High School Environmental Science Worksheets
If you're a high school student studying environmental science, you may be searching for supplemental resources to enhance your learning experience. One valuable tool that can support your understanding of important concepts are worksheets specifically tailored to the subject. Worksheets provide an organized and structured format for practicing and applying knowledge, making them a useful entity for high school environmental science students.
Table of Images 👆
- Science Lab Safety Worksheets High School
- Science Research Paper Worksheets
- Forensic Science Worksheets High School
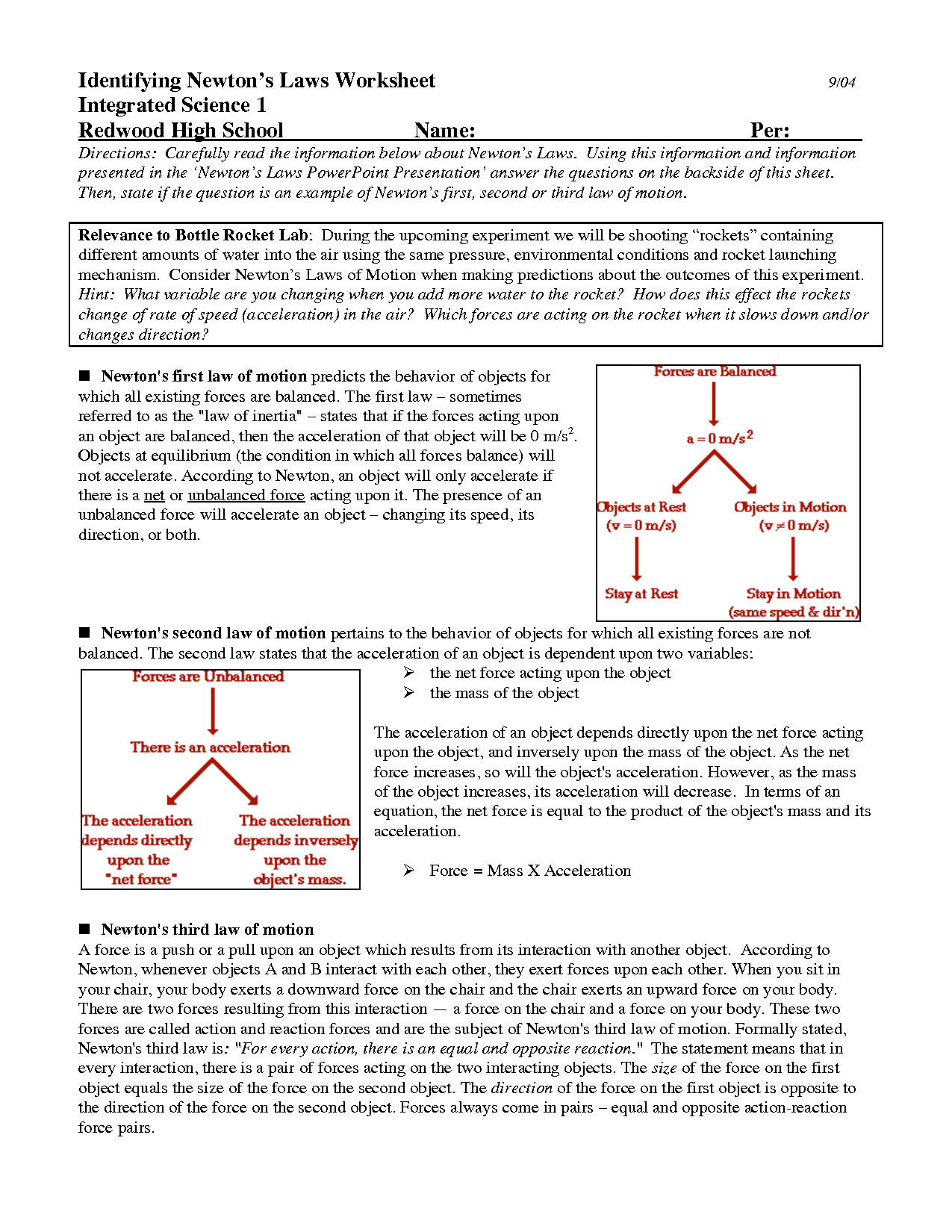
- Physical Science Newtons Laws Worksheet Answers
- Environmental Science Lorax Worksheet
- Water Pollution Worksheets High School
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets High School
- Physical Evidence Forensic Science Worksheet
- High School Science Worksheets
- Middle School Science Worksheets
- Editing Paragraphs Worksheet High School
- AP Environmental Science
- Holt Environmental Science Worksheets Answers
- Environmental Science Worksheets Printable
- Environmental Science Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Newtons Laws Worksheet High School
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
What is the definition of environmental science?
Environmental science is the interdisciplinary study of the environment, encompassing the biological, physical, and social sciences, aimed at understanding the natural world and the interactions between humans and the environment. It involves assessing, analyzing, and addressing environmental issues and challenges to promote sustainability and conservation of natural resources for future generations.
Describe the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources.
Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished or regenerated within a human lifetime, such as solar power, wind energy, and biomass. On the other hand, nonrenewable resources are finite and cannot be replaced once they're depleted, like fossil fuels and minerals. The key distinction is that renewable resources can be naturally restored over time, while nonrenewable resources are exhaustible and will eventually run out.
Explain the concept of ecological succession.
Ecological succession is the gradual process through which ecosystems change and develop over time. It involves a series of predictable stages that occur in response to disturbances such as fires, floods, or human activities. The process starts with pioneer species colonizing an area and eventually giving way to more complex and diverse communities. As the environment stabilizes and conditions change, different species better adapted to those conditions replace earlier ones, leading to a more mature and diverse ecosystem. Ultimately, ecological succession leads to a climax community that is in a state of balance and represents a stable endpoint of the succession process.
Describe the greenhouse effect and its impact on the Earth's climate.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming effect on the planet. These gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, allow sunlight to enter and heat the Earth's surface, but then trap some of that heat as it tries to escape back into space. While the greenhouse effect is essential for regulating the Earth's temperature and making it habitable, human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to enhanced global warming and climate change. The impact includes rising temperatures, melting ice caps, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems, posing serious challenges for both humans and the environment.
What are the major factors contributing to air pollution?
The major factors contributing to air pollution include emissions from vehicles, industrial processes, power plants, wildfires, and agricultural activities. These sources release pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, volatile organic compounds, and carbon monoxide into the atmosphere, leading to poor air quality and negative health impacts. In addition, natural factors such as dust storms and volcanic eruptions can also contribute to air pollution.
Explain the process of eutrophication and its effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Eutrophication is the process where excessive nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus enter aquatic ecosystems, leading to an overgrowth of algae and plant life. This excessive growth depletes oxygen levels in the water as the plants die and decompose, causing hypoxia or low oxygen levels in the water, which can lead to fish kills and harm other aquatic organisms. Eutrophication can also disrupt the balance of the ecosystem by altering water quality, reducing biodiversity, and promoting harmful algal blooms, ultimately leading to a decline in overall aquatic ecosystem health and productivity.
Describe the various methods of solid waste management.
Solid waste management methods include waste minimization, recycling, composting, incineration, and landfilling. Waste minimization involves reducing waste generation through source reduction and reuse. Recycling involves converting waste materials into new products to prevent waste of potentially useful materials. Composting is the biological decomposition of organic waste into valuable soil amendments. Incineration is the combustion of waste materials to convert them into heat, ash, gas, and heat. Landfilling involves burying waste in designated landfill sites to reduce the environmental impact and potential health hazards of waste.
What is biodiversity and why is it important for ecosystem stability?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms within an ecosystem, including different species, genetic diversity, and the variety of habitats. Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem stability as it promotes resilience to environmental changes and disturbances. A diverse ecosystem is better able to adapt to disruptions, such as climate change, diseases, or natural disasters. Different species play unique roles in maintaining ecosystem functions, such as nutrient cycling, pollination, and pest control. A loss of biodiversity can disrupt these interactions, leading to negative impacts on ecosystem health and ultimately affecting human well-being. Overall, biodiversity is essential for maintaining the balance and stability of ecosystems.
Explain the concept of sustainable development and provide an example.
Sustainable development is the practice of meeting current environmental, economic, and social needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves responsibly managing resources to ensure long-term viability while promoting equity and preserving environmental health. An example of sustainable development is the installation of solar panels in a community to generate clean energy, reduce carbon emissions, and decrease dependence on fossil fuels, thus contributing to both environmental preservation and economic growth in a sustainable way.
Describe the main causes and consequences of deforestation.
Deforestation is primarily caused by agricultural expansion, logging, and urbanization, leading to the clearing of forests for these purposes. The consequences of deforestation include loss of biodiversity, disruption of ecosystems, acceleration of climate change due to decreased carbon sequestration, and increased soil erosion and flooding. Deforestation also impacts indigenous communities and contributes to the extinction of species and the loss of vital ecosystem services essential for human well-being.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



































Comments