Geometry Angles and Triangles Worksheet
Are you searching for a reliable resource to help your students practice their geometry skills? Look no further! Our Geometry Angles and Triangles Worksheet is the perfect tool for reinforcing important concepts in a fun and interactive way. With a focus on angles and triangles, this worksheet is designed to engage students and help them develop a solid understanding of these fundamental geometry topics.
Table of Images 👆
- Angles Worksheet
- Geometry Rules Angles and Triangles
- 6th Grade Math Worksheets Angles
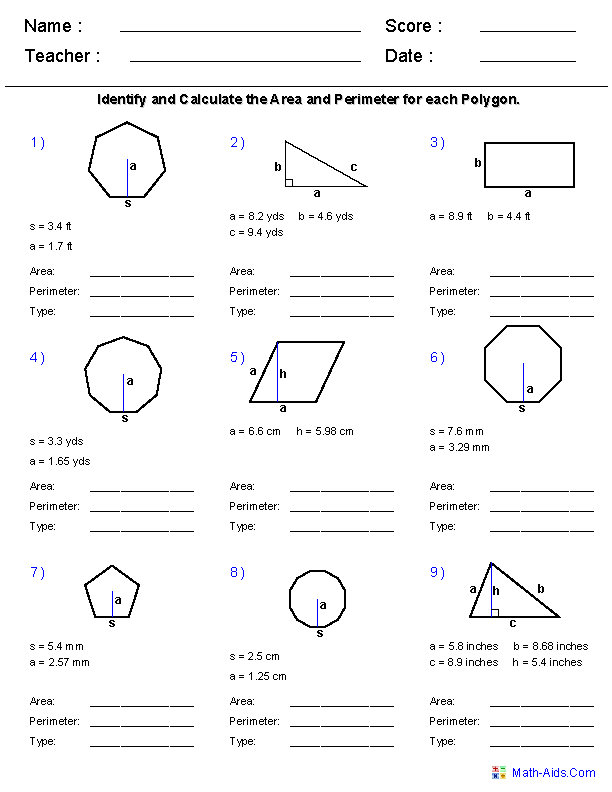
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets
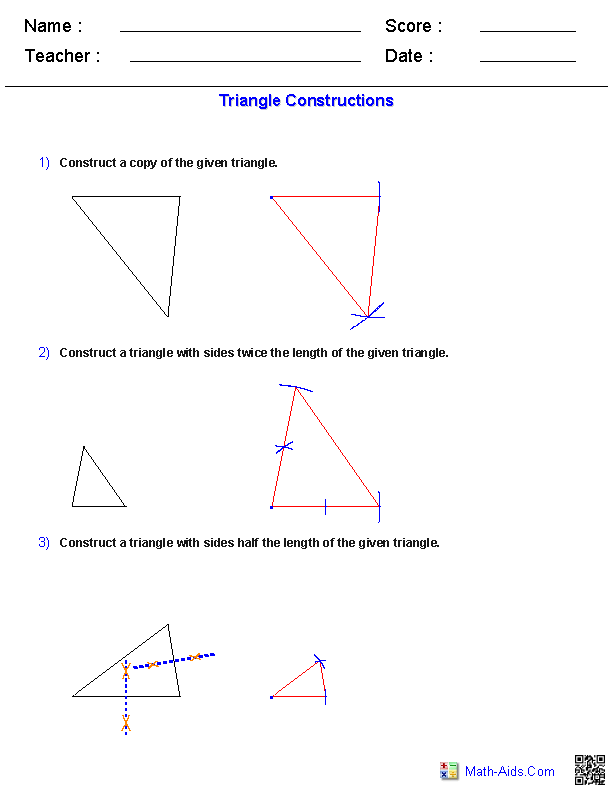
- Math Triangle Constructions Worksheet
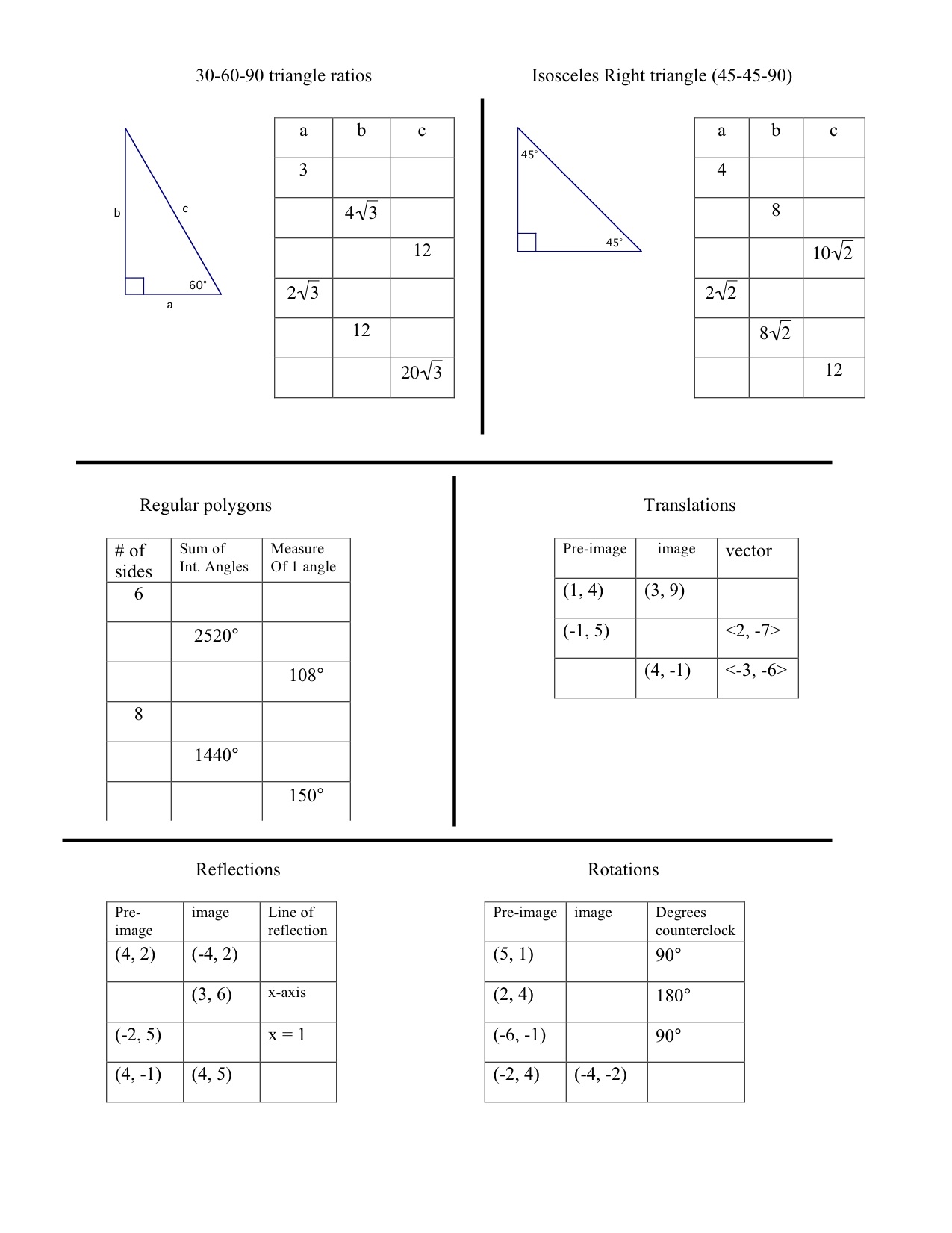
- Special Right Triangles Worksheet Answer Key
- Triangle Missing Angle Worksheet
- Math Angle Relationships
- Identifying Types of Triangles Worksheet
- 8th Grade Math Worksheets Algebra
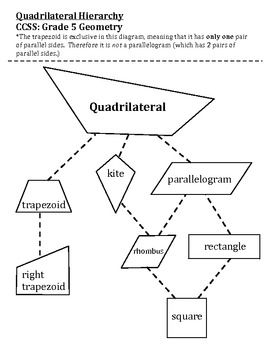
- Quadrilateral Hierarchy Chart
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of an acute angle?
An acute angle is an angle that is less than 90 degrees, meaning it is between 0 and 90 degrees. It is smaller than a right angle (90 degrees) and an obtuse angle (greater than 90 degrees).
Describe the properties of a right angle.
A right angle is a 90-degree angle formed when two lines or line segments intersect. It is perfectly perpendicular, meaning the lines are at 90 degrees to each other, forming an L shape. The sides of a right angle are equal in length and opposite sides are parallel. A right angle is fundamental in geometry and widely used in various mathematical and engineering applications.
How would you define an obtuse angle?
An obtuse angle is an angle that measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. It is larger than a right angle (90 degrees) and is characterized by its openness and seeming "obtuseness" compared to acute angles.
Explain the concept of adjacent angles.
Adjacent angles are two angles with a common vertex and a common side. They share the vertex point and one side, but do not overlap. The sum of adjacent angles is always 180 degrees, making them linear pairs. In other words, they are next to each other and share a common side, making them closely related and connected in terms of their positions and measurements in relation to one another.
What are complementary angles? Provide an example.
Complementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. For example, if one angle measures 30 degrees, then its complementary angle will measure 60 degrees, because 30 + 60 equals 90 degrees.
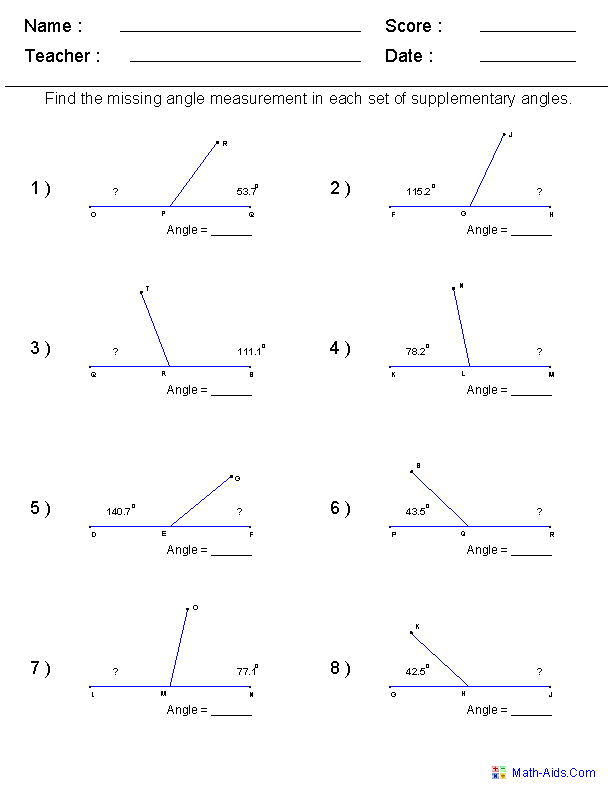
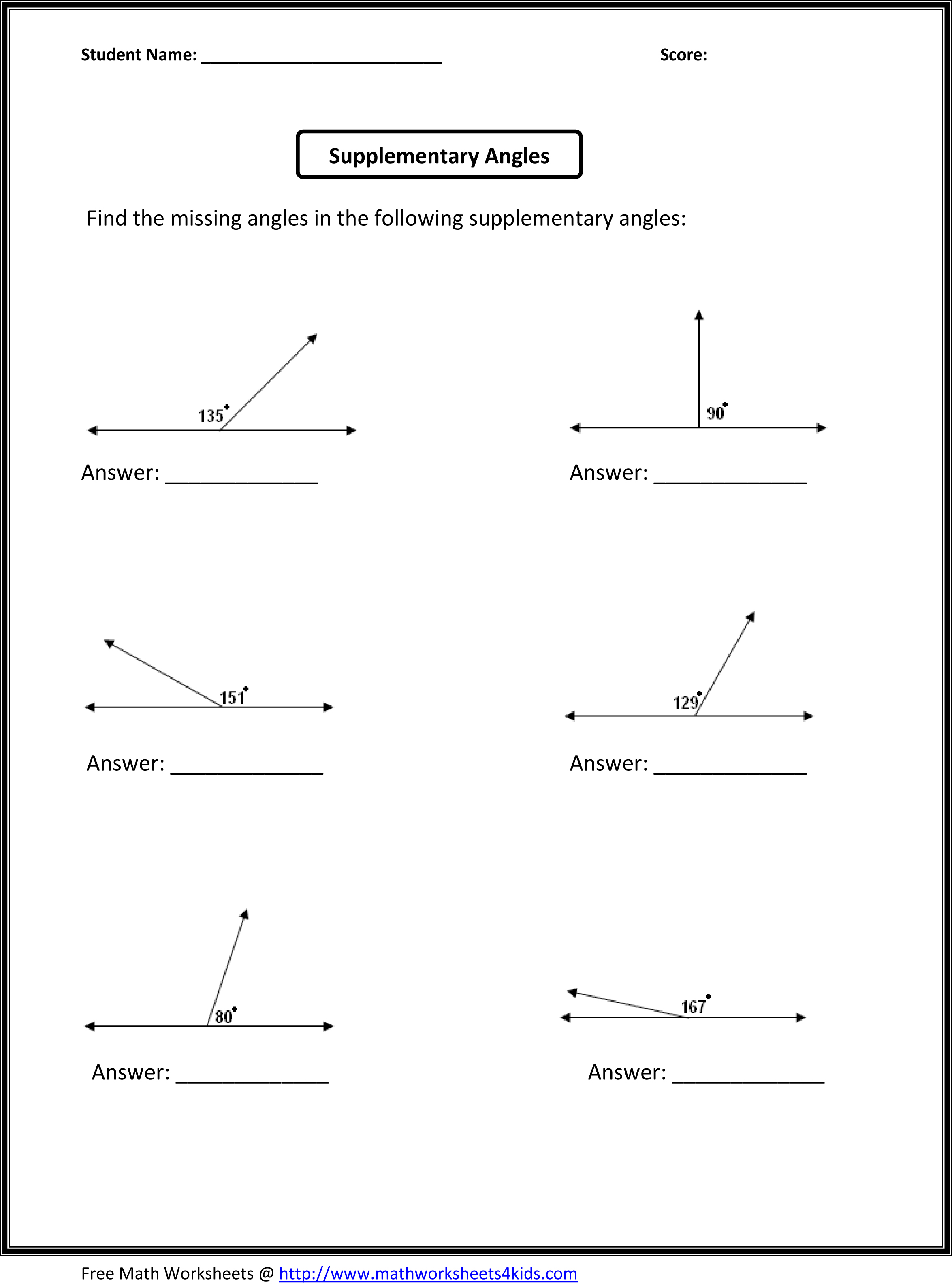
Define supplementary angles and provide an example.
Supplementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees. In other words, when supplementary angles are placed adjacent to each other, they form a straight line. An example of supplementary angles is 60 degrees and 120 degrees because 60 degrees + 120 degrees = 180 degrees.
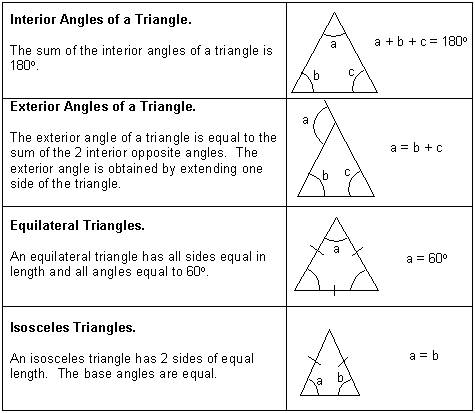
Describe the properties of an equilateral triangle.
An equilateral triangle is a polygon with three equal sides and three equal angles. Each interior angle of an equilateral triangle measures 60 degrees. The height, centroid, circumcenter, and orthocenter of an equilateral triangle all coincide at the same point. Additionally, the three medians of an equilateral triangle are equal in length and intersect at 60 degrees.
What is the definition of an isosceles triangle? Give an example.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with at least two sides of equal length. This means that two of its three sides are of the same length. For example, a triangle with side lengths of 5, 5, and 3 would be an isosceles triangle since two sides have the same length.
Explain the concept of a scalene triangle.
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle where all three sides have different lengths. Unlike equilateral triangles where all sides are equal, or isosceles triangles where two sides are equal, a scalene triangle has no sides of equal length. This means that all three angles in a scalene triangle are also different, making it a unique and versatile shape in geometry.
Describe the properties of a right-angled triangle.
A right-angled triangle has one angle equal to 90 degrees, known as a right angle. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, which is the longest side in the triangle. The lengths of the other two sides are called the legs, with one side adjacent to the right angle and the other side opposite one of the acute angles. The Pythagorean theorem relates the lengths of the sides in a right-angled triangle, stating that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two legs.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments