Heart Anatomy Worksheet Answers
The heart is a fascinating organ that plays a crucial role in our bodies. Understanding its structure and functions can be both educational and beneficial to our health. If you're searching for comprehensive heart anatomy worksheet answers, this blog post will provide you with a reliable resource to study and enhance your knowledge.
Table of Images 👆
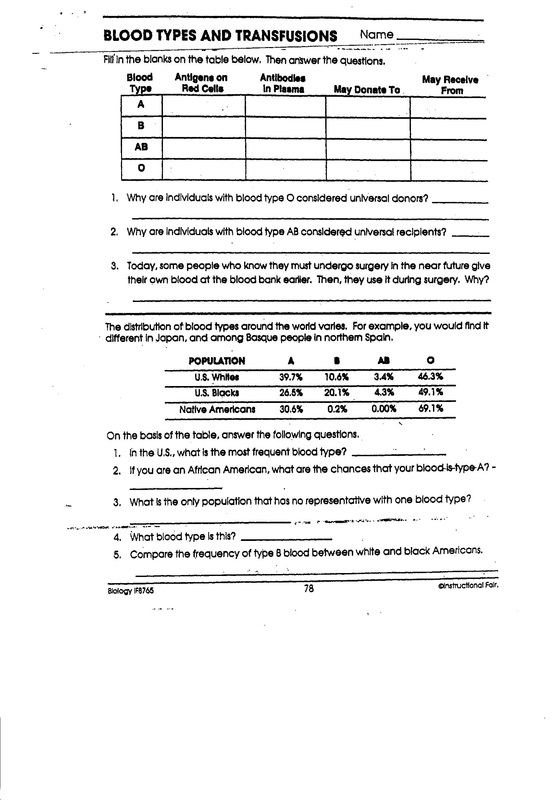
- Circulatory System Worksheet Answer Key
- Circulatory System Heart Diagram Worksheet
- Blank Circulatory System Diagram Worksheet
- Anatomy of the Review Sheet 21 Spinal Cord
- Gross Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves Review Sheet
- Nervous System Spinal Cord Diagram
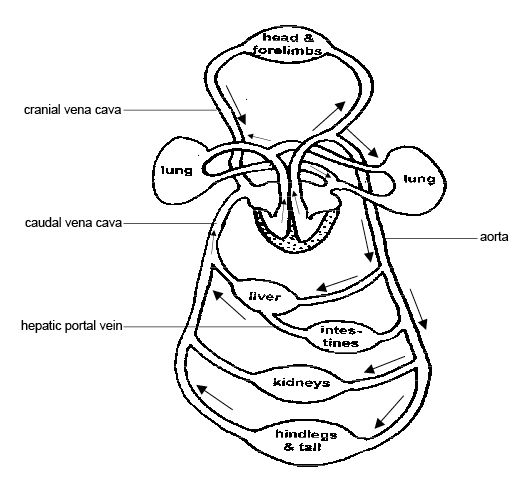
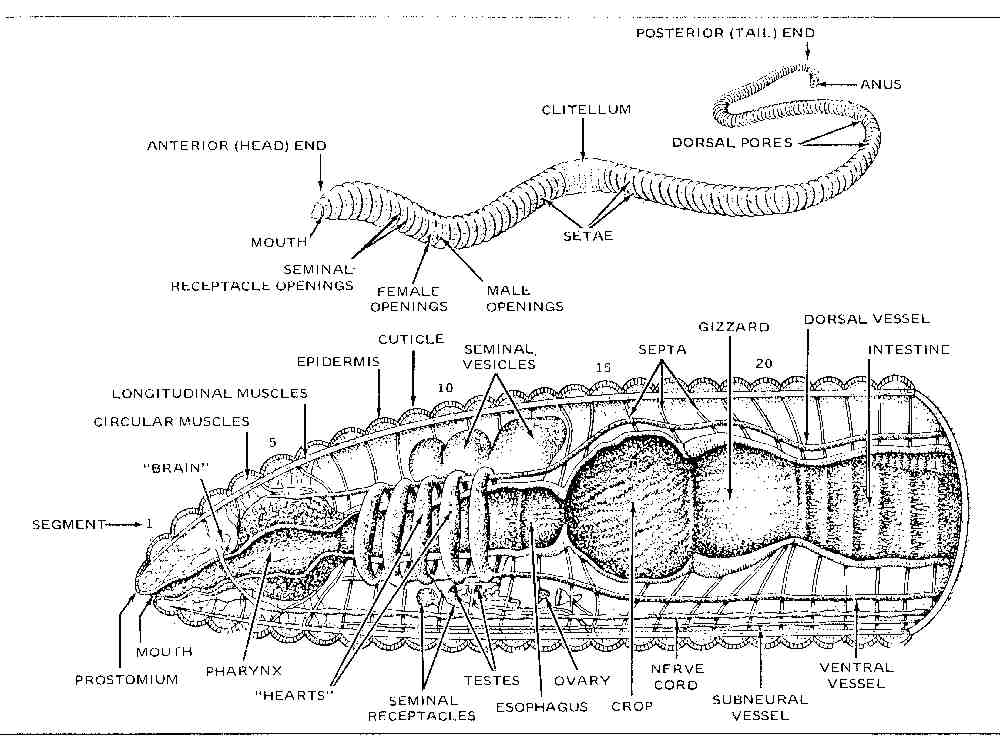
- Earthworm Systems Diagram
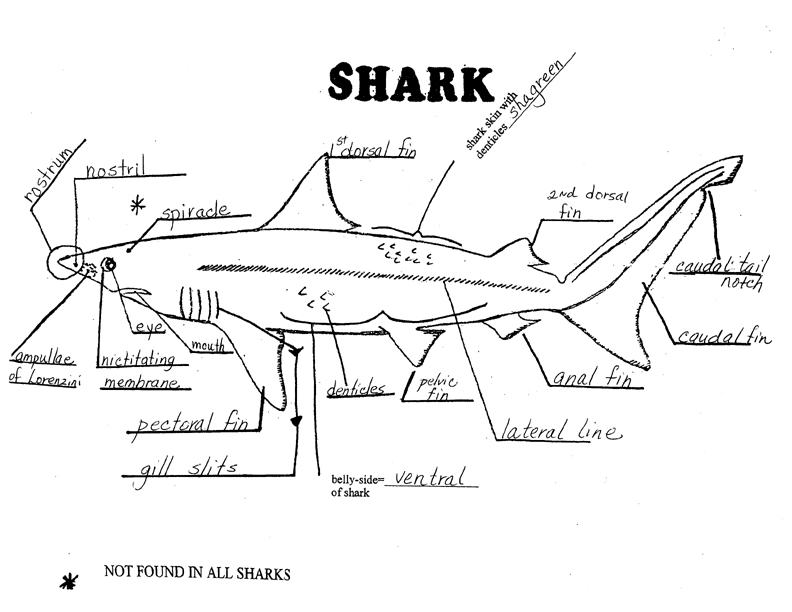
- Dogfish Shark External Anatomy Diagram
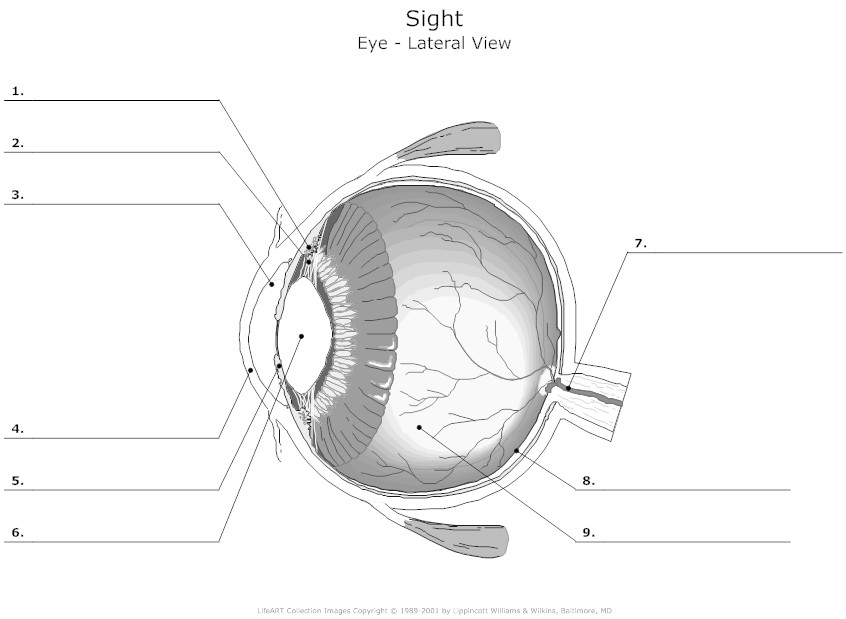
- Human Eye Diagram Unlabeled
- Biological Drawings Line
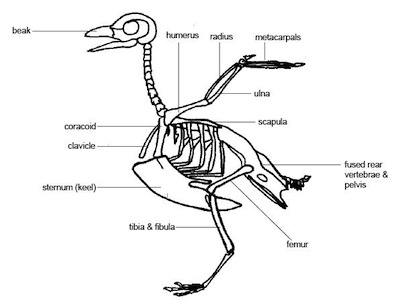
- Bird Bone Structure Diagram
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the main function of the heart?
The main function of the heart is to pump oxygenated blood throughout the body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to cells and removing waste products for circulation back to the lungs for oxygenation.
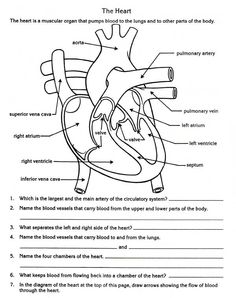
What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, which is then pumped to the right ventricle and sent to the lungs for oxygenation. The oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, is pumped to the left ventricle, and then circulated to the rest of the body.
Describe the structure and function of the atria.
The atria are the upper chambers of the heart that receive blood returning to the heart from the body and lungs. Their structure is thin-walled as they primarily act as reservoirs to collect and store blood before it is pumped into the lower chambers, the ventricles. The atria contract to push blood into the ventricles during the heart's filling phase, allowing for efficient and synchronized blood flow through the heart. This process ensures that oxygen-rich blood is efficiently circulated to the body and oxygen-depleted blood is sent to the lungs for reoxygenation.
What is the purpose of the heart valves?
The purpose of the heart valves is to ensure that blood flows in only one direction through the heart chambers. These valves open and close with each heartbeat, allowing blood to move from one chamber to the next and ultimately out to the rest of the body, while preventing it from flowing backward.
Explain the pathway of blood flow through the heart.
Blood flows through the heart in the following pathway: Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava. It then passes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle, from where it is pumped through the pulmonary valve to the pulmonary artery and travels to the lungs to get oxygenated. Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium, passing through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood through the aortic valve into the aorta, which distributes the blood to the rest of the body.
What is the significance of the coronary arteries?
The coronary arteries are significant because they supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle, allowing it to function properly. Without adequate blood flow through these arteries, the heart may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, leading to conditions like heart attacks or coronary artery disease. Proper functioning of the coronary arteries is essential for a healthy heart and overall cardiovascular system.
What is the difference between the pulmonary and systemic circulation?
The main difference between pulmonary and systemic circulation is the location and function of each. Pulmonary circulation is responsible for pumping oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation, while systemic circulation pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body to supply nutrients and oxygen to tissues and organs. In essence, pulmonary circulation focuses on the exchange of gases in the lungs, while systemic circulation delivers oxygenated blood throughout the body.
Describe the structure and function of the heart's electrical conduction system.
The heart's electrical conduction system is comprised of specialized cells that coordinate the heartbeat. The system begins with the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart's natural pacemaker, which initiates electrical signals. These signals then travel through the atria, causing them to contract. The signal then reaches the atrioventricular (AV) node, where it briefly pauses to allow the ventricles to fill with blood before continuing down the bundle of His, Purkinje fibers, and throughout the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood to the rest of the body. This coordinated electrical pathway ensures that the heartbeats in a synchronized manner, maintaining efficient blood flow and circulation.
What is the role of the pericardium?
The pericardium is a double-layered membrane that surrounds and protects the heart. Its main roles include providing physical support and protection for the heart, limiting the heart's motion and preventing overfilling with blood, and creating a barrier between the heart and other surrounding structures in the chest cavity. Additionally, the pericardium helps maintain the heart's position within the chest cavity and provides lubrication to reduce friction as the heart beats.
How does the heart ensure a one-way flow of blood throughout the body?
The heart ensures a one-way flow of blood throughout the body through the use of valves. Valves within the heart chambers open and close in a coordinated manner to allow blood to flow in one direction only, preventing backflow. This mechanism ensures that blood is efficiently pumped from the heart to the rest of the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments