Graph Worksheets 3rd Grade
Graph worksheets for 3rd grade are a valuable tool for helping young learners develop their understanding of data representation and analysis. These worksheets provide a variety of engaging activities and exercises that focus on graphing skills and concepts, making them perfect for teachers, homeschooling parents, or anyone looking to enhance their child's math education.
Table of Images 👆
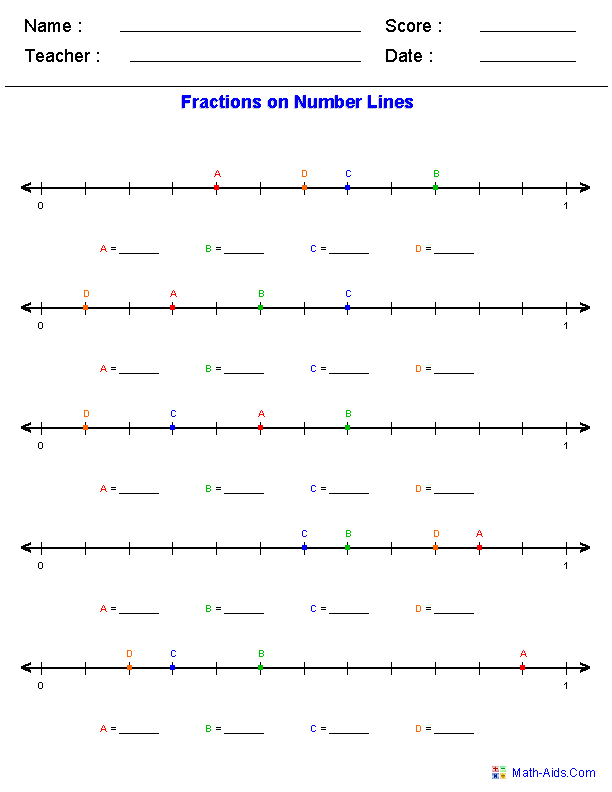
- Free Printable Math Graph Worksheets
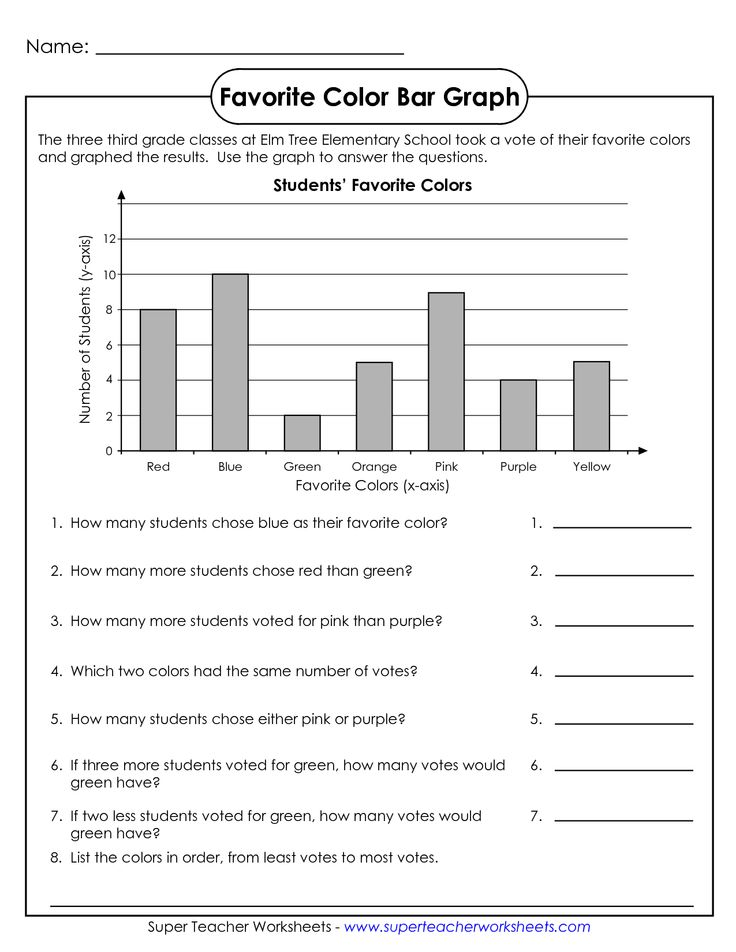
- Bar Graph Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Bar Graph and Pictograph Worksheets 3rd Grade
- 4th Grade Rounding Worksheets
- Math Aids Equivalent Fractions
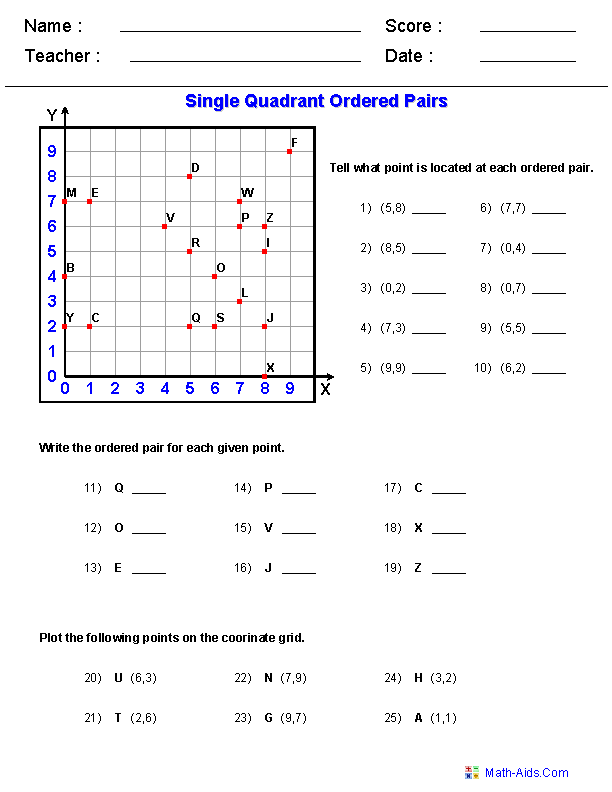
- 5th Grade Graphing Ordered Pairs Worksheet
- 3-Digit Addition with Regrouping
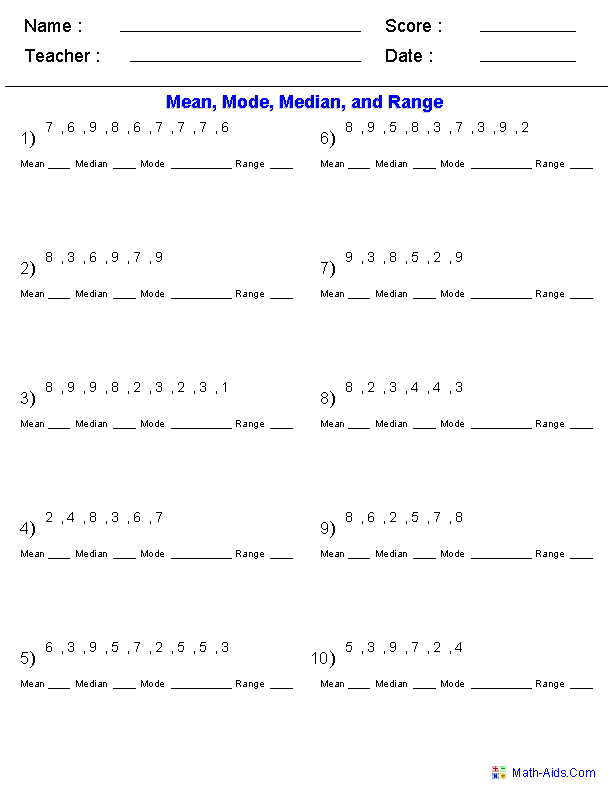
- Mean Median Mode and Range Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Spelling Worksheets
- 5 Grade English Worksheets
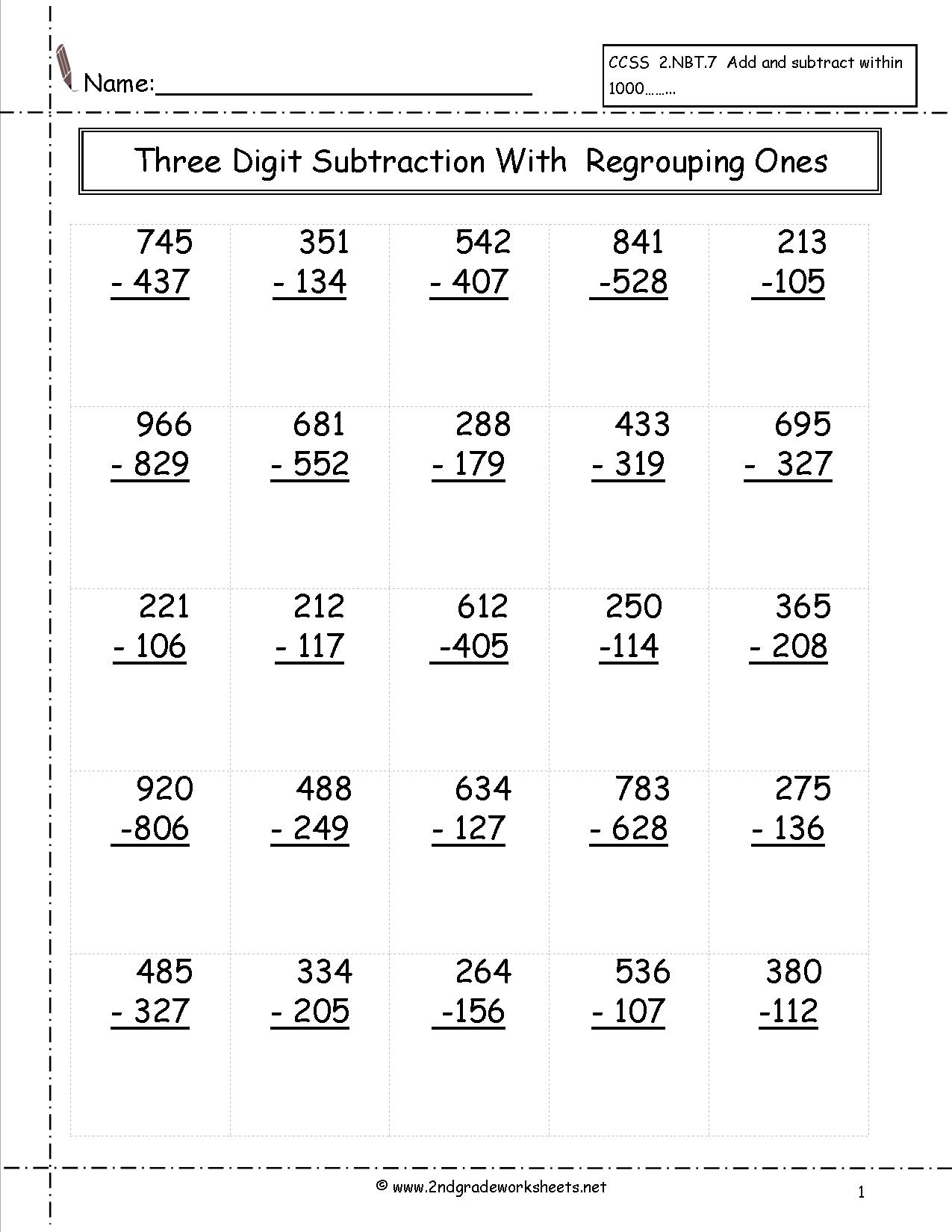
- Three-Digit Subtraction Worksheets
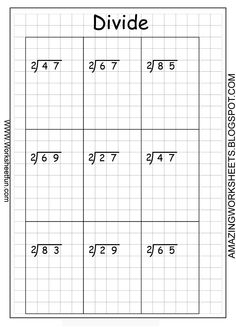
- Long Division Worksheets by 2
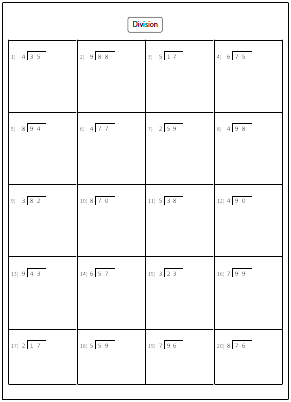
- Grade Long Division Worksheet
More 3rd Grade Worksheets
Telling Time Worksheets 3rd GradeTime Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Multiplication Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Math Division Worksheets Printable
Short Reading Comprehension Worksheets 3rd Grade
Soil Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Cursive Writing Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Multiplication Properties Worksheet
First Day of School Worksheets 3rd Grade
What is a graph?
A graph is a data structure that consists of a set of nodes (vertices) connected by edges. It is used to represent relationships and connections between different elements in a network, such as social networks, road networks, or communication networks. Graphs are a fundamental concept in computer science and mathematics for modeling various real-world situations and analyzing complex systems.
What is the purpose of a graph?
The purpose of a graph is to visually represent data or information in a clear and concise manner, making it easier to analyze and interpret trends, patterns, and relationships within the data. Graphs help in summarizing complex data sets, identifying outliers, presenting comparisons, and communicating findings effectively to a wider audience.
How is data represented on a graph?
Data is represented on a graph by mapping the data points onto the graph's axes, with one variable typically displayed on the horizontal axis (x-axis) and the other variable on the vertical axis (y-axis). Each data point is then plotted at the intersection of these axes based on its corresponding values, allowing patterns, trends, and relationships within the data to be visually interpreted and analyzed.
What are the different types of graphs?
Some common types of graphs include bar graphs, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and histograms. Bar graphs present data using rectangular bars of varying heights, while line graphs connect data points with lines. Pie charts show data as parts of a whole, with each segment representing a percentage. Scatter plots display individual data points as dots on a graph. Histograms are similar to bar graphs but show the distribution of numerical data rather than categories. Other types of graphs include box plots, area graphs, and network graphs, each with their own unique application and use in presenting data visually.
How do you read information from a graph?
To read information from a graph, start by understanding the axes and labels to identify the data being presented. Look at the data points or lines on the graph to see patterns, trends, or relationships between the variables. Pay attention to the scale and units on the axes to accurately interpret the data. Compare different parts of the graph, such as peaks, troughs, or intersections, to draw conclusions about the information being displayed.
What are the key components of a graph?
The key components of a graph include nodes (or vertices) which represent entities or objects, and edges (or links) which represent relationships or connections between the nodes. Together, nodes and edges form the structure of a graph, allowing for representation and analysis of complex relationships and patterns within data. Additionally, graphs may also include attributes or properties associated with nodes or edges, providing more context and information for analysis.
How can graphs help us understand patterns or trends?
Graphs can help us understand patterns or trends by visually representing data in a clear and organized manner. By plotting data points on a graph, we can easily identify the relationships between variables, observe any fluctuations or trends over time, and spot any outliers or anomalies. Graphs provide a visual representation that allows us to interpret complex information quickly and make informed decisions based on the patterns or trends that are revealed.
How can we use graphs to compare and contrast data?
Graphs can be used to compare and contrast data by visually representing the information in a way that allows for easy interpretation. By plotting the data on a graph, such as a bar graph, line graph, or pie chart, it becomes simpler to identify trends, patterns, similarities, and differences between different sets of data. This visual representation can help to quickly grasp the information and make comparisons more effectively than looking at raw numbers or text alone.
How do we create a graph using given data?
To create a graph using given data, you can use a software tool like Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or an online graphing tool. Input your data into the software, select the type of graph you want to create (such as a bar graph, line graph, or pie chart), and customize the graph based on your preferences. Make sure to label the axes, add a title, and choose the appropriate colors and styles to make your graph clear and visually appealing.
How can we interpret and analyze data using graphs?
Interpreting and analyzing data using graphs involves visually representing data in order to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. By examining the visual representation provided by graphs, one can compare different data points, detect outliers, and draw insights from the data. Different types of graphs, such as bar graphs, line graphs, scatter plots, and pie charts, can be used to showcase various aspects of the data, allowing for a more comprehensive analysis. Additionally, graph analysis can help in making data-driven decisions, forecasting future trends, and communicating findings effectively to others.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments