Heat Worksheet First Grade Free
Worksheets are a valuable educational tool for first-grade students to reinforce their understanding of various subjects. With interactive activities and engaging exercises, worksheets provide an excellent opportunity for young learners to develop their skills in a fun and effective manner. When it comes to teaching the concept of heat, first-grade students can benefit greatly from free heat worksheets designed specifically for their level of understanding.
Table of Images 👆
More 1st Grade Worksheets
First Grade Reading Comprehension WorksheetsTelling Time Worksheets for First Grade
Math Worksheets Subtraction 1st Grade
For First Grade Addition Worksheets
First Grade Handwriting Practice Worksheets
First Grade Fraction Worksheets
Free Printable Phonics Worksheets First Grade
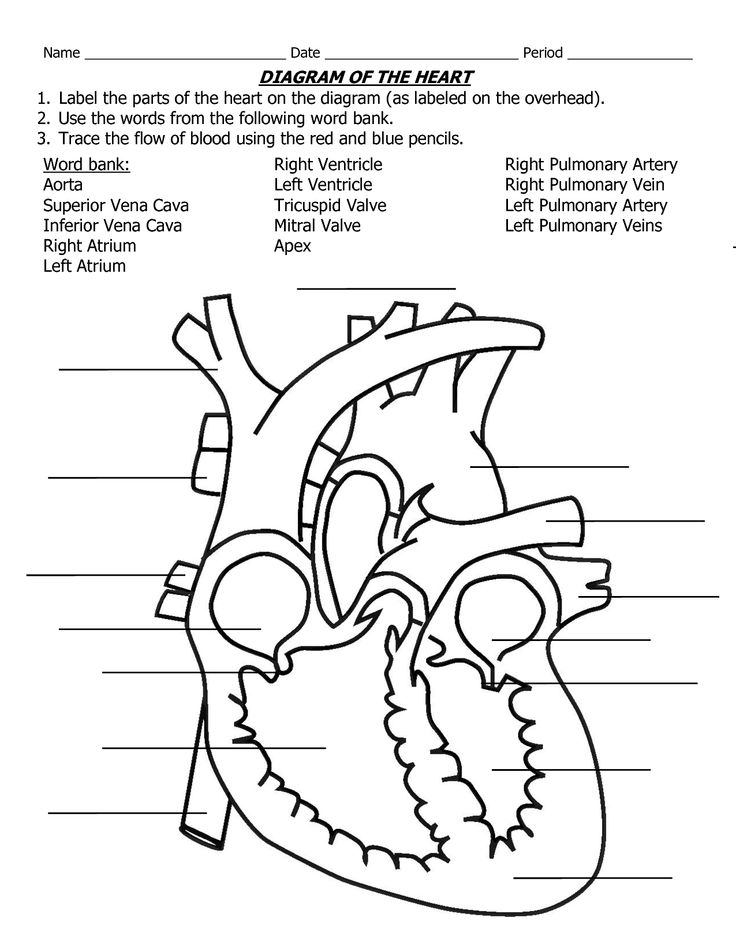
Heart Worksheets for First Grade
First Grade Science Worksheets Matter
Following Directions First Grade Worksheets
What is heat?
Heat is a form of energy that results from the movement of atoms and molecules within a substance. It is transferred from one object to another due to a temperature difference, typically flowing from hotter objects to cooler ones. Heat plays a crucial role in various natural processes and is important for cooking, heating, and powering many technologies.
How does heat travel?
Heat can travel through three main processes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material or between materials that are in direct contact. Convection occurs when heat is transferred through the movement of liquids or gases. Radiation involves the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation, which can travel through vacuum.
What are some sources of heat?
Sources of heat include the sun, fire, electrical heaters, stoves, furnaces, burning fossil fuels like coal or oil, geothermal energy, and even the human body which generates heat as a byproduct of metabolism.
How do we feel heat?
We feel heat through a process called thermoreception, which involves specialized nerve endings called thermoreceptors in our skin that detect changes in temperature. When these receptors sense heat, they send signals to the brain via the nervous system, which then interprets this information as the sensation of warmth or heat.
What are some ways to keep warm in cold weather?
To stay warm in cold weather, you can dress in layers, wear a hat and gloves to prevent heat loss from your head and hands, drink warm beverages, stay active to generate body heat, use blankets and quilts when indoors, and make sure to seal any drafts in your home to retain heat.
How does heat affect materials?
Heat can affect materials in various ways depending on their composition and structure. In general, increased heat can cause materials to expand, change phase (solid to liquid to gas), lose strength, soften, deform, or even burn or decompose. Thermal expansion can lead to dimensional changes, while phase changes can alter the state and properties of the material. The specific impact of heat on a material will depend on factors such as its thermal conductivity, melting point, and chemical stability.
What is a thermometer used for?
A thermometer is used to measure temperature accurately, by indicating the level of hotness or coldness of a substance, object, or environment. It is commonly used in medical settings to monitor body temperature, as well as in various industries, food preparation, and weather forecasting to ensure proper functioning and safety.
How do we measure temperature?
Temperature is typically measured using a thermometer, which can be a digital device or a traditional glass tube filled with mercury or colored alcohol. The thermometer is placed in the substance or environment whose temperature is being measured, and the reading on the scale indicates the temperature in degrees Celsius, Fahrenheit, or Kelvin. Other devices such as thermocouples, thermistors, and infrared thermometers can also be used to measure temperature based on different principles of physics.
What are some examples of heat energy being converted into other forms of energy?
Some examples of heat energy being converted into other forms of energy include a car engine converting the heat energy from burning fuel into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle, a stove converting heat energy into thermal energy to cook food, and a power plant converting heat energy from burning coal or natural gas into electrical energy to power homes and businesses.
How does insulation help to keep heat in or out?
Insulation helps to keep heat in or out by creating a barrier that slows down the transfer of heat between the inside and outside of a building. Insulation materials such as fiberglass, foam, or cellulose trap tiny pockets of air that hinder the movement of heat through conduction, convection, and radiation, therefore reducing the amount of heat lost in cold weather and heat gained in hot weather, ultimately maintaining a more stable temperature inside the building.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments