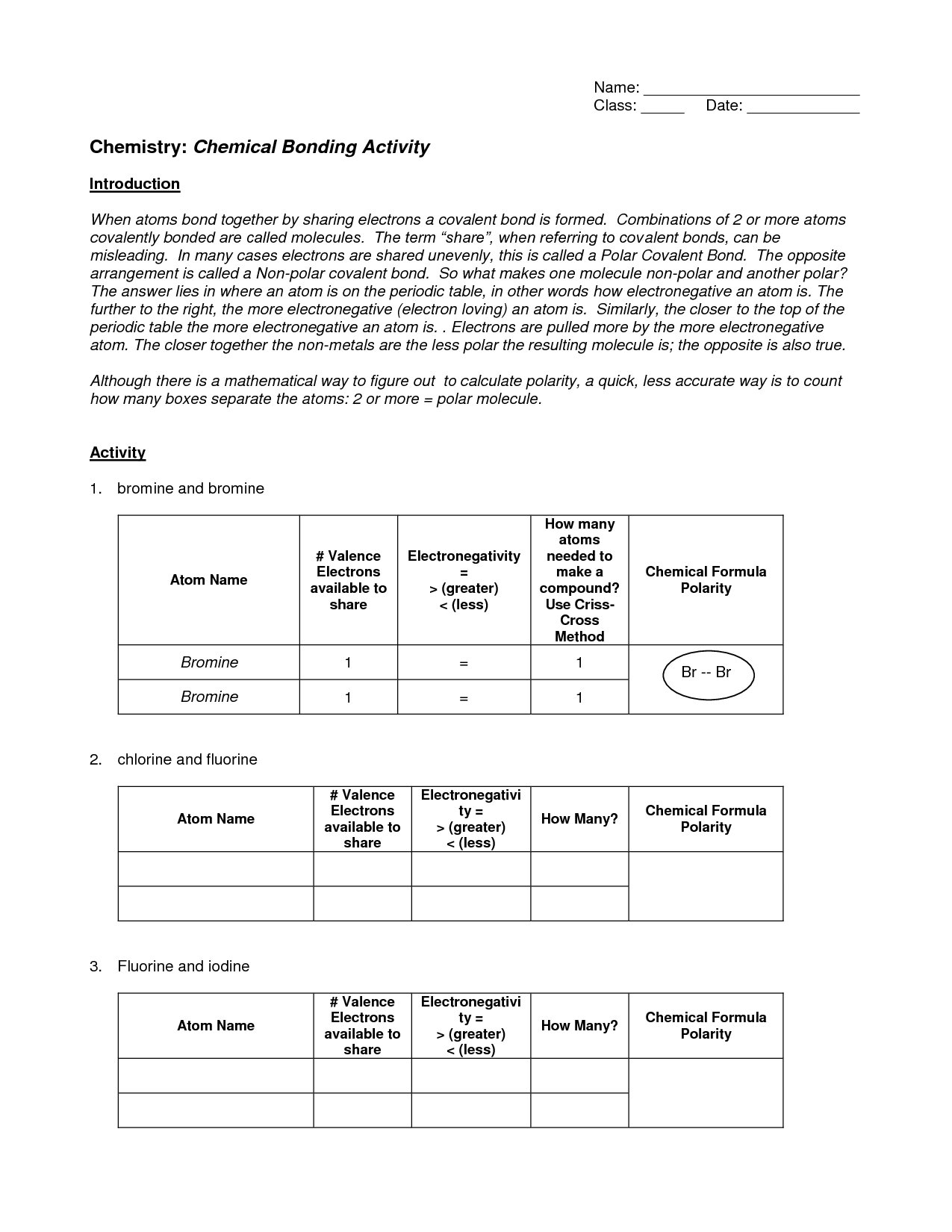
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answers Activity
- Directed Reading for Content Mastery Answers
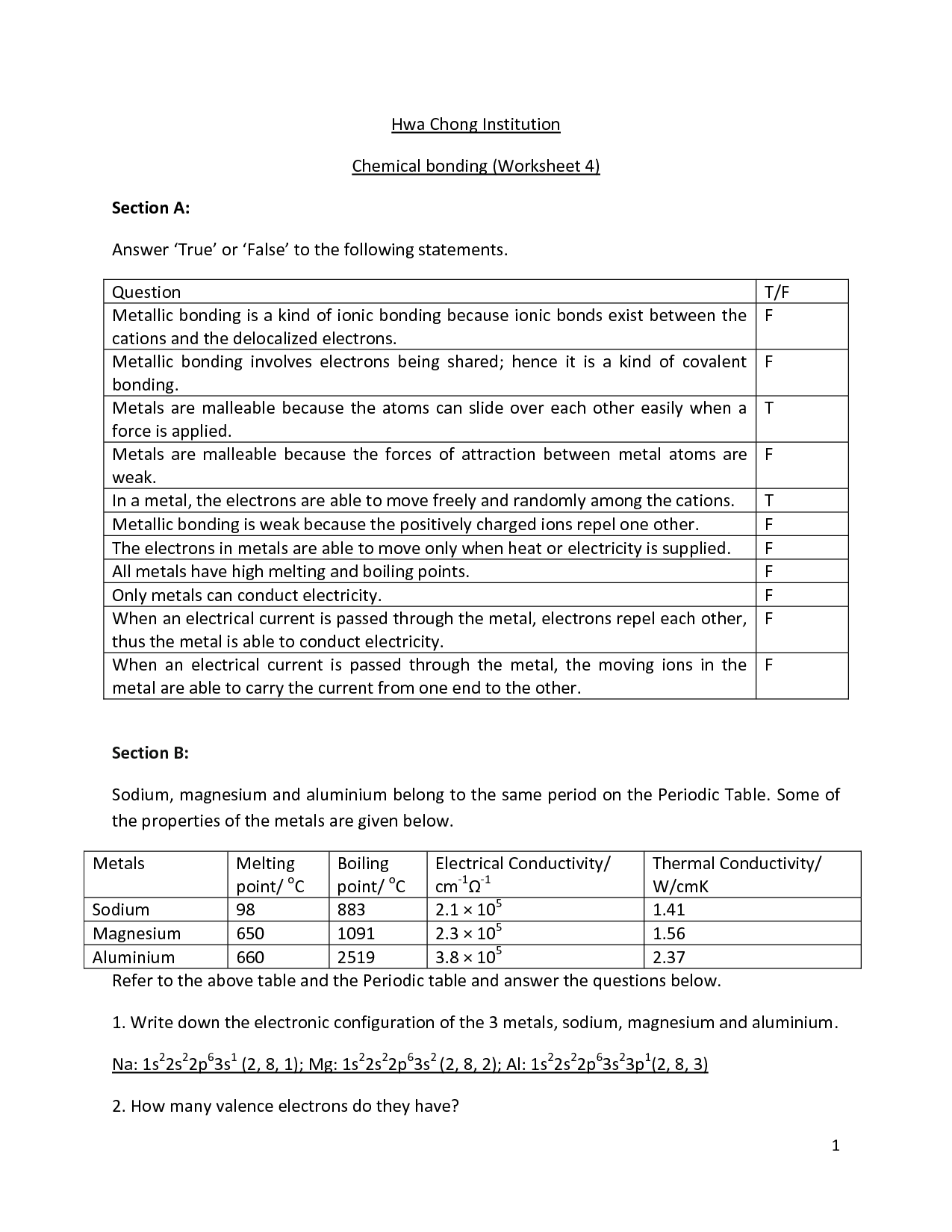
- Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answers
- Chemistry of Life Answer Key Chapter 2
- Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Worksheet
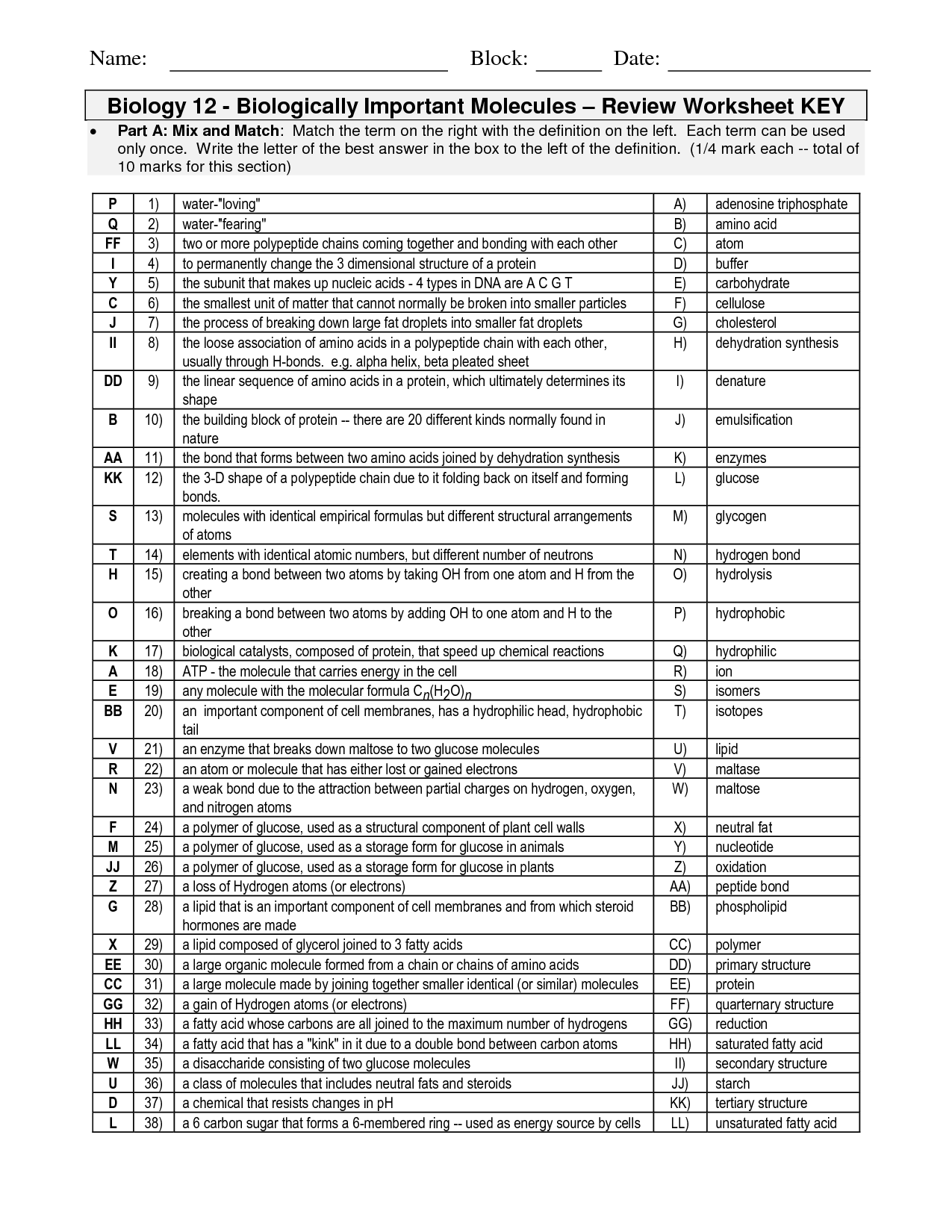
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are chemical bonds?
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in a molecule. These bonds are formed when atoms share, donate, or receive electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. There are three main types of chemical bonds: covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds, each with its own set of properties and behaviors. Chemical bonds are crucial for the formation of compounds and play a fundamental role in determining the physical and chemical properties of substances.
What are the three types of chemical bonds?
The three types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, and metallic bonds involve a sea of delocalized electrons shared between a lattice of metal atoms.
How do ionic bonds form?
Ionic bonds form when one atom donates an electron to another atom, resulting in one atom becoming positively charged (cation) and the other becoming negatively charged (anion). The attraction between these opposite charges then holds the two atoms together in a stable bond.
What is the difference between covalent and polar covalent bonds?
The main difference between covalent and polar covalent bonds is the sharing of electrons. In a covalent bond, electrons are shared equally between atoms, resulting in a nonpolar molecule. On the other hand, in a polar covalent bond, electrons are shared unequally, leading to a partial negative charge on one atom and a partial positive charge on the other atom, creating a polar molecule. This difference in electron sharing causes variations in the strength and properties of the bonds.
What is electronegativity and how does it affect bond polarity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond. It affects bond polarity by determining how the electrons are shared between atoms. When two atoms with different electronegativities form a bond, the shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, creating a polar or uneven distribution of charge within the bond. This results in the formation of polar covalent bonds, where one atom has a partial negative charge and the other has a partial positive charge.
How are Lewis structures used to determine bond formation?
Lewis structures are used to determine bond formation by showing how atoms within a molecule are connected through the sharing or transfer of electrons. By following the octet rule and arranging electrons around atoms, Lewis structures help to visualize the types of bonds (covalent, ionic) formed between atoms, as well as the overall structure and geometry of the molecule. The presence of lone pairs and formal charges in Lewis structures also provide insights into the stability and reactivity of molecules, ultimately helping to predict and understand bond formation.
What is the octet rule and how does it relate to chemical bond formation?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to have a full outer shell of 8 electrons, similar to the noble gases. This rule relates to chemical bond formation by guiding how atoms interact with each other to achieve stability. Atoms will form chemical bonds with other atoms to either gain, lose, or share electrons to reach this stable octet configuration. Covalent bonds involve a sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds involve a transfer of electrons. By following the octet rule, atoms are able to form more stable molecules and compounds.
What is a metallic bond and what are its properties?
A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond that exists between atoms in a metal. In metallic bonds, electrons are shared equally among all the atoms, forming a sea of electrons that are free to move throughout the metal's structure. This gives metals several properties, including high electrical conductivity, high thermal conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster. Metals also tend to have high melting and boiling points due to the strength of metallic bonds holding the atoms together.
How does bond length and strength vary across the periodic table?
Bond length and strength vary across the periodic table due to differences in atomic size, electronegativity, and the type of bond being formed. Generally, as you move down a group in the periodic table, bond length increases due to the addition of energy levels and atomic size. In contrast, as you move from left to right across periods, bond strength increases due to higher electronegativity values, leading to greater attraction between atoms. Additionally, the type of bond (such as covalent, ionic, or metallic) also plays a significant role in determining bond length and strength within different regions of the periodic table.
How can intermolecular forces affect the physical properties of substances?
Intermolecular forces determine the physical properties of substances by influencing how molecules interact with each other. Stronger intermolecular forces lead to higher boiling points, melting points, and viscosity since more energy is required to overcome these forces. Additionally, the type of intermolecular forces present can affect other properties such as solubility, surface tension, and volatility. Overall, intermolecular forces play a crucial role in the behavior of substances in different states of matter.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments